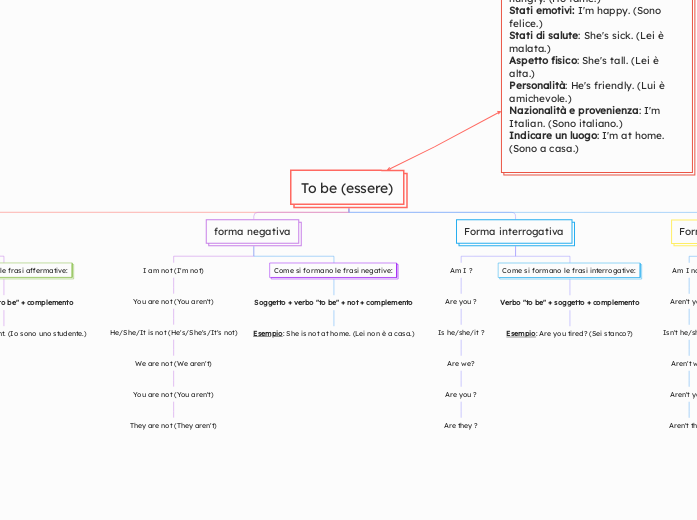
To be (essere)
forma affermativa
I am
You are
He/She/It is
We are
You are
They are
Come si formano le frasi affermative:
Soggetto + verbo "to be" + complemento
Esempio: I am a student. (Io sono uno studente.)
forma negativa
I am not (I'm not)
You are not (You aren't)
He/She/It is not (He's/She's/It's not)
We are not (We aren't)
You are not (You aren't)
They are not (They aren't)
Come si formano le frasi negative:
Soggetto + verbo "to be" + not + complemento
Esempio: She is not at home. (Lei non è a casa.)
Forma interrogativa
Am I ?
Are you ?
Is he/she/it ?
Are we?
Are you ?
Are they ?
Come si formano le frasi interrogative:
Verbo "to be" + soggetto + complemento
Esempio: Are you tired? (Sei stanco?)
Forma interrogativa negativa
Am I not?
Aren't you?
Isn't he/she/it?
Aren't we?
Aren't you?
Aren't they?
Come si formano le frasi interrogative negative:
- Si inverte il soggetto e il verbo.
- Si aggiunge "n't" alla forma contratta del verbo "to be".
Esempi: Aren't you coming to the party? (Non vieni alla festa?)
Isn't she beautiful? (Non è bellissima?)