af True Jarrel [STUDENT] 5 år siden
1338
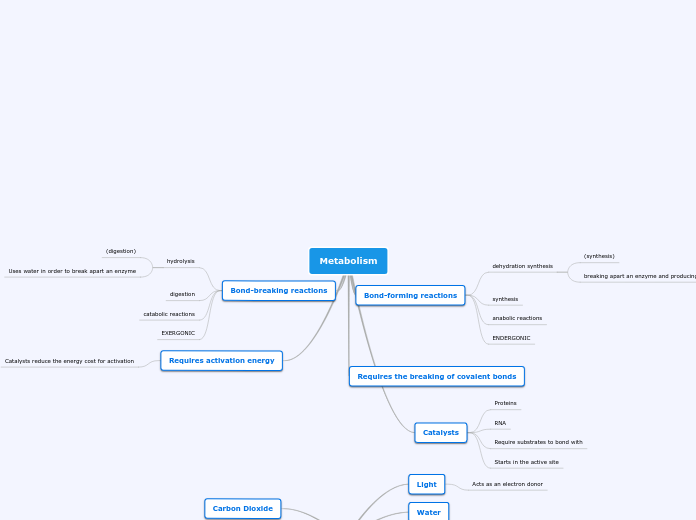
Metabolism
Cellular respiration is a multi-step process involving glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, each contributing to the production of ATP. Glycolysis, occurring in the cytosol, converts glucose into pyruvate, generating NADH and a net gain of 2 ATP.