1. Fluid statics:
The fluid which is in state of rest is called as static fluid and its study is called as fluid statics.
2. Fluid kinematics:
The fluid which is in state of motion is called as moving fluid. The study of moving fluid without considering the effect of external pressures is called as fluid kinematics.
3. Fluid dynamics:
The branch of science which studies the effect of all pressures including the external pressures on the moving fluid is called as fluid dynamics.
The branch of science which studies the effect of all pressures including the external pressures on the moving fluid is called as fluid dynamics.
1. Hydroelectric Power Plants
In hydroelectric power plants, water is used to generate electricity on a large-scale basis. Water stored in the dam possesses potential energy, which is converted into the electrical energy in the power generation unit of the plant.
2. Hydraulic machines
Machines that operate on a fluid like water and oil are called hydraulic machines. The fluid as the capacity to lift heavy loads and exert extremely high pressures. Some hydraulic machines are used to perform various machining operations.
3.Automobiles
No automobile can run without fluid. Fluids perform three crucial operations in automobiles: generation of power, lubrication, and cooling of the engine.
4. Thermal power plants
Thermal power plants are one of the major suppliers of power in various parts of the world, and water working as the fluid is their most important component.
others are nuclear power plants, heat engines and air conditioners and refrigerators and many more.
Applications of Fluids
SPECIFIC WEIGHT-The specific weight, also known as the unit weight, is the weight per unit volume of a material.
specific volume-Specific volume is a property of materials, defined as the number of cubic meters occupied by one kilogram of a particular substance.
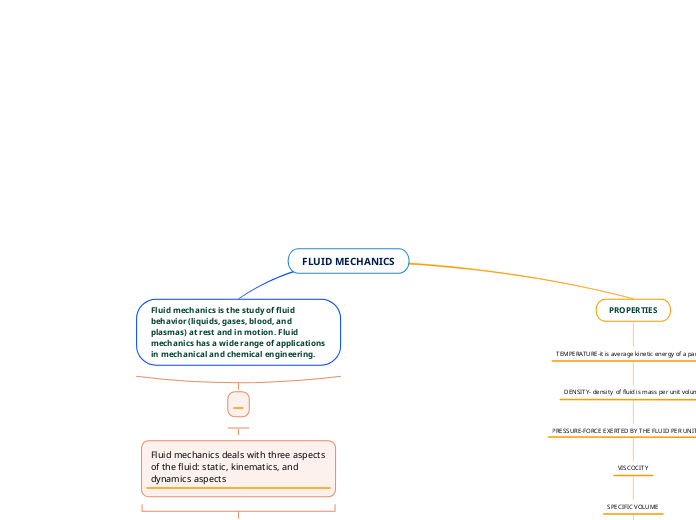
Fluid mechanics deals with three aspects of the fluid: static, kinematics, and dynamics aspects
viscocity- Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. It determines the fluid strain rate that is generated by a given applied shear stress
FLUID MECHANICS
PROPERTIES
TEMPERATURE-it is average kinetic energy of a particle.
DENSITY- density of fluid is mass per unit volume
PRESSURE-FORCE EXERTED BY THE FLUID PER UNIT AREA
VISCOCITY
SPECIFIC VOLUME
SPECIFIC GRAVITY- W=mg, density and specific weight are related by gravity
Fluid mechanics is the study of fluid behavior (liquids, gases, blood, and plasmas) at rest and in motion. Fluid mechanics has a wide range of applications in mechanical and chemical engineering.