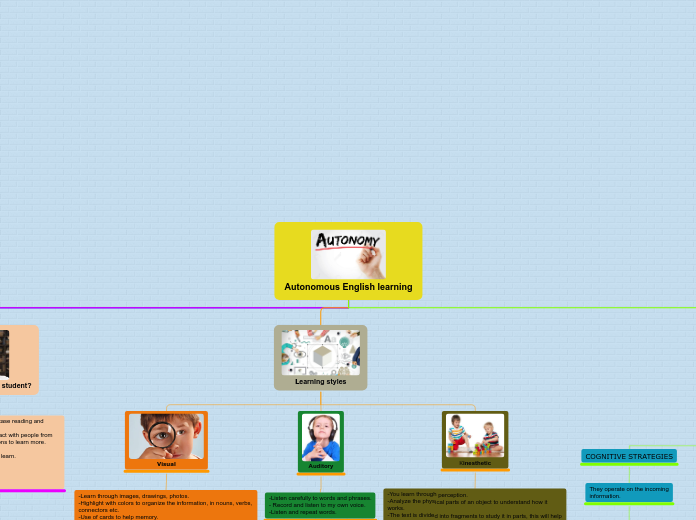
Autonomous English learning

Definition
Autonomous learning takes place when students take control and responsibility for their own instruction, in this way they learn at the desired speed and capture and assimilate it according to their need.

Characteristics of an autonomous student
-Have prior knowledge on the subject.
-Pay more attention to content.
-Discipline, assign a specific time to study.
How to be an autonomous student?
-Constant feedback on the subject, in this case reading and watching videos in English.
-Use ICT for example messenger and interact with people from other countries, also make use of applications to learn more.
-Time, organize it to have one especially to learn.
-Learn with friends and teachers.
-Have the ability to learn by yourself.

Learning styles

Visual
-Learn through images, drawings, photos.
-Highlight with colors to organize the information, in nouns, verbs, connectors etc.
-Use of cards to help memory.
Auditory
-Listen carefully to words and phrases.
- Record and listen to my own voice.
-Listen and repeat words.
Kinesthetic
-You learn through perception.
-Analyze the physical parts of an object to understand how it works.
-The text is divided into fragments to study it in parts, this will help you memorize.

Learning strategies
"Mental steps or operations that learnes use to learn
a new lenguage and to regulate their efforts to do so"
Wenden, (1988:18)
COGNITIVE STRATEGIES
They operate on the incoming
information.
-Repetition, imitating.
-Resourcing.
-Traslation.
-Note - taking.
-Deduction.
-Contextualization.
METACOGNITIVE STRATEGIES
They are used for planning, monitoring
y evaluating the learning activity.
Directed attention.
Deciding in advance to concentrate
on general aspects of task.
Selective attention.
Paying attention to specific
aspects of a task.
Self-monitoring.
Checking one's performance
as one speacks.
Self-evaluation.
Appraising one's performance
in relation to one's
own standards.
Self-reinforcement.
Rewarding oneself for success.