Physical Environment Interactions Pt. 2
Climate Change

The greenhouse effect
1. Solar radiation enters earths atmosphere
2. Some heats earths surface: some is reflected
3. Greenhouse gases trp some reflected heat

What are greenhouse gases
Gases that trap heat in the earths atmosphere
Examples
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Nitrous oxide
Ozone
Water vapor

Why would warmer climate be a good thing
Longer growing season
More food
More time at the beach
Longer construction season
Fewer bus,plain, train delays
More cruises holidays and trips
Fewer power outages
More space for people to live
Climate Basics

Climate Graphs
Two graphs in one
Line graph showing temperature
Measure in°C
Y axis on left side
Plot monthly values in middle of each column
Coneect dots with a red lign
Bar graph showing precipitation
Draw bars for each month precip
Measured in mmper month
Y axis on right side
Colour them blue
Growing season
Draw a line at 5.6°C
Colour the space between the line and your red temp line

Climate Vs. Weather
Climate
Average weather of a place, over long period of time
Weather
Day to day
Temperature
Precipitation (rain,snow,hail)
Humidity
Wind
Temperature Range
Highest temp. minus lowest temp.

Factors Affecting Climate
L.O.W.E.R. Near water

Latitude
The higher the latitude the lower the temperature

Ocean Currents
Ocean currents affect the temp. of air that passes over it
When 2 currents meet the weather is often damp & foggy
Wind & air masses
Air moisture releasing precipitation
Less precipitation inland (Continental loocation)
Oceans contain moisture
Elevation
The higher the elevation the lower the temperature
When air rises, it expands, because there is less air pressure
As air expands it loses heat
Higher elevation = more moisture
Relief
Mountains block precipitation
As the moist air rises up the windward side at mountain range it expands & cools
Leeward = dry side, Nickname: Rain shadow
Windward = wet side

Near Water
Farther away from water bodies = hot summers, cold winters & less precip.
Closer to water bodies = colder summers, warmer winters & more precip.

Soil & Vegetation
Four components that make true soil
Minerals
Minerals needed by plants and animals
Bacteria and organic materials
Decomposed plants and animals. That give nutrients to plants
Gives soil its dark color
Air
Plants need air in the roots
Moisture
Water dissolves nutrients into soil so plants can suck them up
How is topsoil formed
Oganic materials are added to the top
How long did it take topsoil to form
6000-1200 yrs
Why does size of rock particle matter to soil
The bigger the rock the more minerals it has
Difference between leaching and calcifiction
Leaching: When soil takes water underground so plants cant use it
Calcification: Soil gives water to plants
Which trees could survive harsh climate, Coniferous or deciduous
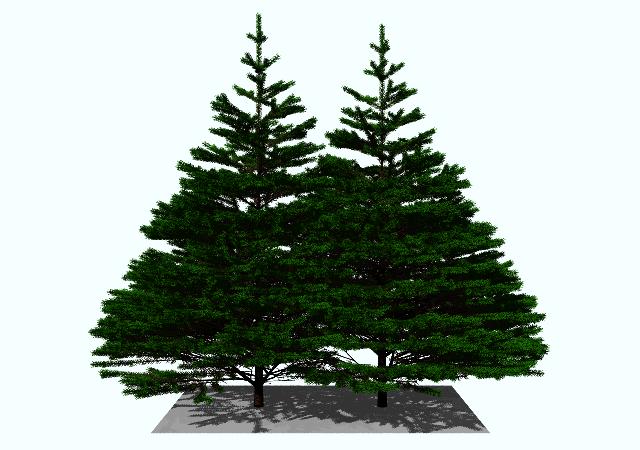

Coniferous trees
They can extract minerals from bad soil
Have sap that works as anti-freeze
Have waxy needles to prevent water loss in droughts
Branches and needles shack of snow easily
Their needles can conduct photosynthesis on warm days even out season

deciduous trees
Can not survive in winter
Types of Precipitation

relief
1. Air mass forced up by mountains
2. Air cools
3. Moisture condenses into clouds
4. Precipitation occurs

Cyclonic
1. Warm & cold air collide
2. Spin
3. Warm air forced up by cold air
4. Air cools
5. Moisture condenses into clouds
6. Precipitation occurs

Convectional
1. Sun heats earth's surface
2. Warm air forms and rises
3. Air cools
4. Moisture condenses into clouds
5. Precipitation occurs

Climate Regions

Pacific
Tempature
Small temp. range
doesn't go below 0°
Precipitation
Less in summer, More in winter
Highprecip.

Mountain
Temperature
Small temp. range
Doesn't go below 0°
Precipitation
More in summer, Less in winter
High precip.

Prarie
Temperature
Large temp. range
goes under 0°
Precipitation
More in summer, Less in winter
Low precip.

Subarctic
Temperature
Large temp. range
Goes under -20°
Precipitation
Low precipitation
More in middle of the year

Arctic
Temperature
Large temp. range
Goes under -20°
Precipitation
Low precip.
More in summer, less in winter
Lower Lakes
Temperature
Large temp. range
Goes under 0°
Precipitation
High precip.
Gets higher throughout the year

Atlantic
Temperature
Small temp. range
Goes below 0°
Precipitation
High precip.
Highest at the beggining and end of a year
Lowest in the middle of the year