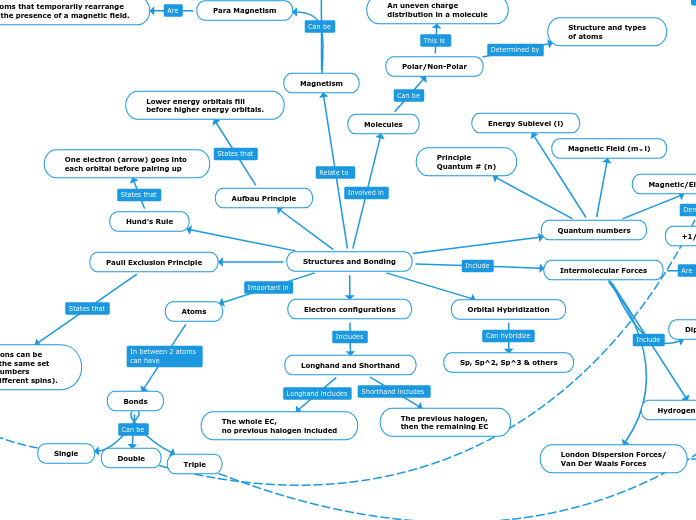
Structures and Bonding
Electron configurations
Longhand and Shorthand
The previous halogen,
then the remaining EC
The whole EC,
no previous halogen included
Quantum numbers
Principle
Quantum # (n)
Magnetic Field (m⌄l)
Magnetic/Electron Spin (m⌄s)
+1/2 or -1/2
Energy Sublevel (l)
Aufbau Principle
Lower energy orbitals fill
before higher energy orbitals.
Hund's Rule
One electron (arrow) goes into
each orbital before pairing up
Pauli Exclusion Principle
No two electrons can be
identified by the same set
of quantum numbers
(must have different spins).
Orbital Hybridization
Sp, Sp^2, Sp^3 & others
Atoms
Bonds
Single
Double
Triple
Molecules
Polar/Non-Polar
An uneven charge
distribution in a molecule
Structure and types
of atoms
Intermolecular Forces
Forces of attraction that appear
between two or more molecules
Dipole-Dipole
Magnetic attraction between
S^+ and S^-
Hydrogen Bonding
A type of dipole-dipole
specific to hydrogens
London Dispersion Forces/
Van Der Waals Forces
Temporary (short-term) forces
that can occur between any two molecules
Polar or non-polar
Magnetism
Para Magnetism
Atoms that temporarily rearrange
in the presence of a magnetic field.
Ferro Magnetism
Certain materials form to
be permanent magnets.
Iron, Cobalt, Nickel
Organic Chemistry
Organic Molecules
Hydrogen and Carbon
Alkane
Only single bonds
Least amount of tension
Methane
Alkene
At least 1 double
bond
Methene
Alkyne
At least 1 triple
bond
Methyne
Most amount of tension
Markovnikov's Rule
Rich get richer
Geometric Isomers
Cis
Functional groups on the
same side of the C chain
Trans
Functional groups on the
opposite side of the C chain
Functional Groups
Hydro Halogenation
Adding a halogen to
the molecule
Alkyl Halide
Hydrogenation
Adding a Hydrogen (H2)
to the molecule
Alkane
Alcohol
Adding Water (H2O)
to the molecule
Controlled Oxidation
Primary Alcohol
Aldehyde
Carboxylic Acid
Ester
Secondary Alcohol
Ketone
Tertiary Alcohol
Dehydration
Ether
Change of function, due to
the change in structure
Thermodynamics
Calorimetry
A measure of the amount
of heat released or absorbed
in a chemical reaction.
q = mc∆T
Enthalpy
∆H⌄x, The sum of
internal energy
Hess's Law
The total enthalpy
change is the sum of
all changes, regardless
of the # of steps/stages
of a reaction.
Chemical Kinetics
Rate of Reactions
Instantaneous Rate
of Change (IROC)
Change at a
certain point
Catalysts!
Average Rate
of Change (AROC)
Change over an
interval (2 points)
Rate Law
The RoR is related to the
[A] and [B] but not directly
proportional in all ways.
r = k[A]^m[B]^n
Collision Theory
a reaction consists of
particles that are always
randomly moving.
Brow nian Motion
These collisions with other
particles/wall of container can cause
the breaking/forming of bonds
Arrhenius Equation
The relationship between
the rate of reaction and
temperature for chemical reactions.
Gibbs Free Energy
∆G, The available
energy has to do work
Endothermic Reaction
A reaction that absorbs heat
Exothermic Reaction
A reaction that releases
heat
Activation Energy
Energy needed for
a reaction to occur
Electrochemistry
Redox Reactions
Spectator Ions
Positive E, spontaneous
Negative E, non-spontaneous
Reducing Agent
Atom that loses
electrons
Oxidizing Agent
Atom that gains
electrons
Half Reactions
Electrolysis
Galvanic Cells
Spontaneous
reactions
Standard Reduction Reaction
Tendency of something
to be reduced
Cell Notation
Anode | Anode(aq) | Cathode
Anode | Anode(aq) || Cathode(aq) | Cathode
Corrosion
Chemical Weathering
Ion is oxidized
Oxidation States
Equals the charge of the atom
within the molecule
Catalysts
Speed up a reaction
Equilibrium
Reverse reaction
When the reaction goes
backwards (right to left)
Closed Systems
No change in matter,
energy can be exchanged
Solubility Equilibrium
Dynamic equilibrium
between the solute and
solvent
Equilibrium Constant
Concentration at the
given equilibrium
Chemical Reaction
Equilibrium
Dynamic Equilibrium
between the products
and reactants of a chemical
reaction
Le Chatelier's Principle
Any disturbance will be adjusted
by the system, occurs at equilibrum
Collision Theory
Collisions can produce products
or reactants, the amount is equal
Phase Equilibrium
Dynamic Equilibrium between
the physical states of
substances
Ie. Same molecule but change in state
Equilibrium Law
Rule of 100
Perfect Squares
Quadratics
Elimination reaction
Loss of smaller molecule
FAVOURITE MEMORY FROM SCH4U
When you did experiments for us to watch,
also the balloon things to make us understand the structures. :)
Galvanic Cell Experiment