Chapter 4: Quadratic Relations
Simple Quadratics
Exponent or Power
A raised number to indicate repeated multiplication of a base number

Exponent Law
A set of rules that can be used to simplify powers
Expression
A mathematical phrase made up of numbers and variables,
connected by operators ( -, +)

Algebra
Distributive Property
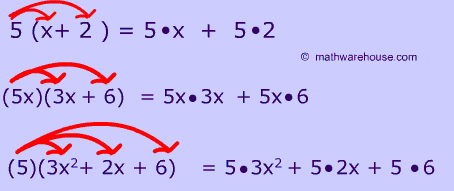
Variables
Strategies on Solving Word Problems
Find The Given.
Sketch a graph
Find the vertex,
value of 'a', direction of opening
1.Obtain info from the graph
2. Sketch important parts
with whatever information
you have
3. Understand

Formula: Y=x^2
Subtopic
Multiply Polynomials

FOIL: (First, Outside, Inside, Last)
Quadratic Expression
A second degree polynomial
Ex: 4x^2+20 and x^2+7x+10 are quadratic expressions
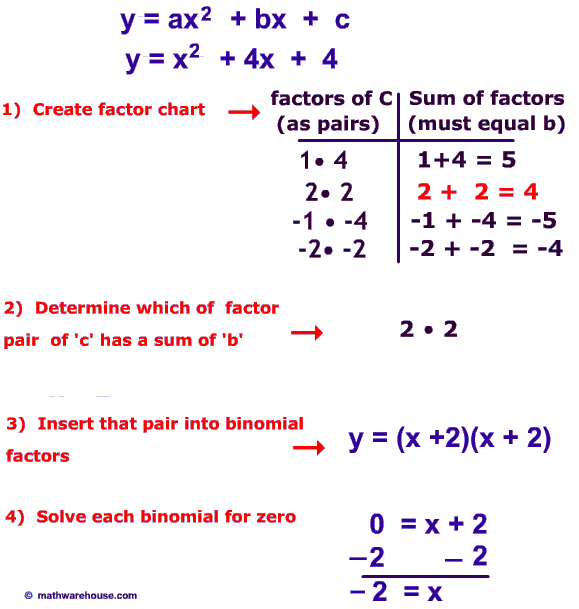
Special Products

Perfect square trinomial

Difference of squares

Common Factors:
Greatest common factors are used in factoring polynomial,
In fact factoring is the opposite of expanding
Quadratic Equations

3 possible outcomes

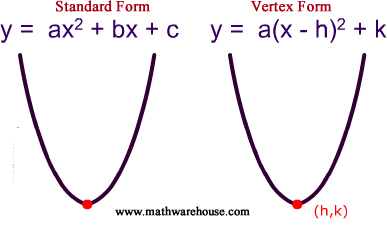
Standard form
What can we read: Direction of opening
and Y-intercept
Vertex form
What We Can Read: Vertex(h,k), Direction of opening,
The min/max value and AOS

Factored form
What We Can Read: Direction of opening
and x-intercepts
Roots
also known ass x-intercepts or zeroes
Solving Quadratic Equations
graphing
Can be used always
factoring
Can be used sometimes/ use when C=0
C.T.S
Can be used always best when in standard form
quadratic formula
always best for precise roots
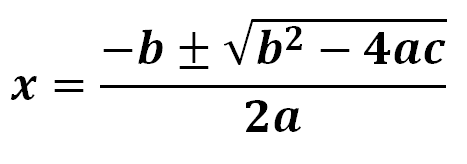
Quadratic Formula.
Used best for precise roots
- If b^2-4ac>0 = to 2 real roots
- If b^2-4ac<0 no real roots
- If b^2-4ac=0 ! real root or 2 equal roots
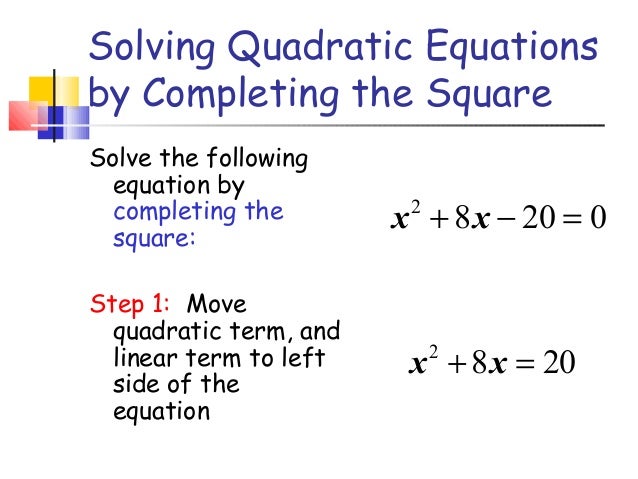
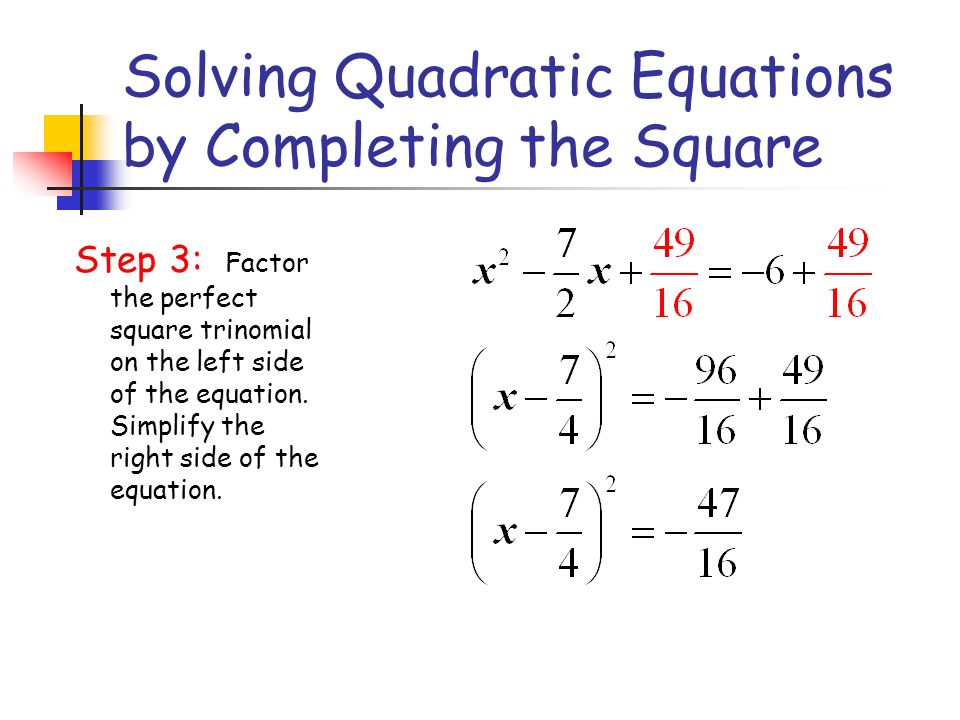
Completing the Square


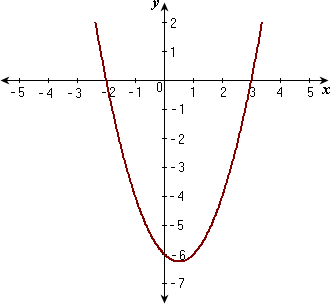
Parabolas
Standard and Vertex form equations
Subtopic

Non-Linear relations
A curved line
Relation
An identified pattern between 2 variable
May be expressed in ordered pairs, a table of values, a graph, or an equation
STEP Method
How to do the step method:
1a, 3a, 5a, and 7a
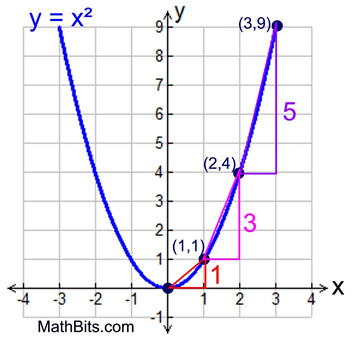
Translation

Reflection
A transformation in which a point and its image are equidistant from the line of reflection

Rotation
A transformation of a geometric shape in which each point is turned about a centre point
Non Linear relations
x is the independent variable
to be solved 1st
y is the dependent variable
solved after x
affected by the independent variable (x)
Vertical Stretch and Compression
Vertical stretch
is 1<a<-1
Vertical compression
is -1<a<1

Some Key definitions
Vertex: A point at which the curve changes direction
Congruent: Equal size and shape
Parabola: a symmetrical open plane curve formed by the
intersection of a cone with a plane parallel to its side
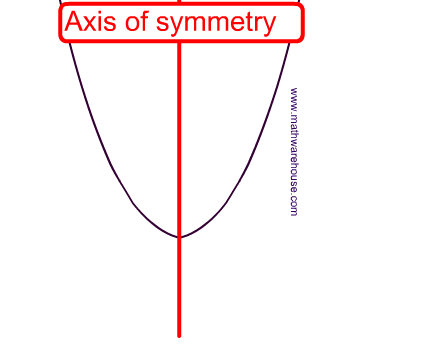
Axis of symmetry: Vertical line drawn through the vertex

Linear relations
Straight line
X- intercepts: The x-coordinates of the point where a line or curve crosses the y- axis, at this point y=0
y-intercepts: the y-coordinate of the point where a line or curve crosses the y- axis, at this point x is 0
Properties of a Parabola
Vertex, Axis of symmetry, Min/Max value, direction
of opening, Values 'x' may take, Values 'y' may take,
stretch or compression factor relative to y=x^2,
Congruent( = in size and shape)

Minimum value occurs when parabola opens upwards

Maximum value occurs when parabola
opens downwards
Zeroes
A value of x which a relation has a value of 0
They correspond to the x- intercept of the graph of the relation
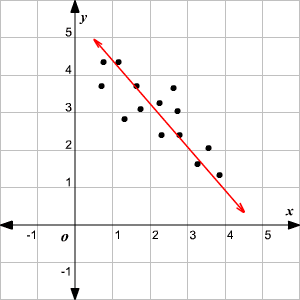
Line of best fit
A straight line to best represent data or a trend in a scatter plot

Curve of best fit
A curved line to best represent data or a trend in a scatter plot
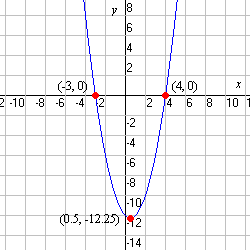
Mirror points
A point that is reflected in the axis of symmetry
Main topic
'a' value, 'k' value and 'h' value
The 'h' value controls the horizontal translation of the parabola (left and right)
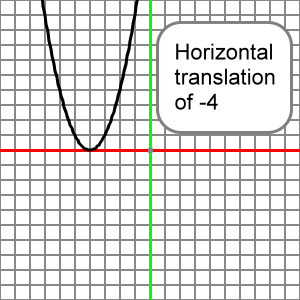
In this case the 'h' value was +4 and
a horizontal translation of 4 to the left
relative to y=x^2
The 'k' value controls the vertical translation of the parabola (up and down)

In this case the 'k' value is -1 and the vertical translation
was 1 down and horizontal translation was 3 to the right relative to y=x^2
The 'a' value can cause a vertical stretch or compression, changing the direction of opening and shape of the curve and/or it can cause a reflection

Right here shows a vertical stretch by a factor of 3
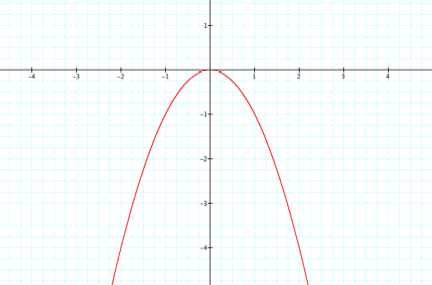
Reflection
a<0

Right here shows a vertical compression by a
factor of 1/2
Quadratic Relations
a relation in the form of y = ax^2 + bx + c
a, b and c are real numbers and a can not equal zero
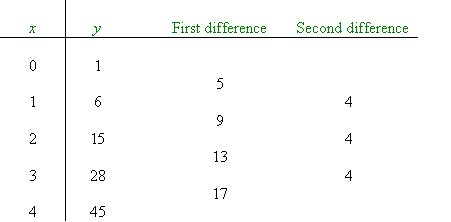
Finite differences
First Differences: The difference between consecutive y-values
Second differences: The differences between consecutive first differences and so on