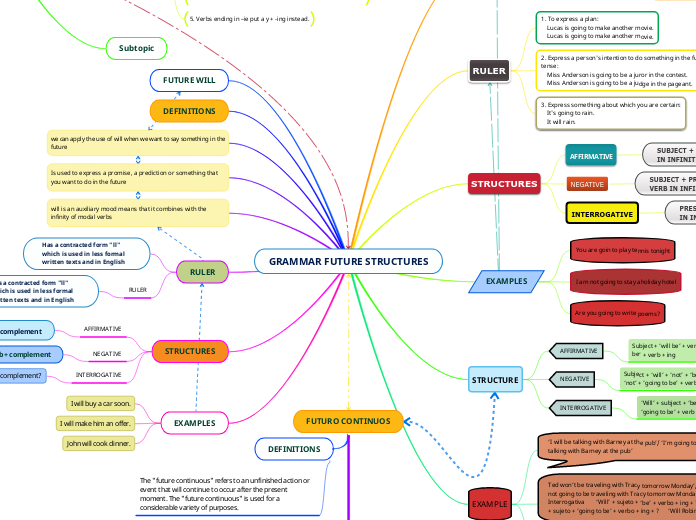
GRAMMAR FUTURE STRUCTURES
GOING TO
DEFINITIONS
Going to is used to express plans or forceful events in the future.
It is important to note that in this form of the future tense the verb to be is used in the present form.
RULER
1. To express a plan:
Lucas is going to make another movie.
Lucas is going to make another movie.
2. Express a person's intention to do something in the future tense:
Miss Anderson is going to be a juror in the contest.
Miss Anderson is going to be a judge in the pageant.
3. Express something about which you are certain:
It's going to rain.
It will rain.
STRUCTURES
AFFIRMATIVE
SUBJECT + PRESENT TO BE + "GOING TO + VERB IN INFINITY + COMPLEMENT
NEGATIVE
SUBJECT + PRESENT TO BE + "NOT"+ "GOING TO + VERB IN INFINITY + COMPLEMENT
INTERROGATIVE
PRESENT TO BE + SUBJECT + "GOING TO" + VERB IN INFINITY + COMPLEMENT + ?
EXAMPLES
You are goin to play tennis tonight
I am not going to stay aholiday hotel
Are you going to write poems?
STRUCTURE
AFFIRMATIVE
Subject + ‘will be’ + verb + ing / Subject + ‘To be’ + ‘going to be’ + verb + ing
NEGATIVE
Subject + ‘will’ + ‘not’ + ‘be’ + verb + ing / Subject + ‘To be’ + ‘not’ + ‘going to be’ + verb + ing
INTERROGATIVE
‘Will’ + subject + ‘be’ + verb + ing + ? / ‘To be’ + subject + ‘going to be’ + verb + ing + ?
EXAMPLE
‘I will be talking with Barney at the pub’/ ‘I’m going to be talking with Barney at the pub’
Ted won’t be traveling with Tracy tomorrow Monday’/ Ted is not going to be traveling with Tracy tomorrow Monday’
Interrogativa ‘Will’ + sujeto + ‘be’ + verbo + ing + ? / ‘To be’ + sujeto + ‘going to be’ + verbo + ing + ? ‘Will Robin be
‘Will Robin be sleeping all afternoon?’/ ‘Is Robin going to be sleeping all afternoon?’
FUTURE WILL
DEFINITIONS
we can apply the use of will when we want to say something in the future
Is used to express a promise, a prediction or something that you want to do in the future
will is an auxiliary mood means that it combines with the infinity of modal verbs
RULER
Has a contracted form "ll" which is used in less formal written texts and in English
RULER
Has a contracted form "ll" which is used in less formal written texts and in English
STRUCTURES
AFFIRMATIVE
Sujeto + will + verb + complement
NEGATIVE
sujeto + will + not + verb + complement
INTERROGATIVE
will + sujeto + verb + complement?
EXAMPLES
I will buy a car soon.
I will make him an offer.
John will cook dinner.
FUTURO CONTINUOS
DEFINITIONS
The "future continuous" refers to an unfinished action or event that will continue to occur after the present moment. The "future continuous" is used for a considerable variety of purposes.
RULES
As we have seen before, to talk about actions that will be taking place at a specific time in the future; which were already being carried out before that specific moment, and which will continue to be carried out afterwards.
In this same sense, to talk about actions that will be taking place in the future and that will be interrupted by another action. This action (verb) that interrupts must go in 'Present simple'.
To make predictions or assumptions about events both in the present and in the future.
To talk about unfinished actions in the present that will continue in the future.
Only and only in interrogative sentences, to ask for information about the future in a very polite way.
PRESENT PROGRESSIVE FUTURE
DEFINITIONS
The present continuous generally refers to situations or actions that are taking place at the moment and, as in Spanish, learning this tense is essential to have fluency and expression in any conversation in English.
RULER
1. All verbs end in –ing.
There is no need to overthink this. Every verb conjugated in the present continuous must have this ending.
2. When a verb ends in a consonant, the last letter must be doubled to add the ending -ing.
3. If the verb ends in silent e, this letter is removed and the ending -ing is added.
4. Verbs that end in double e keep this ending and add –ing to the end.
5. Verbs ending in –ie put a y + -ing instead.
Subtopic
STRUCTURES
AFFIRMATIVE
Subject + verb to be + verb in gerund + object
NEGATIVE
Subject + verb to be + not + verb in gerund + complement
INTERROGATIVE
Verb to be + subject + verb in gerund + object + ?
EXAMPLE
I am singing in the rain
I am not singing in the rain
Am I singing in the rain?