Common
Ancestor
Prokaryote
Eubacteria
3 Major morphologies
Bacillus
(Rod shaped)

Bacillus coagulans
Spirala
(Spiral shaped)
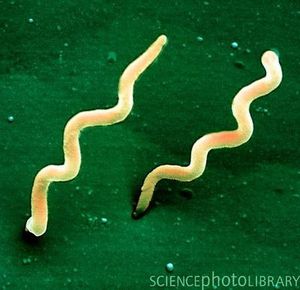
borrelia
Archaea
Representative Species
Methanogens
Extreme Thermophiles
Psychrophiles
Eukaryote
Protista
3 Major Groupings
Autotrophic
(Plant like)
Phyla examples
Euglenophyta
Chrysophyta
Chlorophyta
pyrrophyta
Heterotrophic
(Animal like)
Phyla examples
Ciliophora
Rhizopoda
Saprotrophic
(Fungi like)
Phyla examples
Myxomycota
Oomycota
- Live in a extreme conditions
- Aquatic or moist areas
- Reproduce Asexually and sexually
some protists cause
diseases such as malaria
Animals
Prorifera

Representative species:
Demosponge
Cnidaria

Representative species:
Jellyfish
Arthropoda
Subphyla
Crustacean

Representative species:
Crab
Chelicerata

Representative Species:
sea spiders
Arachnid

Representative species:
Spider
Hexapoda

Representative species:
butterfly
Myriapoda

Representative species
Rotifera
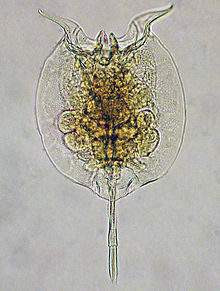
Representative Species:
Eurotatoria
Mollusca

Representative species:
Snail
Annelida

Representative species:
earthworm
Nematoda

Representative species:
Ascaridida
Platyhelminthes
Chordata
Subphyla
vertebrates
Classes
Class Agnatha
- jawless

Representative species:
lampreys
Class Chondrichthyes
- fins
- cartilage

Representative species:
sharks
Class Osteichthyes
- mouth with many teeth
- some without scales
- bony

Representative species:
bony fish
Class Amphibia
- Cold-bloded
- spend time on
land and water

Representative species
Frog
Class Reptilia
- are cold blooded
- can regulate body temp

Representative species:
Chameleon
Class Aves
- Warm blooded

Representative species:
Hummingbird
Class Mammalia
- hair
- sweat glands
- temperature regulation

Representative species:
Koalas
3 Major Groupings
Monotremes
- oviparous (egg-laying)
Marsupials
- Give birth to fetal
underdeveloped babies
- Superior to Monotremes
because marsupials are
more likely to survive as they
are not in fragile eggs
Placental
- majority mammals
- Substances sent to
fetus to grow in womb
- Superior to Marsupials
because the babies are more
developed when given birth to
Orders
Primates
- well developed hands
and feet, with fingers and toes

Representative species:
Gorilas
carnivore
- is an animal or plant that
eats the flesh of animals

Representative Species:
Lion
Chiroptera

Representative species:
Bat
Cephalochordate
Urochordata
Echinodermata

Representative species:
Starfish
- Lack Membrane bound Organelles
- Contain cytoplasm, ribosomes, genetic material
- Single celled organisms
- Membrane bound Organelles
- Contain plasma membrane with cytoplasm
- Single or multicellular
Plants
Bryophytes
Moss
Seedless Vascular

Ferns
Coccus
(spherical)
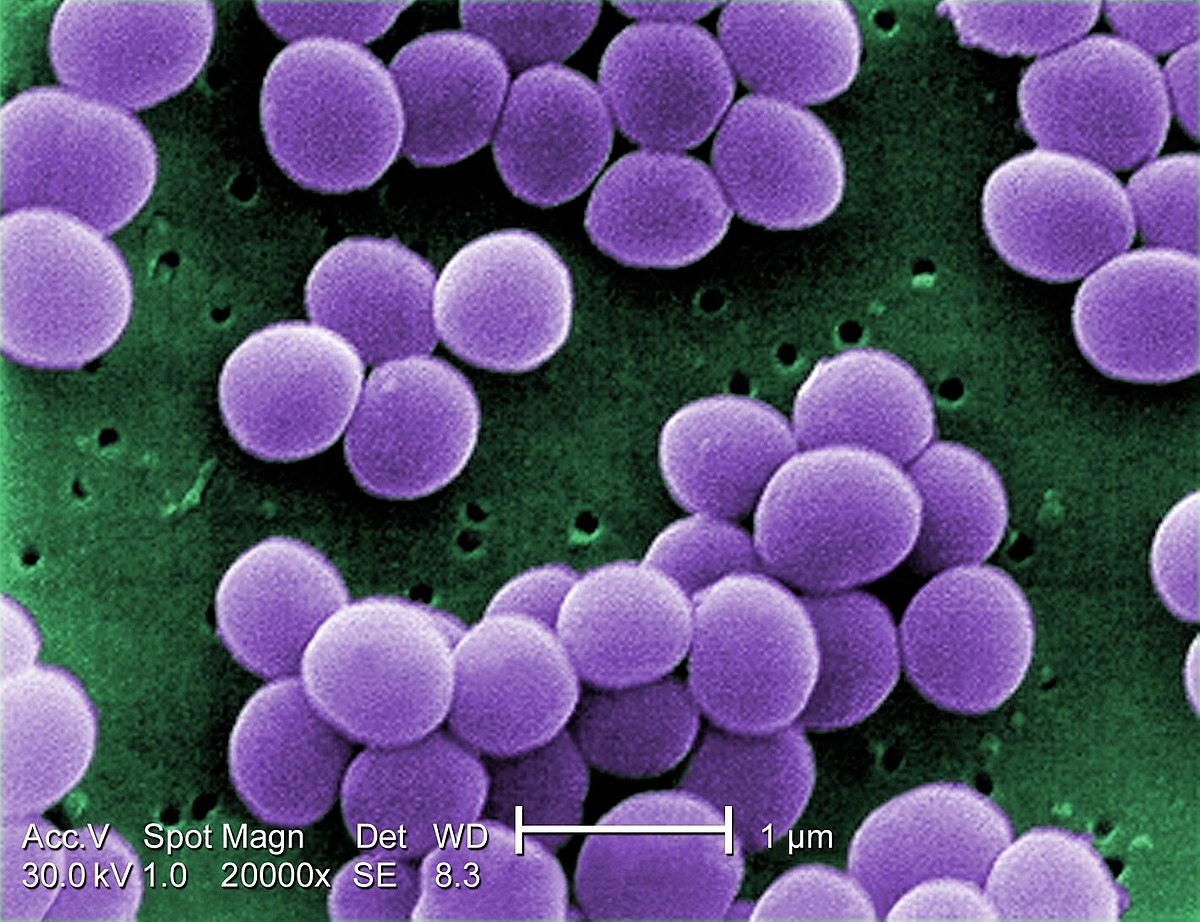
Staphylococcus
Gymnosperms

Conifers
Angiosperms

Dicotyledon
Monocot
Dicot
Fungi
Phyla
Ascomycota

Saccharomyces cerevisiae
(Brewers yeast)
Glomeromycota

Acaulospora
Chirtridiomycota
Allomyces
zygomycota

Black bread mold
(Rhizopus stolonifer
Basidiomycota
- Unicellular
- Aquatic Species

Mushrooms
- Multicellular
- Asexual
- Reproduce via zygospores
- Develop small finger like sacs
- Hyphae
- Unlike other two domains
- Do not contain peptidoglycan wall
- Most live in extreme environments
Feeding strategies
Human Influence
Harmful: Eubacteria is known
for its negative effect on the human
body. These pathogens are the root cause of many diseases such as strep throat and
fever
Beneficial: Many bacteria are decomposers
of producers and recycle certain nutrients. This makes them a vital part of biochemical processes in our body
- Multicellular
- Photosynthetic
- Membrane bound organelles
- Produces flowers
- Seeds enclosed within ovary
- Simplest land plant
- Reproduce in wet and moist conditions
- Unicellular
- Spores
- Low oxygen environments
- Digestive tracts of some animals
- Extremely hot environments
- Live in extremely cold
environments
Human impact
- Use digestive enzymes
to break down/consume
nutrients
- Consumers
- Obtain energy by feeding
off other animals/ plants
- Produce own food
- Photosynthetic
- Single or multicellular
Forms Symbiotic relationship
with some plants and roots to
benefit both parties
Move via Flagella or
pseudopods
Move via flagella
Uses cilia to move around
Move slowly via pseudopods
Tends to follow light
and moves via flagella
Moves via flagella
moves via flagella
Moves via flagella
- Eukaryotes
- Multicellular
- Heterotrophic
- Exoskeleton
- Segmented Bodies
- Jointed Appendages
- Bilateral Symmetry
- Open Circulatory System
Arthropods cover a
wide variety of subphyla
- A hard exoskeleton
made of calcium
- Two pairs of antennae
- Six pairs of appendages
- jointed appendages
- hardened exoskeleton
- hard exoskeleton
- jointed legs
- Three body segments
- notochord
- dorsal hollow nerve cord
- pharyngeal slits
- Post anal tail
Chordata covers a
variety of subphylum
- Well developed brain
- endoskeleton is cartilage or bone
- aquatic areas
- evolved to have
gills
(fish)
- gill pouches (slits)
- notochord
- dorsal nerve cord
(Corals)