von Heba Azeef Vor 5 Jahren
346
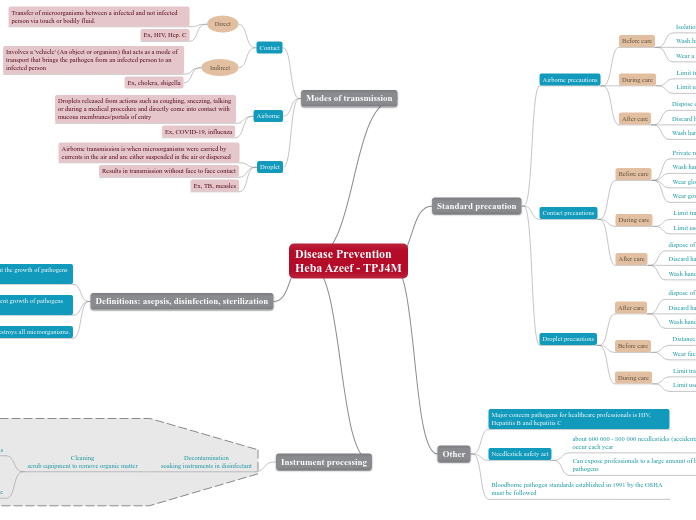
Disease Prevention Heba Azeef - TPJ4M
von Heba Azeef Vor 5 Jahren
346

Mehr dazu
high-level disinfection used when sterilization is not possible
boiling
Sterilization kill all microorganisms
pressure steam
dry heat
chemical
use or storage
Ex, cholera, shigella
Involves a 'vehicle' (An object or organism) that acts as a mode of transport that brings the pathogen from an infected person to an infected person
Ex, HIV, Hep. C
Transfer of microorganisms between a infected and not infected person via touch or bodily fluid.
Wear facial protection such as a mask or face shield
Distance of three feet from everyone
dispose of PPE in a sealed bag
Limit use of unnecessary equipment
Limit transportation
Wear gown if needed
Wear gloves
Private room
Discard hazardous trash
Dispose of PPE in a sealed bag
Limit unnecessary contact with medical equipment
Limit transport
Wear a form of respiratory protection such as a mask
Wash hands
Isolation with specific room settings