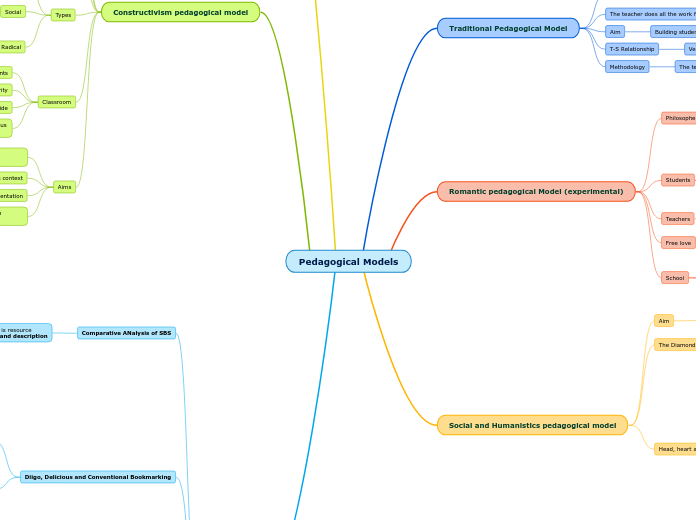
Pedagogical Models
Traditional Pedagogical Model
The student has a passive and memoristic role.
If they want to learn, they have to repeat and repeat the information
The teacher does all the work for the student to understand
There is no innovation, much less creativity
Aim
Building student character through discipline
T-S Relationship
Vertical
Teacher is the authority
Methodology
The teacher does it and the students imitate it, repetition
Romantic pedagogical Model (experimental)
Philosopher and pedagogue Alexander Neil was its exponent.
Neil said: emotional education is more important than intellectual education
All people are good by nature
They just need to be guided to know their strengths and abilities
He considered, students can to learn trough freedom
Students
They choose what they want to learn according their natural interests, values and prior knowledge
It can be a problem because there is not a curriculum
Thanks to emotional education they are more prepared for face challenges
Teachers
Help the students to develop their abilities and internal qualities.
Any kind of the guidance of the teacher was an imposition
It reduce the freedom of the children
Free love
Students could maintain relationships with anyone they wanted, including teachers
School
It is the obligation of the school to offer a suitable space to explore interests and enough time to perform this task.
Students are not very well prepared relative to other students
Social and Humanistics pedagogical model
Aim
To value and respect and individual on their own personality and uniqueness
The Diamond model
The individual is empowered to take on ownership for their own life through positive experiences
Head, heart and hands
Head
Cognitive knowledge
Heart
Emotional and spiritual learning
Hands
Practical and physical skills
The learning zone model
Comfort zone
A safe zone, here we are familiar without risks
Learning zone
We make new discoveries about ourselves, other people and the world
Panic zone
Area of experience where little or no learning can take place
The zone of proximal development
What a learner can do without help
What learner cannot do with help
"Vygotsky's Theory of Cognitive"
The model stresses that learning is most successful in a social context
A child for instance follows a mentor's example
Behavioral Pedagogical Model
Its exponent was the psychologist and philosopher, Skinner
Students
Study and learn at their own pace
However, they receive effort for behaviors that move them to successfully accomplish the task.
He/ she is not a passive spector
Learning by doing
Use hand-on active learning exercises
Work though exercises until they repeatedly apply desirable search behaviours such as use of quotation marks.
Know their capacities and abilities for themselves
It requires issuing the answer or the solution to the problem situation
Correct behaviors are selectively reinforced
Instruction sequences programmed in small steps with immediate reinforcement and behavior modification achieve the desired goal
Aim
Shaping technical productive behavior
T-S relationship
Teacher is the intermediary
Methodology
Setting and controlling instructional objectives
Constructivism pedagogical model
Approach
To learning that holds that people actively construct or make their own knowledge
The reality is determined by the experiences of the learner
Teacher
Facilitate or guide the student
Creates a collaborative problems-solving environment
Scaffolding (key of effective teaching)
Adult continually adjusts the level of him/her help in response to the learner's level of performance
Students
They are responsibles of their knowledge/ education
They link knowledge with experiences
Learning is an active process
Information may be passively received, but understanding cannot be
Types
Cognitive
Learning is relative to the stage of cognitive development
Social
Learning is a collaborative process
Knowledge is a individuals' interaction with their culture and society
Radical
States that the knowledge individuals create tell us nothing about reality
Classroom
Knowledge will be shared between teacher and students
Teacher and student will share authority
Teacher is a facilitator or guide
Learning group will consist of small numbers of heterogeneous students
Aims
To provide experience with the knowledge construction process
To embed learning in realistics context
To encourage the use of multiple modes of representation
To encourage awareness of the knowledge construction process
Last part
Comparative ANalysis of SBS
The goal of SBS is resource
bookmarking and description
Storing a link and describing it using metadata.
Storage
Something inside the "Mosaic" browser
Hotlist
Link storage
Bookmarks
Store of link
Favorites in Internet Explorer
Services
Backflip
Blink
BookmarkBox
Bookmarks Plus
etc
Stopped working after the dot-com boom
2003
The coming of Delicious and the rest of SBS
Websites
Digg
Reddit
Propeller
They are focused on the social
boormarking of items associated with news.
Diigo, Delicious and Conventional Bookmarking
Diigo's innovation is the most used and widespread bookmarking too.
Diigo
Its highlighting and annonation functionalities
It has a set of functions that enhance
its versality and capacity as an SBS
It is competing with Delicious in India,USA,China and Germany in relation of its intensity of use, and the ranking of the service
SWOT
Diigo tool after applying SWOT
Strenghs
Intuitive interface
Resources on the web can be found from anywhere
Cloud tags show the topics the user is interested in
Weaknesses
It make some browser slower
It "compels" to share
It doesn't allow and instant feedback
between users that add comment
Opportunities
It is extremely usefol for on line research
It shows expert bookmrks systems,
whose intineraries can be considered as a reference
Shared bookmarking strategies enhance
knowledge learning
Threats
A lack of homogeneity and agreement of tags
The constant improve of SBS
Incipent developments to combine its use with conventional browsers
Conclusion
Virtual environment that foster learning is becoming extremely valuable.
Virtual communities become closely linked groups
Collaborative tagging generates new collaboragtive learning contexts
Personal interactions make and strengthen
the collaborative learning process.
Diigo is a metacognitive toll.
It displays different ways to learn, think,
and build knowledge
This tool is a step forward compared to other SBS because it has improved functionalities