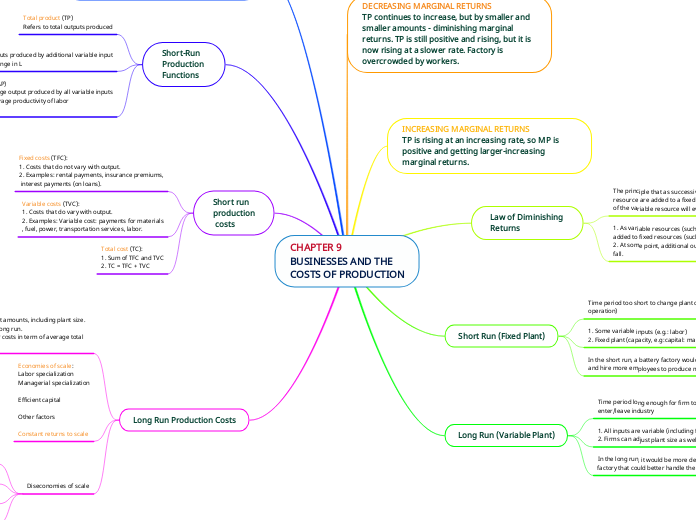
CHAPTER 9
BUSINESSES AND THE
COSTS OF PRODUCTION
DECREASING MARGINAL RETURNS
TP continues to increase, but by smaller and smaller amounts - diminishing marginal returns. TP is still positive and rising, but it is now rising at a slower rate. Factory is overcrowded by workers.
INCREASING MARGINAL RETURNS
TP is rising at an increasing rate, so MP is positive and getting larger-increasing marginal returns.
Law of Diminishing
Returns
The principle that as successive increments of a variable resource are added to a fixed resource, the marginal product of the variable resource will eventually decrease.
1. As variable resources (such as labor) are continuously added to fixed resources (such as machines),
2. At some point, additional output (marginal product, MP) will fall.
Short Run (Fixed Plant)
Time period too short to change plant capacity (size of operation)
1. Some variable inputs (e.g.: labor)
2. Fixed plant (capacity, e.g:capital: machines, factory size)
In the short run, a battery factory would purchase more inputs and hire more employees to produce more batteries.
Long Run (Variable Plant)
Time period long enough for firm to adjust plant capacity and enter/leave industry
1. All inputs are variable (including factory size)
2. Firms can adjust plant size as well as enter and exit industry.
In the long run, it would be more desirable to build a new factory that could better handle the increased production.
NEGATIVE MARGINAL RETURNS
TP falls and MP becomes negative. Additional worker reduces total outputs. Too many workers are hired.
Short-Run
Production
Functions
Total product (TP)
Refers to total outputs produced
Marginal product (MP)
Refers to additional outputs produced by additional variable input
MP = Change in TP / Change in L
Average product (AP)
Refers to the average output produced by all variable inputs
Also called the average productivity of labor
AP = TP / L
Short run
production
costs
Fixed costs (TFC):
1. Costs that do not vary with output.
2. Examples: rental payments, insurance premiums,
interest payments (on loans).
Variable costs (TVC):
1. Costs that do vary with output.
2. Examples: Variable cost: payments for materials
, fuel, power, transportation services, labor.
Total cost (TC):
1. Sum of TFC and TVC
2. TC = TFC + TVC
Long Run Production Costs
1. The firm can change all input amounts, including plant size.
2. All costs are variable in the long run.
3. Long run ATC: Now consider costs in term of average total costs.
Economies of scale:
Labor specialization
Managerial specialization
Efficient capital
Other factors
Constant returns to scale
Diseconomies of scale
control and coordination problems
Communication problems
Worker alienaton
Shirking