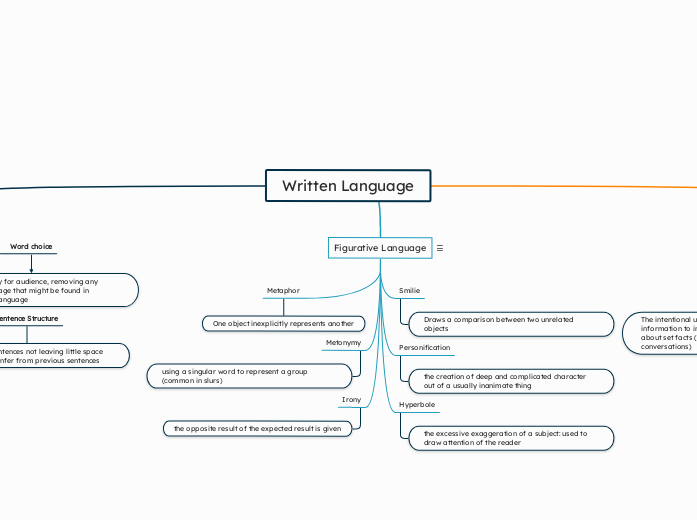
Written Language
Academic Language:
Word choice
Prioritizes clarity for audience, removing any colloquial language that might be found in conversational language
Sentence Structure
Uses complete sentences not leaving little space for the reader to infer from previous sentences
Figurative Language
Smilie
Draws a comparison between two unrelated objects
Personification
the creation of deep and complicated character out of a usually inanimate thing
Hyperbole
the excessive exaggeration of a subject: used to draw attention of the reader
Metaphor
One object inexplicitly represents another
Metonymy
using a singular word to represent a group (common in slurs)
Irony
the opposite result of the expected result is given
Slanting Language
Selection
the careful selection of particular facts or information to paint the view of a subject in a particular way (it is present in both interpreting information and presenting information, both intentionally and unintentionally)
Charged Language
The intentional use of language when reporting information to influence the opinion of the reader about set facts (commonly abused in political conversations)