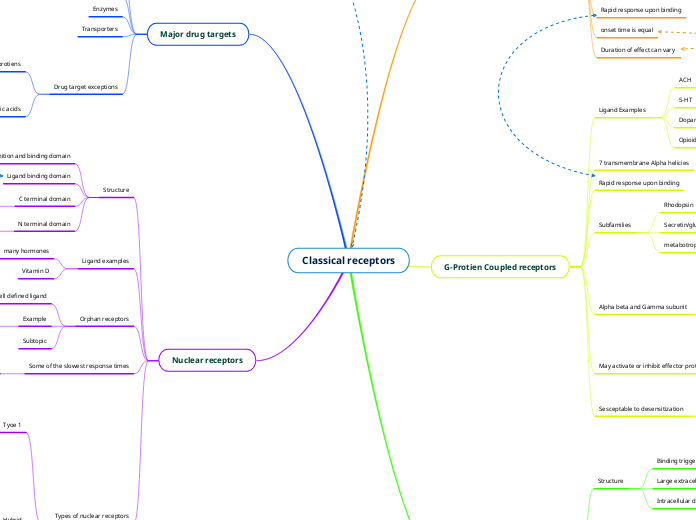
Classical receptors
Ligand Gated ion channel
Receptor Examples
Nicotinic ACH receptor
5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 (5-HT3) receptors
GABA type A receptor
5 subunit ligand
2 neurotransmitter binding receptors
Upon binding, channel changes
conformation to allow ions to pass
primarily mediate chloride transport
Rapid response upon binding
onset time is equal
Duration of effect can vary
G-Protien Coupled receptors
Ligand Examples
ACH
5-HT
Dopamine
Opioids
7 transmembrane Alpha helicies
Rapid response upon binding
Subfamilies
Rhodopsin
Secretin/glucagon
metabotropic glutamate receptor/Ca sensor
Alpha beta and Gamma subunit
Beta and gamma stay bound
upon binding Alpha subunit converts GDP to GTP
GTP activates effector protien
Alpha subunit may continue affect
effector protein randomly
Beta and Gamma subunits may bind targets
May activate or inhibit effector protien
Sesceptable to desensitization
Occurs through phosphorylation of cytoplasm tail
Caused by excessive activation of GPCR
Clinically, may need to increase dosage over time
Kinase linked receptors
Structure
Binding triggers dimerization of receptor
Large extracellular binding site
Intracellular domain
Ligand examples:
Insulin
Growth factors
Cytokines
bacterial lipopolysaccharides
Receptor examples
Receptor tyrosine kinases
Growth factor receptors
Toll like receptors
Serine/Threonine kinase
Transforming growth factor receptor
Cytokine receptors
Associate with Cytosolic tyrosine kinases
Major drug targets
Classical receptors
Main topic of lecture
ion channels
Enzymes
Transporters
Drug target exceptions
Drugs target other specific protiens
structural protiens
Signaling protiens
Drugs target nucleic acids
DNA/RNA metabolism
Antisense and siRNA targets
Nuclear receptors
Structure
DNA Recognition and binding domain
Ligand binding domain
C terminal domain
Governs nuclear localization
N terminal domain
Controls interactions with cofactors
Ligand examples
many hormones
Vitamin D
Orphan receptors
No well defined ligand
Example
RXR receptor
Subtopic
Some of the slowest response times
Hours to days
Types of nuclear receptors
Tyoe 1
Found in cytoplasm
Form homodimers on ligand
primarily bind:
Glucocorticoids
Mineralocorticoids
oestrogen, progesterone, androgen
Hybrid
Form obligate heterodimers with RXR
Examples
Thyroid hormone receptor
Vitamin D receptor
Type 2
primarily in nucleus
form homodimers with Retinoid x receptor
common receptor types
Fatty acid receptors
Cholesterol receptors
xenobiotic receptors
Activates drug metabolizing
enzymes such as CYTP3A