af jhon sanchez 4 år siden
529
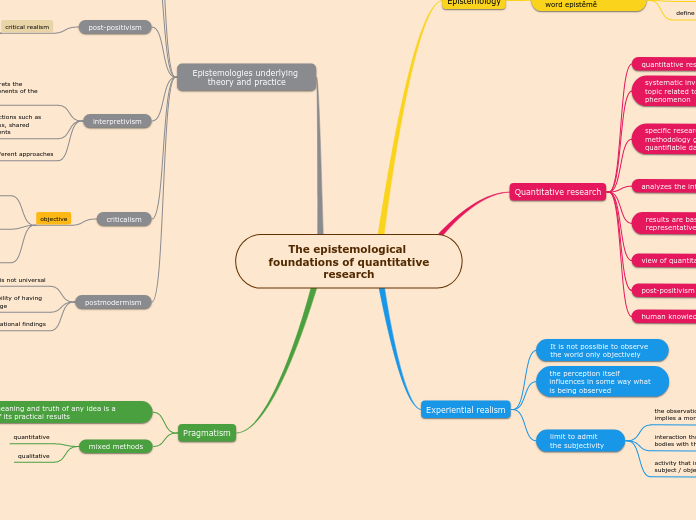
The epistemological foundations of quantitative research
af jhon sanchez 4 år siden
529

Mere som dette
they are verifiable.
standardized.
reliable
definitive
culture is changeable.
Publicize and challenge power structures.
changing the existing and limiting social conditions
deep appreciation and appreciation of society and culture
change limiting social conditions.
it is vital to see the differences that characterize people.
incorporates human interest in a study.
prior understanding of other theories and concepts
all observation is fallible or imperfect
there is a reality independent of our thinking about which science can study
approach to reality as best they can.
computational techniques
mathematical
statistical