Unit 1
What is Anatomy & Physiology?
Graphing Data
Topic 1.0 What is Anatomy and Physiology
Should Knows
Anatomy, Physiology, Homeostasis,
Illness, Positive Feedback Loop, Negative
Feedback Loop
Should Do's
1. Contrast anatomy and physiology.
2. Explain the difference between a positive and negative feedback loop and provide an example of each.
3. Explain why illnesses occur.
What is the Difference Between Anatomy & Physiology?
Subtopic
What Causes Illness?
If you don't maintain a healthy cycle then, your body cannot maintain homeostasis.
What Are Feedback Loops?
What are the stagers in a Feedback loop?
How does Positive and Negative Feedback Regulate Body Functions?
The flu is an example of Positive and negative feedback. Wh
Feedback loops is what maintains homeostasis.
Topic 1.1 Anatomic Terms
SHOULD DO'S
1. Demonstrate the anatomical position
2. Describe the human body using directional and
regional terms
3. Identify three planes most commonly used in the
study of anatomy
4. Distinguish between the posterior (dorsal) and the
anterior (ventral) body cavities, identifying their
subdivisions and representative organs found in
each
5. Describe serous membrane and explain its function
What are the two body positions?
Superior (or cranial) - a position above or higher than another part of the body.
Inferior (or caudal) - lower than another part of the body.
What are the different Body directions?
Front & Back
Anterior (or ventral) - toward the front of the body.
Posterior (or dorsal) - direction toward the back of the body.
Right & Left
Lateral - toward the side of the body.
Toward & Away
Proximal - nearer to
Distal - farther from
Medial - toward the middle of the body.
Superficial - closer to the surface of the body.
Deep - farther from the surface of the body.
Investigating Diabetes
Should Knows
Define: polydipsia, hyponotermia, diabetes, hypotonic, hyperttonic, and isotonic
Should Do's
Explain why people with diabetes experience hyponometria and polydipsia.
How do cells maintain
homeostasis?
Active transport
Use energy to move substances
(solute) against the concentration
gradient
Passive transport
moment of substances WITH the
concentration gradient
NO ENERGY USED!
Diffusion
moment of solute
Osmosis
movement of water
Hypertonic
- Higher solute OUTSIDE
-Higher water INSIDE
Isotonic
- Equal solute
- Equal water
Hypotonic
- Higher solute INSIDE
- Higher water OUTSIDE
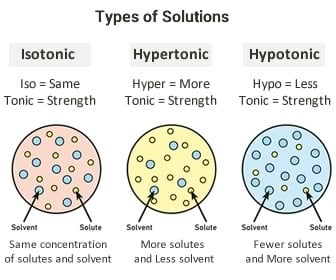
The types of solutions
Levels of organization
1. Chemical Level
2. Cellular level
3. Tissue level
4. Organ level
5. System level
6. organism level
Homeostasis and feedback loop^
Biological pathways used to restore the system to
normal or to amplify a response
What is the feedback pathway?
Stimulus - the variable the
disrupts homeostasis
Control center (the brain) -
process the stimulus
Receptor - receives the stimulus
Subtopic
what is Homeostasis ?
Ability of a system to maintain the
"normal condition"
Medical Instagram
Should Know's: Recall the four modern imaging tools Should Do's 1. Discuss the uses, advantages, and drawbacks
of X-ray and MRI imaging.
2. Describe how the different tools are used for
diagnosis.
types of imaging
X-Rays
Advantage: Produces a high energy beam that
passes through soft tissue and strike bone tissue
but doesn't pass through
Disadvantages: patients able to develop cancer from
over exposure
Purpose: used to diagnose fractures and bone deficit
orders
CAT scans
advantages: Can make soft tissue visible
for diagnosis through the computer
MRI
Advantages: uses a magnetic field to generate and
image instead of radiation. 360-degree view of the body
region being investigated
Disadvantages: Patients having metal implants
can not be exposed to MRI
Purpose: Used to diagnose spinal cord injury, brain,
and nervous system disorders
PET
Purpose: diagnose heart disease, brain
abnormalities, cancer spread, infection, bone
and thyroid disease.