Conditions for and Impediments to Social Change
Leadership & Roles of Elites
Charismatic Leader
Grandiose Promise
Susceptible Population
A susceptible population is not a weak population, it is simply a group of people whose needs are not being met. In post-WWI Germany, people needed a strong front and they needed hope. Hitler exploited the desperation and promised many things which is how he created social change.
Subtopic
Magnetic, popular people that seem to exist in an extraordinary bubble tend to have the most power over the masses. Sociologist Max Weber theorized that these leaders are some of the most important people in sparking social change and have an end goal that they can impose on the population for bad or good. Some examples of these leaders are Adolf Hitler, Joseph Stalin, Martin Luther King Jr., and Opera Winfrey.
Modernizing Elites
Politicians
Celebrities
Agents of the Law
CEOs/Corporations
Subtopic
Leaders and elites contribute to social change by proposing new norms, setting trends, and gathering large followings. Large followings spread social change that they see leaders and elites demonstrating. A list of key leaders and elites relevant today:
Populace Readiness
Attitude of Populace
Political Views
Educational Background
Values established in youth
Impediments to Change
Traditional Cultural Values
Routine/Norm
Challenge to World View
[Peasant] Resistance
Modernity/Modernization
Traditional World View
Expense
Social Science Inquiry
Participatory Research
Advocacy Research
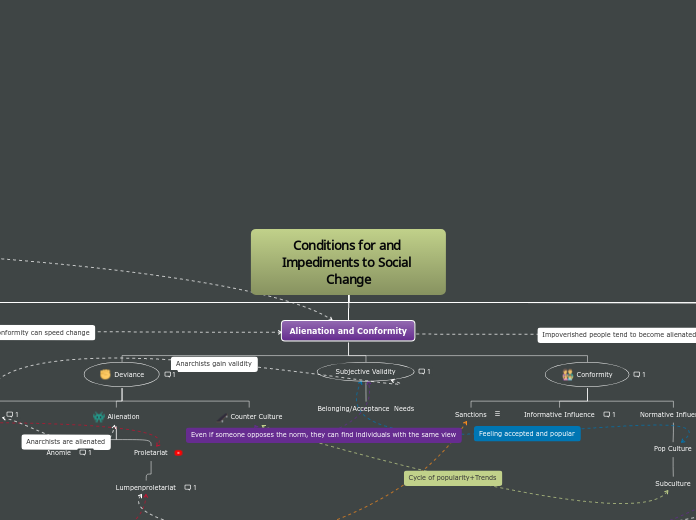
Alienation and Conformity
Deviance
Anarchy
Alienation
Anomie
Proletariat
Lumpenproletariat
Counter Culture
Subjective Validity
Belonging/Acceptance Needs
Conformity
Sanctions
Informative Influence
Normative Influence
Pop Culture
Subculture
Poverty and Affluence in Canada
Relative Income Inequality
Highest Quintile
Lowest Quintile
Absolute I.I
Wage Gap
Public Policy Questions
Example: Public policy around gov. compensation during COVID changed with the creation of CERB
Values and Social Change in Canada
Pluralism/Inclusiveness
Singularity
Feminism
Employment Equity Act
Act to increase equality in income distribution in 1996 between people of marginalized groups
Now Pay Equity Act to mitigate gender pay discrimination
Charter of Rights and Freedoms: Section 28 says men and women are equal under the law
Participation Rates
Percentage of women employed, typically lower than men
Equality
Systemic Discrimination
Climate Crisis
Dominant Paradigm
Alternative Environmental Paradigm

Capitalism/Classism
Wall Street