Chapter 21: An Introduction to Geopolitics
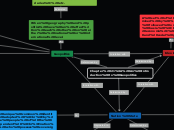
Ideology
A set of beliefs determined by
nation followed on a daily basis.
Includes economic, political, and social goals
Basic Ideologies
Authoritarianism
Strict authority by the government with limited political and individual freedom
Absolute Monarchy
Authority given to the monarch
with no official leaders
Examples: Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Oman
One-Party Nation State
Only one political party exists
and have all political power
Examples: Libya, North Korea
Religious Nation State
Political power held by spiritual
leaders whose religious beliefs
form political framework
Examples: Iran, Afghanistan (1996-2001)
Military-Authoritarianism
Power is held by military officials
seized from an elected government
Examples: Algeria, Chile, Iraq
Democratic States
Citizens exercise political power by picking official leaders who advocate their wishes
Majority rules desicion-making system
Freedom of religion, assembly, expression, and the press guaranteed
Example: Canada, Australia, India
Communist State
Ownership of most goods is held
by the state and has some form
of authoritarian government
Examples: Cuba, Vietnam, North Korea
Nation State
A unique common identity adopted
by the people of the independent
nation, who possess sovereignty
Set apart by religion, history, language, customs, ethnicity, and community
Europe
Renaissance (late
1400s to early 1600s)
Changed people's
views on governance
Power usually resided in the hands of
a dynasty or single ruler within borders
Empires of Alexander the Great, Genghis Khan, ancient Rome, Northern Nigeria
Nation State Formation
Created between1900 and 1999
Decolonization of Africa, Asia,
the Caribbean, and Middle East
World War II
New nations established when
the Soviet Union broke up
Role Played by National Sovereignty
A legal concept with the ability to create policies and enforce laws within its borders without interference from other states
Canada
Arctic region is diminishing
Climate change
Northwest Passage seen as international waters by the U.S. and Russia instead of Canadian territorial waters
Canada's sovereignty being
challenged by the Arctic
Borders
The limit of a nation's laws and security, while branding a specific geographical
area with a national identity
Armed forces from one country cross the border of another without being invited,
the country's national sovereignty is being threatened
Borders are determined as a result of
negotiations between countries concerned
Globalization
The process of interaction and integration among people and the world's economical, financial, technological, geographical, cultural and political systems
Given a rise to a number of forces
that are weakening the concept of
national sovereignty
Geopolitics
When geography and politics have an effect on each other on either a national or international level.
Physical borders, environmental
boundaries, air and sea boundaries, etc.
Political Decisions
Climate/Environment
Population Size and Control
Trade Agreements
Military Alliances
Economy and Stability
International Conflict
Border Determining
Links from TV to radio to economical telephone across Canada
Conflicts
Mid 1940
1980s
United States and Soviet Union
Rivalry, distrust, and growing suspicion between ideologies used politically
Cold War
1947-1991
Economic incompatibility
Imperialism accusations
Economic, military, and political
influence exerted over a spherical
area of superpowers
After the Cold War
Created a relaxation of tension between
communist and democratic nations
Various forms of government were
adopted by the Soviet Union
Power blocs that deteriorated
to the point of war between
two relations
Has not brought an end to geopolitics