METAL
LEAD
Chronic exposure
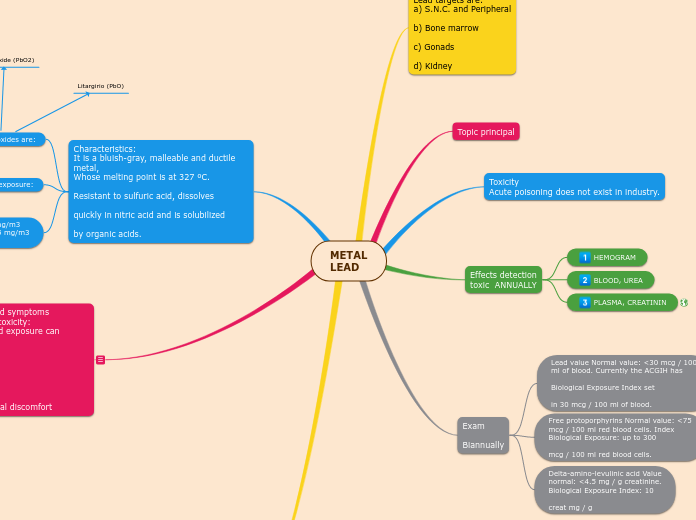
Lead targets are:
a) S.N.C. and Peripheral
b) Bone marrow
c) Gonads
d) Kidney
Topic principal
Toxicity
Acute poisoning does not exist in industry.
Effects detection
toxic ANNUALLY
HEMOGRAM
BLOOD, UREA
Exam
Biannually
Lead value Normal value: <30 mcg / 100
ml of blood. Currently the ACGIH has
Biological Exposure Index set
in 30 mcg / 100 ml of blood.
Free protoporphyrins Normal value: <75
mcg / 100 ml red blood cells. Index
Biological Exposure: up to 300
mcg / 100 ml red blood cells.
Delta-amino-levulinic acid Value
normal: <4.5 mg / g creatinine.
Biological Exposure Index: 10
creat mg / g
Characteristics:
It is a bluish-gray, malleable and ductile metal,
Whose melting point is at 327 ºC.
Resistant to sulfuric acid, dissolves
quickly in nitric acid and is solubilized
by organic acids.
Its main oxides are:
Minium (Pb3O4)
Lead dioxide (PbO2)
Litargirio (PbO)
Uses and exposure:
Lead and zinc mines.
Pb and Zn metallurgy.
Manufacture of accumulators
C.M.P.: 0,15 mg/m3
TLV-TWA: 0,05 mg/m3
(ACGIH)