AIS Ch 3
Internal Controls
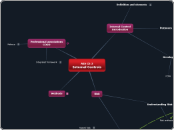
Risk
Understanding Risk
Can affect businesses'
bottom line
Risk professionals
Risk structure
Hollander, Denna, & Cherrington
Risk Taxonomy
Brown's Risk Taxonomy
Hazard Risk
Strategic Risk
Operational Risk
Fianacial Risk
Other risk taxonomies
Methods
Professional associations
COSO
Integrated framework
Makeup
Internal Control
Introduction
Purposes
Definition and elements
Development
SOX
FCPA