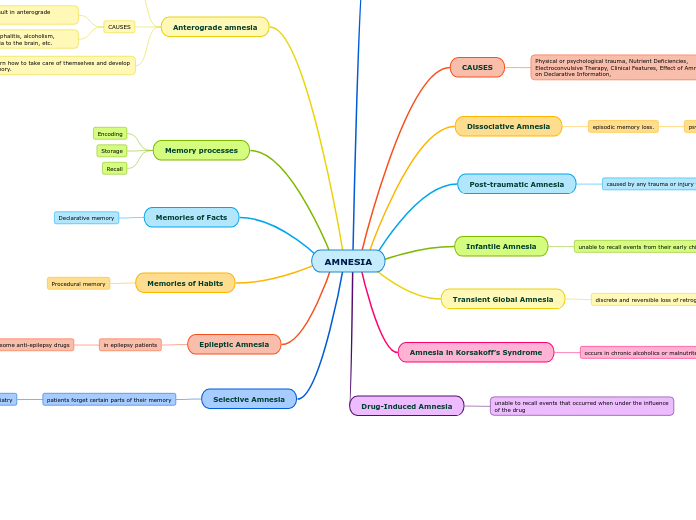
AMNESIA
Retrograde amnesia
Inability to recall the past
CAUSES
Sometimes when the hippocampus is damaged
Also cerebrovascular accidents, stroke, head trauma, substances abuse, etc.
CAUSES
Physical or psychological trauma, Nutrient Deficiencies, Electroconvulsive Therapy, Clinical Features, Effect of Amnesia on Declarative Information,
Dissociative Amnesia
episodic memory loss.
psychological causes
Post-traumatic Amnesia
caused by any trauma or injury to the head.
anterograde amnesia, retrograde amnesia, or both
temporary or permanent
Infantile Amnesia
unable to recall events from their early childhood
due to the development of the brain at an early age
Transient Global Amnesia
discrete and reversible loss of retrograde memory function
abnormalities in the hippocampal area, transient reduced cerebral blood flow, transient seizures, or migraine attacks
Amnesia in Korsakoff’s Syndrome
occurs in chronic alcoholics or malnutrited patients
presence of both anterograde and retrograde amnesia.
Drug-Induced Amnesia
unable to recall events that occurred when under the influence of the drug
Anterograde amnesia
affects the ability to form new memories but not memories of the past.
CAUSES
Damage to the hippocampus can result in anterograde amnesia
Also a stroke, trauma, surgery, encephalitis, alcoholism, Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, anoxia to the brain, etc.
patients can learn how to take care of themselves and develop procedural memory.
Memory processes
Encoding
Storage
Recall
Memories of Facts
Declarative memory
Memories of Habits
Procedural memory
Epileptic Amnesia
in epilepsy patients
response to some anti-epilepsy drugs
Selective Amnesia
patients forget certain parts of their memory
often used for treatment purposes in psychiatry