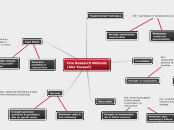
Five Research Methods (Alia Youssef)
Experimental Technique
Def.: examination in seeking facts or principles
E.g.: An investigator wants to evaluate whether a new technique to teach math to elementary school students is more effective than the standard teaching method.
Correlation
Def.: relationship between two variables
E.g.: There is a positive correlation between suicide and depression.
Naturalistic
Def.: observing subjects in their natural environment, no intervention.
E.g.: studying the differences in risk taking behavior between boys and girls by observing them in different settings.
Case Study
Def.: descriptive & in-depth study about a person, group or event.
E.g.: conducting a study to investigate the musical abilities of an individual with an exceptional ability to write songs.
Surveys
Def.: gathering information & data from individuals (inspecting)
E.g.: gathering people's opinions about "sushi"