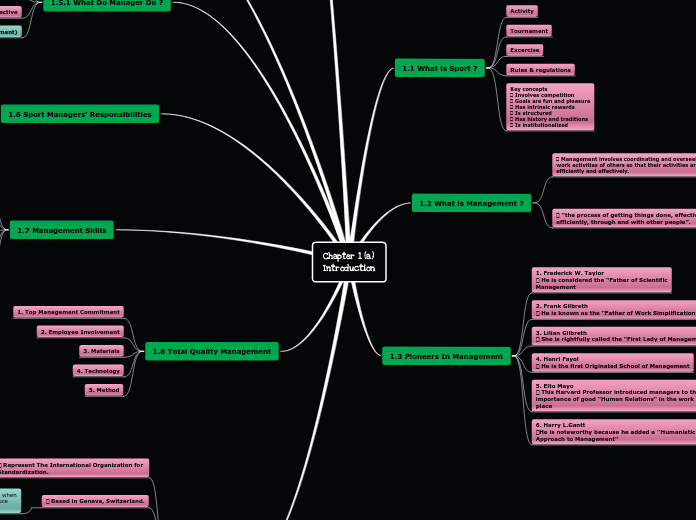
Chapter 1 (a)
Introduction
1.1 What is Sport ?
Activity
Tournament
Excercise
Rules & regulations
Key concepts
Involves competition
Goals are fun and pleasure
Has intrinsic rewards
Is structured
Has history and traditions
Is institutionalized
1.2 What is Management ?
Management involves coordinating and overseeing the
work activities of others so that their activities are completed
efficiently and effectively.
“the process of getting things done, effectively and
efficiently, through and with other people”.
Efficiency
- Means doing the thing right/correctly; refers to the
relationship between inputs and outputs; seeks to minimize
resource costs
- Getting the most output for the least inputs
Effectiveness
- Means doing the right things; attaining organizational goals
1.3 Pioneers In Management
1. Frederick W. Taylor
He is considered the “Father of Scientific
Management
2. Frank Gilbreth
He is known as the “Father of Work Simplification”
3. Lilian Gilbreth
She is rightfully called the “First Lady of Management”
4. Henri Fayol
He is the first Originated School of Management
5. Elto Mayo
This Harvard Professor introduced managers to the
importance of good "Human Relations" in the work place
6. Harry L.Gantt
He is noteworthy because he added a ''Humanistic
Approach to Management''
1.4 Sport Management Today and Future
The responsibility for performance involves combining and coordinating human, technological, and financial resources to achieve organizational goals.
Organizations by their nature are complex and difficult to manage. As long as society, the economy, and technology remained somewhat stable or changed only slowly, management had time to make the adjustments necessary to maintain and improve performance.
Gradual change has now been replaced by rapid change and managers face new challenges brought on by changing environment.
These include intense competition and new performance standards that every management team must now achieve.
1.5 Possible Careers
Athletic Directors
Player's Agent
Sport Broadcasting
Recreation Management
1.5.1 What Do Manager Do ?
Efficient
(resource usage-low waste)
Effective
(ends- goal attainment)
1.6 Sport Managers’ Responsibilities
1. Human Resources
2. Financial Resources
3. Physical Resources
4. Informational Resources
1.7 Management Skills
1. Technical Skills
- Ability to use the tools, procedures and techniques of a specialized field
2. People Skills
- Ability to work with understand mentor and motivate others, both individually and in groups
3. Communication Skills
- Ability to get your ideas across clearly and effectiveness
4. Conceptual Skills
- Ability to coordinate
all of the organization’s
interests and activities
5. Decision Making Skills
- The ability to select alternatives to solve problems
1.8 Total Quality Management
1. Top Management Commitment
2. Employee Involvement
3. Materials
4. Technology
5. Method
1.9 What is ISO?
Represent The International Organization for
Standardization.
1. ISO 9000: This define the key terms and acts as a road map for the other standards within the series.
Based in Geneva, Switzerland.
2. ISO 9001: This defines the model for a quality system when a contractor demonstrates the capability to design, produce and install products or services
Quality system standard applicable to any
product, service or process anywhere in the world
3. ISO 9002: This a quality system model for quality assurance in production and installation.
ISO International Standards ensure that products
and services are safe, reliable and of good quality.
4. ISO 9003: This a quality system model for quality assurance in final inspection and testing.
5. ISO 9004: This provides quality management guidelines for
any organization wishing to develop and implement a quality
system. Guidelines are also available to determine the
extent to which each quality system model is applicable.
6. ISO 14000: an evolving series that provides business
management with the structure for managing environmental
impacts, including the basic management system,
performance evaluation, auditing, labeling and life cycle
assessment.
Chapter 1 (b)
1.1 What is Manager?
A person in a organization, responsible to work more than one person
1.2 Measuring Managerial Performance
Performance efficiency
Resource Usage
Low Waste
Performance effectiveness
Goal Attaintment
High Attainment
1.3 Good Managers Vs Poor Manager
The Good Managers The Poor Managers
-Integrity
Industriousness
Ability to get along with
people
Business knowledge
The Poor Managers
Lack integrity
Unable to understand others
Do not work well with others
Lack integrity
1.4 How Are Managers Different from Operative Employees
Operatives
Work directly to jobs
Managers
Direct the activities
1.8 Sport Industry Environment
Internal Environment
Management
Mission
Resources
System Process
Structure
External Environment
Customers
Supporter
Work force
Society
Economy
Government
Chaos in the External
Environment & Interactive Management
1.5 Managerial Levels
TOP MANAGERS
e.g
Types Of Manager
Management Skills
Management Functions
Planning
Organizing
Conceptual
People Skills
General
CEO
MIDDLE MANAGERS
e.g
Types Of Manager
Management Skills
Management Functions
Planning
Organizing
Leading
Controlling
Balance conceptual
Technical
People Skills
Functional
Head of Department
FIRST LINE MANAGERS
e.g
Types Of Manager
Management Skills
Management Functions
Leading
Controlling
Technical
People Skills
Project Managers
Supervisor
1.6 Management Roles
Interpersonal Roles
Leader Roles
Informational Roles
Spoker Person
Decisional Roles
Negotiator
1.7 Management Process / Function
P, O, L, C