von Mohamed CHAGRA Vor 9 Monaten
429
📌 PMP Training Structure - Mind Map Format
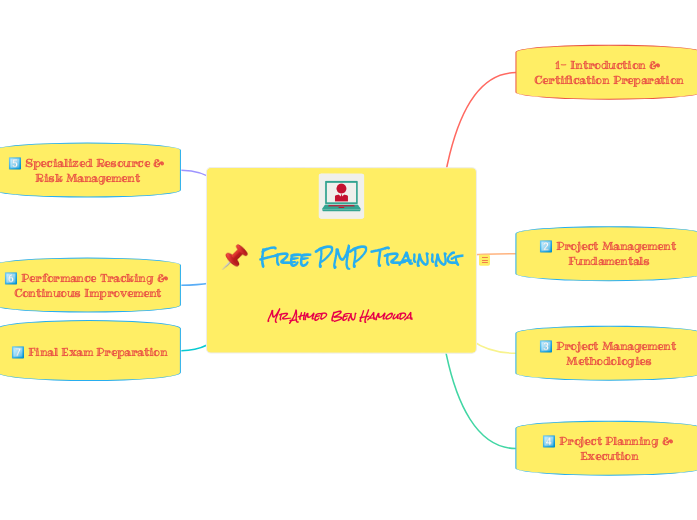
von Mohamed CHAGRA Vor 9 Monaten
429

Mehr dazu
The PMP training program follows a structured and logical progression, covering all the essential competencies required to manage a project according to PMI (Project Management Institute) standards. Here’s how it is organized:
🔹 1. Introduction & Certification Preparation
Chapter 0 provides candidates with a solid foundation by explaining the basics of PMP certification: its history, prerequisites, the exam process, and how to manage training credits (PDUs). This ensures a clear understanding of requirements before diving into the technical content.
Timeline & Budget
Lean
Kanban
Scrum
This chapter covers how to build, manage, and lead a project team. It focuses on team dynamics, motivation, conflict resolution, and leadership strategies.
✅ Definition: A project team is a group of individuals with diverse skills working together to achieve project goals.
✅ Types of Project Teams:
🔹 Key takeaway: Each team type requires different leadership and management approaches.
🔹 Team Development Stages:
1️⃣ Forming → Team members get to know each other, roles are unclear.
2️⃣ Storming → Conflicts arise as people express opinions.
3️⃣ Norming → Team starts working effectively together.
4️⃣ Performing → Team reaches peak productivity.
5️⃣ Adjourning → Project ends, team disbands.
🔹 Key takeaway: A project manager must guide the team through each stage.
✅ Servant Leadership → Focuses on empowering the team.
✅ Transformational Leadership → Inspires through vision and motivation.
✅ Transactional Leadership → Focuses on clear goals, rewards, and discipline.
✅ Democratic Leadership → Encourages team participation in decisions.
✅ Autocratic Leadership → Top-down decision-making, useful in crises.
🔹 Key takeaway: Different situations require different leadership styles.
✅ Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs → People must fulfill basic needs before focusing on growth.
✅ Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory → Hygiene factors (salary, policies) prevent dissatisfaction, but motivators (recognition, growth) drive performance.
✅ McGregor’s Theory X & Theory Y →
🔹 Key takeaway: A good project manager understands what motivates each team member.
✅ Sources of Conflict:
✅ Conflict Resolution Techniques (PMI Standards)
1️⃣ Collaborating (Win-Win) → Find a mutual solution (Best approach).
2️⃣ Compromising (Give and Take) → Both sides adjust expectations.
3️⃣ Smoothing (Accommodating) → Focus on common interests.
4️⃣ Forcing (Win-Lose) → PM makes a firm decision (Useful in crises).
5️⃣ Avoiding → Ignore the conflict (Worst approach).
🔹 Key takeaway: Collaboration is the best way to resolve conflicts in teams.
✅ Tools to Monitor Performance:
📌 RACI Matrix → Defines who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed for tasks.
📌 KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) → Measures team productivity and efficiency.
📌 360° Feedback → Team members provide feedback on each other.
📌 Burnout Prevention → Monitoring stress levels, workload balancing.
🔹 Key takeaway: Regular check-ins and feedback loops improve team performance.
✅ Effective Communication Strategies:
📌 Active listening → Understand team concerns before responding.
📌 Clear expectations → Define roles, tasks, and deadlines.
📌 Regular meetings → Daily stand-ups, weekly check-ins.
📌 Conflict resolution through dialogue → Open discussions before escalation.
📌 Use of collaboration tools → Slack, MS Teams, Trello for efficient communication.
🔹 Key takeaway: Poor communication is a major cause of project failure.
✅ A strong team is key to project success.
✅ Leadership styles must be adapted to the team’s needs.
✅ Understanding motivation theories helps improve productivity.
✅ Conflict resolution is crucial to maintaining a positive team dynamic.
✅ Clear communication and performance monitoring improve team efficiency.
📌 Understand Tuckman’s model and its 5 team stages.
📌 Know the differences between leadership styles and when to use them.
📌 Be familiar with motivation theories and their applications.
📌 Learn conflict resolution techniques and which approach works best.
📌 Understand the importance of effective communication in teams.
✅ Effective Communication Strategies:
📌 Active listening → Understand team concerns before responding.
📌 Clear expectations → Define roles, tasks, and deadlines.
📌 Regular meetings → Daily stand-ups, weekly check-ins.
📌 Conflict resolution through dialogue → Open discussions before escalation.
📌 Use of collaboration tools → Slack, MS Teams, Trello for efficient communication.
🔹 Key takeaway: Poor communication is a major cause of project failure.
✅ Tools to Monitor Performance:
📌 RACI Matrix → Defines who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed for tasks.
📌 KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) → Measures team productivity and efficiency.
📌 360° Feedback → Team members provide feedback on each other.
📌 Burnout Prevention → Monitoring stress levels, workload balancing.
🔹 Key takeaway: Regular check-ins and feedback loops improve team performance.
✅ Sources of Conflict:
✅ Conflict Resolution Techniques (PMI Standards)
1️⃣ Collaborating (Win-Win) → Find a mutual solution (Best approach).
2️⃣ Compromising (Give and Take) → Both sides adjust expectations.
3️⃣ Smoothing (Accommodating) → Focus on common interests.
4️⃣ Forcing (Win-Lose) → PM makes a firm decision (Useful in crises).
5️⃣ Avoiding → Ignore the conflict (Worst approach).
🔹 Key takeaway: Collaboration is the best way to resolve conflicts in teams.
✅ Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs → People must fulfill basic needs before focusing on growth.
✅ Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory → Hygiene factors (salary, policies) prevent dissatisfaction, but motivators (recognition, growth) drive performance.
✅ McGregor’s Theory X & Theory Y →
🔹 Key takeaway: A good project manager understands what motivates each team member.
✅ Servant Leadership → Focuses on empowering the team.
✅ Transformational Leadership → Inspires through vision and motivation.
✅ Transactional Leadership → Focuses on clear goals, rewards, and discipline.
✅ Democratic Leadership → Encourages team participation in decisions.
✅ Autocratic Leadership → Top-down decision-making, useful in crises.
🔹 Key takeaway: Different situations require different leadership styles.
🔹 Team Development Stages:
1️⃣ Forming → Team members get to know each other, roles are unclear.
2️⃣ Storming → Conflicts arise as people express opinions.
3️⃣ Norming → Team starts working effectively together.
4️⃣ Performing → Team reaches peak productivity.
5️⃣ Adjourning → Project ends, team disbands.
🔹 Key takeaway: A project manager must guide the team through each stage.
✅ Definition: A project team is a group of individuals with diverse skills working together to achieve project goals.
✅ Types of Project Teams:
🔹 Key takeaway: Each team type requires different leadership and management approaches.
This chapter focuses on identifying, analyzing, and managing stakeholders throughout a project's lifecycle. Effective stakeholder engagement is key to project success.
✅ Definition: A stakeholder is any individual, group, or organization impacted by the project or who can influence its success.
✅ Types of Stakeholders:
🔹 Key takeaway: Identifying stakeholders early helps prevent conflicts and align expectations.
🔹 Step 1: Identify Stakeholders
🔹 Step 2: Stakeholder Analysis
🔹 Key takeaway: The more influence a stakeholder has, the more engagement they require.
✅ Sponsor:
✅ Customer / End User:
✅ Project Manager (PM):
✅ Functional Manager:
✅ PMO (Project Management Office):
✅ Change Control Board (CCB):
✅ Steering Committee:
🔹 Key takeaway: Each stakeholder plays a different but crucial role in project success.
✅ Definition: A document outlining how to manage stakeholder expectations and communications.
✅ Key Elements:
🔹 Key takeaway: A well-structured engagement plan helps keep stakeholders aligned.
✅ Definition: A document listing all stakeholders, their roles, influence, and engagement strategy.
✅ Typical Content:
🔹 Key takeaway: Keeping the stakeholder register updated helps manage expectations effectively.
✅ Stakeholders can influence project success and must be identified early.
✅ The Power/Interest Grid helps prioritize stakeholder engagement.
✅ The Sponsor, Customer, PM, and PMO all have distinct responsibilities.
✅ A Stakeholder Engagement Plan ensures clear communication and alignment.
✅ The Stakeholder Register is a living document for tracking stakeholders.
📌 Know the key roles and responsibilities of each stakeholder.
📌 Understand how to classify stakeholders using the Power/Interest Grid.
📌 Be familiar with the Stakeholder Register and its contents.
📌 Learn how to manage conflicts between stakeholders.
📌 Know the difference between stakeholder identification, analysis, and engagement.
✅ Definition: A document listing all stakeholders, their roles, influence, and engagement strategy.
✅ Typical Content:
🔹 Key takeaway: Keeping the stakeholder register updated helps manage expectations effectively.
✅ Definition: A document outlining how to manage stakeholder expectations and communications.
✅ Key Elements:
🔹 Key takeaway: A well-structured engagement plan helps keep stakeholders aligned.
✅ Sponsor:
✅ Customer / End User:
✅ Project Manager (PM):
✅ Functional Manager:
✅ PMO (Project Management Office):
✅ Change Control Board (CCB):
✅ Steering Committee:
🔹 Key takeaway: Each stakeholder plays a different but crucial role in project success.
✅ Change Control Board (CCB)
✅ Steering Committee
✅ PMO (Project Management Office)
✅ Functional Manager
✅ Project Manager (PM)
✅ Customer / End User
✅ Sponsor
🔹 Step 1: Identify Stakeholders
🔹 Step 2: Stakeholder Analysis
🔹 Key takeaway: The more influence a stakeholder has, the more engagement they require.
✅ Definition: A stakeholder is any individual, group, or organization impacted by the project or who can influence its success.
✅ Types of Stakeholders:
🔹 Key takeaway: Identifying stakeholders early helps prevent conflicts and align expectations.
This chapter focuses on understanding the business environment in which projects operate. It introduces the key organizational structures, the difference between projects, programs, and portfolios, and the importance of business cases and feasibility studies in project selection.
📖 1. Understanding the Business Environment
📖 2. Difference Between Projects, Programs, and Portfolios
📖 3. Organizational Structures and Project Influence
📖 4. Business Case & Feasibility Study
📖 5. Benefits Management Plan
📖 6. External Factors Influencing Projects
✅ Projects exist within a larger business environment that affects their execution.
✅ Organizational structure determines project authority and decision-making power.
✅ A business case and feasibility study are crucial for project approval.
✅ A benefits management plan ensures long-term value realization.
✅ External factors (EEFs) impact project planning and execution.
📌 Know the difference between projects, programs, and portfolios.
📌 Understand how different organizational structures impact projects.
📌 Familiarize yourself with business case and feasibility study components.
📌 Be aware of external factors (EEFs) that affect projects.
📌 Link project benefits to organizational strategy to justify project approval.
Ce chapitre permet aux candidats de comprendre les bases de la certification PMP, les prérequis, le processus d’examen, et la gestion des PDUs.
📖 1. Présentation de la Certification PMP
📖 2. Exigences et Prérequis pour l'Examen
📖 3. Structure et Format de l'Examen
📖 4. Processus d’Inscription et Coût
📖 5. PDUs et Maintien de la Certification
📖 6. Stratégies pour Bien Se Préparer
✅ La certification PMP est une référence mondiale en gestion de projet.
✅ Il est essentiel de bien se préparer en maîtrisant le PMBOK et les concepts agiles/hybrides.
✅ L’examen n’évalue pas seulement la théorie mais aussi l’application pratique des concepts.
✅ Le renouvellement se fait en accumulant 60 PDUs sur 3 ans.
📌 Comprendre le PMBOK : Lire et maîtriser les concepts clés.
📌 S'entraîner avec des examens blancs : Simuler les conditions réelles.
📌 Utiliser des outils comme le mind mapping : Organiser ses connaissances.
📌 Rejoindre une communauté PMP : Partager et apprendre avec d'autres candidats.
✅ Cycle de renouvellement : tous les 3 ans
✅ Acquisition de PDUs (Professional Development Units)
🔹 Inscription via PMI.org
🔹 Coût de l’examen :
✅ Durée : 4 heures
✅ Nombre de questions : 180 questions (QCM)
✅ Format :
🔹 Expérience professionnelle requise :
🔹 Formation obligatoire :
🔹 Dossier d’éligibilité :