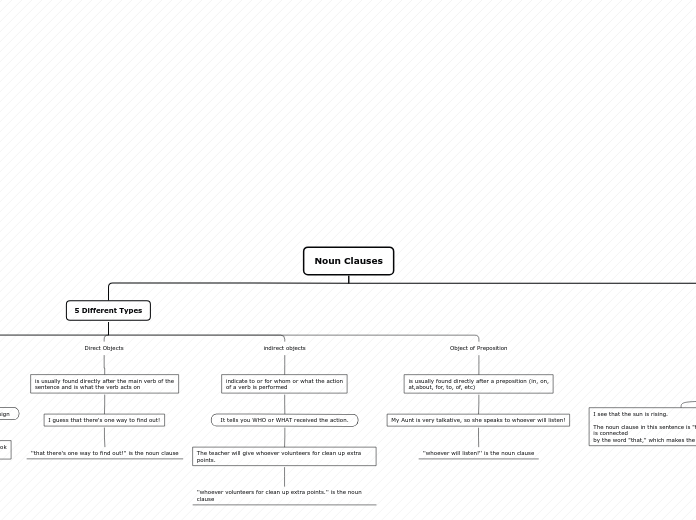
Noun Clauses
5 Different Types
Subjects
The gerund will be located al the beginning of the sentence and it’s what the sentence talks about (main topic).
How you study matters significantly to your success.
'' How you study '' is the noun clause
Appositives
are used to give more details about the subject
usually enclosed between commas or any punctuation sign
The beast, a tiger with stripes which was starting to look
ravenous, was starting to salivate as it eyed its prey.
''a tiger with stripes which was starting to look
ravenous'' is the noun clause
Direct Objects
is usually found directly after the main verb of the
sentence and is what the verb acts on
I guess that there's one way to find out!
''that there's one way to find out!'' is the noun clause
indirect objects
indicate to or for whom or what the action
of a verb is performed
It tells you WHO or WHAT received the action.
The teacher will give whoever volunteers for clean up extra points.
''whoever volunteers for clean up extra points.'' is the noun clause
Object of Preposition
is usually found directly after a preposition (in, on,
at,about, for, to, of, etc)
My Aunt is very talkative, so she speaks to whoever will listen!
''whoever will listen!'' is the noun clause
What is a noun clause?
Is a clause that plays the role of a noun
EXAMPLES:
I see that the sun is rising.
The noun clause in this sentence is "that the sun is rising." It is connected
by the word "that," which makes the clause dependent.
I see the sun.
The noun in this sentence is "sun."
They're introduced with a relative or adverb pronoun
Where: Place
Why: Reason
If: Condition
That: People / Things
When: Time
Whether: Condition
Who: People
Whom: People (formal)
Which: Things