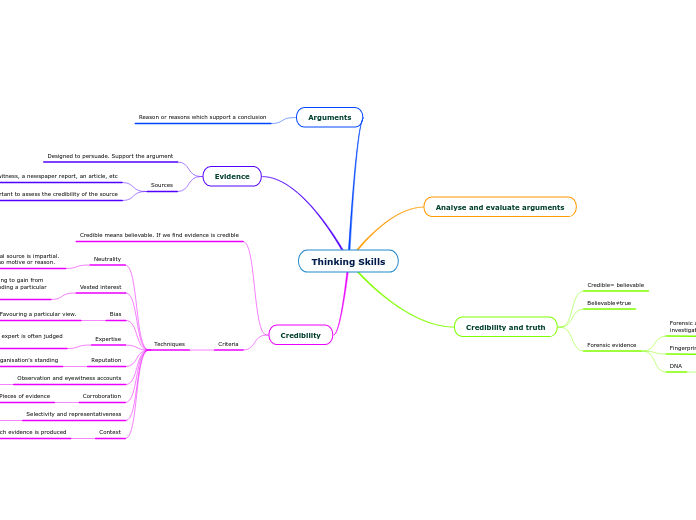
Thinking Skills
Analyse and evaluate arguments
Credibility and truth
Credible= believable
Believable≠true
Forensic evidence
Forensic are used by the police in the
investigation of crimes
Expert witnesses
Fingerprints
DNA
Sometimes contaminated
Arguments
Reason or reasons which support a conclusion
Evidence
Designed to persuade. Support the argument
Sources
eyewitness, a newspaper report, an article, etc
It is important to assess the credibility of the source
Credibility
Credible means believable. If we find evidence is credible
Criteria
Techniques
Neutrality
A neutral source is impartial.
It has no motive or reason.
Vested interest
People have something to gain from
promoting and defending a particular
point of view.
Bias
Favouring a particular view.
A biased viewpoint may reduce the credibility
of the source
Expertise
Evidence given by an expert is often judged
to be highly credible
Expertice is only credible if it is relevant
Reputation
A person's character or an organisation's standing
Observation and eyewitness accounts
Eyewitness= credible
Hearsay evidence= less credible
Corroboration
Pieces of evidence
Support each other.
Selectivity and representativeness
Evidence is always selective
Campaigning groups, newspapers, broadcasts
Context
Setting or situation in which evidence is produced