af Daniel Genesee 3 år siden
202
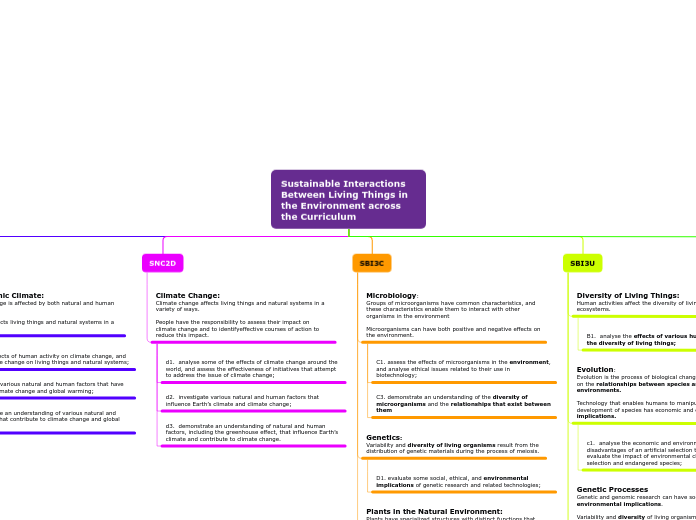
Sustainable Interactions Between Living Things in the Environment across the Curriculum
af Daniel Genesee 3 år siden
202

Mere som dette