af Franco Meza 4 år siden
590
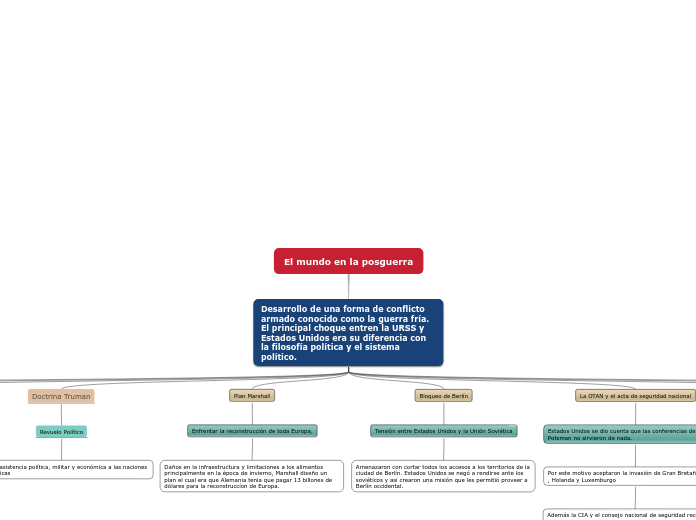
El mundo en la posguerra
af Franco Meza 4 år siden
590

Mere som dette
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
Los soviéticos lanzaron el primer satélite artificial al espacio como prueba, Estados Unidos estableció la NASA.
Como había mucha competencia, gracias a esto la tecnología avanzo demasiado.
Tenia que estar preparados para un posible ataque hacia Alemania
Por este motivo aceptaron la invasión de Gran Bretaña, Bélgica , Holanda y Luxemburgo
Además la CIA y el consejo nacional de seguridad recopilaron estrategias de inteligencia para aconsejar al presidente en las políticas
Amenazaron con cortar todos los accesos a los territorios de la ciudad de Berlín. Estados Unidos se negó a rendirse ante los soviéticos y así crearon una misión que les permitió proveer a Berlín occidental.
Daños en la infraestructura y limitaciones a los alimentos principalmente en la época de invierno, Marshall diseño un plan el cual era que Alemania tenia que pagar 13 billones de dólares para la reconstruccíon de Europa.
Decide on the fourth point of view
Type in the name of the last character whose perspective on the issue you are going to present.
Example: Leslie Burke, Jesse's new next-door neighbor, and best friend.
Proveían asistencia política, militar y económica a las naciones democráticas
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
Whose character does the third point of view belong to?
Type in his/her name.
Example: Mr. Aarons, Jesse's father.
What does the character think, say or do that suggests their perspective on the issue?
Type in a quote and try to maintain the citation format.
Example: 'He would like to show his drawings to his dad, but he didn't dare. (...) He'd thought his dad would be pleased. He wasn't. What are they teaching in that damn school? he had asked.' (Paterson, 2.8)
La única forma de manejar las relaciones con la unión soviética era pretender el alcance de políticas vigorosas, así provocando el bloqueo del comunismo en el mundo.
What kind of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
Decide on the second point of view
Name the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view you are presenting.
Example: Miss Edmunds, Jesse's music teacher.
Type in a quote that points out the character's position about the issue.
Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'She said he was unusually talented, and she hoped he wouldn't let anything discourage him.' (Paterson, 2. 8)
Se incrementaron tensiones entre las dos potencias domiantes
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
Desarrollo de una forma de conflicto armado conocido como la guerra fría. El principal choque entren la URSS y Estados Unidos era su diferencia con la filosofía política y el sistema político..
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
Tomaron la decisión de dividir Alemania y Berlín en cuadro zonas. Además estas eran ocupadas por las cuadro potencias aliadas.
What type of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer: