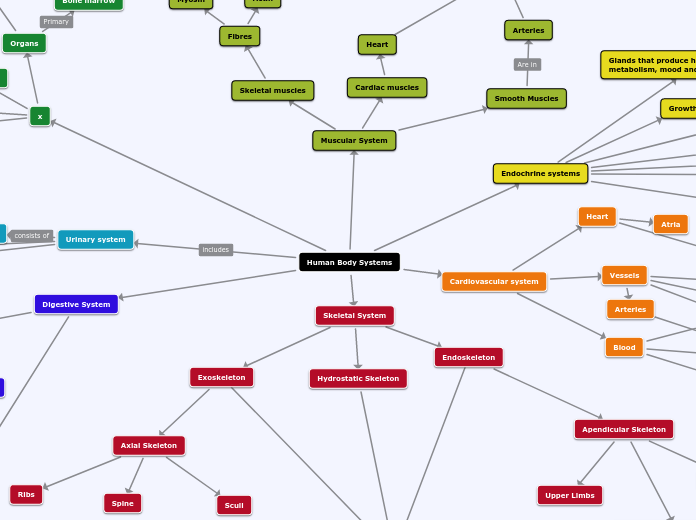
Human Body Systems
Skeletal System
Endoskeleton
Apendicular Skeleton
Bones of the shoulder griddle
Upper Limbs
Pelvic Gridldes
Hydrostatic Skeleton
Bones
Cartilage
This system is the framework of our bodys and contains 206 bones
Connects at joints
Bone tissue
Exoskeleton
Axial Skeleton
Ribs
Spine
Scull
Muscular System
Skeletal muscles
Fibres
Myosin
Actin
Cardiac muscles
Heart
Smooth Muscles
Arteries
Heart and Movement
Digestive System
Mouth
Esophagus
Stomach
Pepsin
Chemical breakdown
Small intestine
large intestine
rectum
Convert food waste products into faces
Undigested food enters from small intestine
Villi
enzymatic digestion
Absorbs Vitamens and minerals
Moves food by peracitis
Salvary glands
Breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components until they can be absorbed into the body
Urinary system
Bladder
Stores urine
Eliminates waste
Kidney
filters waste and extra fluid
eliminates waste from the body, regulates blood volume and blood pressure, controls levels of electrolytes and metabolites
Cardiovascular system
Blood
Platlets
Red blood cells
White blood cells
Vessels
Blood flow through the body
Made up of blood vessels that carry blood away and towards the heart. The system takes oxygen, hormones, etc to cells and removes the waste
Veins
Provide nutrients
Arteries
Heart
Atria
Ventricle
Endochrine systems
Glands that produce hormones for growth, metabolism, mood and other functions
Growth
Pituatiary
Water blance
Metabolism
Thyroid
Reproduction
Ovaries
Testicles
Calcium and glucose
Parathyroids
Pancreas
Stress
Adrenals
x
Organs
Tonsills
Spleen
Bone marrow
Thymus
Lymph nodes
Lymph capillaries
removes excess fluid and waste
Lymph vessels