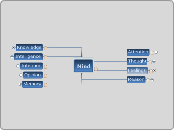
Mind
Mind
n 1: that which is responsible for one's thoughts and feelings; the seat of the faculty of reason; "his mind wandered"; "I couldn't get his words out of my head" [syn: head, brain, psyche, nous] 2: recall or remembrance; "it came to mind" 3: an opinion formed by judging something; "he was reluctant to make his judgment known"; "she changed her mind" [syn: judgment, judgement] 4: an intellectual being; "the great minds of the 17th century" [syn: thinker] 5: attention; "don't pay him any mind" 6: your intention; what you intend to do; "he had in mind to see his old teacher"; "the idea of the game is to capture all the pieces" [syn: idea] 7: knowledge and intellectual ability; "he reads to improve his mind"; "he has a keen intellect" [syn: intellect]
v 1: be offended or bothered by; take offense with, be bothered by: "I don't mind your behavior" 2: be concerned with or about something or somebody [syn: worry] 3: be in charge of or deal with; "She takes care of all the necessary arrangements" [syn: take care] 4: pay close attention to; give heed to; "Heed the advice of the old men" [syn: heed, listen] 5: be on one's guard; be cautious or wary about; be alert to; "Beware of telephone salesmen" [syn: beware] 6: keep in mind [syn: bear in mind] [ant: forget]
Memory
6 entries found for.memory
memory
( P ):
log in for this definition ofand other entries
in, available only
tomemoryMerriam-Webster Medical Dictionarymembers.memoryDictionary.com
Premium
memory
\Mem"o*ry\, n.;
pl..
[OE. memorie, OF. memoire, memorie, F. m['e]moire, L.
memoria, fr. memor mindful; cf. mora delay. Cf.,,,.]
1. The faculty of the mind by which it retains the knowledge
of previous thoughts, impressions, or events.Memory is the purveyor of reason. --Rambler.2. The reach and positiveness with which a person can remember; the
strength and trustworthiness of one's power to reach and represent
or to recall the past; as, his memory was never wrong.3. The actual and distinct retention and recognition of past ideas
in the mind; remembrance; as, in memory of youth; memories of
foreign lands.4. The time within which past events can be or are remembered; as,
within the memory of man.And what, before thy memory, was done From the begining. --
Milton.5. Something, or an aggregate of things, remembered; hence,
character, conduct, etc., as preserved in remembrance, history, or
tradition; posthumous fame; as, the war became only a memory.The memory of the just is blessed. --Prov. x. 7.That ever-living man of memory, Henry the Fifth. --Shak.The Nonconformists . . . have, as a body, always venerated her
[Elizabeth's] memory. --Macaulay.6. A memorial. [Obs.]These weeds are memories of those worser hours. --Shak.Syn:
,,,.Usage: Memory is the generic term, denoting the power by which we
reproduce past impressions. Remembrance is an exercise of that
power when things occur spontaneously to our thoughts. In
recollection we make a distinct effort to collect again, or call
back, what we know has been formerly in the mind. Reminiscence is
intermediate between remembrance and recollection, being a
conscious process of recalling past occurrences, but without that
full and varied reference to particular things which characterizes
recollection. ``When an idea again recurs without the operation of
the like object on the external sensory, it is remembrance; if it
be sought after by the mind, and with pain and endeavor found, and
brought again into view, it is recollection.'' --Locke.
, to put on
record; to record. [Obs.] -- Chaucer. Gower.MemoriesDemurMartyrMemoirRememberMemoryRemembranceRecollectionReminiscenceTo draw to
memory
memory
n 1: something that is
remembered; "search as he would, the memory was lost" 2: the
cognitive processes whereby past experience is remembered; "he can
do it from memory"; "he enjoyed remembering his father"
[syn:] 3:
the power of retaining and recalling past experience; "he had
a good memory when he was younger" [syn:,] 4:
an electronic memory device; "a memory and the CPU form the
central part of a computer to which peripherals are attached"
[syn:,,] 5: the
area of cognitive psychology that studies memory processes;
"he taught a graduate course on learning and
memory"rememberingretentionretentivenessstoragestorememory
board
- The mental faculty of retaining
and recalling past experience.
- The act or an instance of
remembering; recollection:spent the afternoon lost in
memory.
- All that a person can remember:It hasn't happened in my memory.
- Something remembered:pleasant childhood memories.
- The fact of being remembered;
remembrance:dedicated to their parents'
memory.
- The period of time covered by
the remembrance or recollection of a person or group of persons:within the memory of humankind.
- Biology.Persistent modification of behavior resulting from an animal's
experience.
- Computer
Science.
- A unit of a computer that
preserves data for retrieval.
- Capacity for storing
information:two gigabytes of memory.
- Statistics.The
set of past events affecting a given event in a stochastic
process.
- The capacity of a material,
such as plastic or metal, to return to a previous shape after
deformation.
- Immunology.The
ability of the immune system to respond faster and more powerfully
to subsequent exposure to an antigen.
[Middle
Englishmemorie, from Anglo-French, from
Latinmemoria, frommemor,.
Seemindful(s)mer-1in Indo-European
Roots.] |
Source:The American Heritage® Dictionary of the English
Language, Fourth EditionCopyright© 2000 by Houghton Mifflin Company.Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
reserved.
|
Source:Merriam-Webster Medical Dictionary,© 2002
Merriam-Webster, Inc. |
Source:Webster's Revised Unabridged Dictionary,© 1996, 1998
MICRA, Inc. |
[]Download or Buy
NowTradition
Shared Memory
History
The chronology of memory
Retention
storage of memories
things remembered
The poweror act of memory
o·pin·ion ( P ) Pronunciation
Key (-pnyn)
n.
A belief or conclusion held with confidence but not substantiated
by
positive knowledge or proof:“The world is not run by thought, nor by
imagination, but by opinion” (Elizabeth Drew).
A judgment based on special knowledge and given by an expert: a
medical opinion.
A judgment or estimation of the merit of a person or thing: has
a low
opinion of braggarts.
The prevailing view: public opinion.
Law. A formal statement by a court or other adjudicative body of
the
legal reasons and principles for the conclusions of the court.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[Middle English, from Old French, from Latin opni, opnin-, from
opnr,
to think.]
Synonyms: opinion, view, sentiment, feeling, belief, conviction,
persuasion
These nouns signify something a person believes or accepts as
being sound or true. Opinion is applicable to a judgment based on
grounds insufficient to rule out the possibility of dispute:“A little
group of willful men, representing no opinion but their own, have
rendered the great Government of the United States helpless and
contemptible” (Woodrow Wilson). View stresses individuality of
outlook: “My view is... that freedom of speech means that you shall
not do something to people either for the views they have or the views
they express” (Hugo L. Black). Sentiment and especially feeling
stress the role of emotion as a determinant: “If men are to be
precluded from offering their sentiments on a matter which may
involve the most serious and alarming consequences... reason is of
no use to us” (George Washington). “There needs protection...
against the tyranny of the prevailing opinion and feeling” (John Stuart
Mill). A belief is a conclusion to which one subscribes strongly: “Our
belief in any particular natural law cannot have a safer basis than our
unsuccessful critical attempts to refute it” (Karl Popper). Conviction
is belief that excludes doubt: “the editor's own conviction of what,
whether interesting or only important, is in the public interest” (Walter
Lippmann). Persuasion applies to a confidently held opinion: “He had
a strong persuasion that Likeman was wrong” (H.G. Wells).
[Download or Buy Now]
Source: The American Heritage® Dictionary of the English
Language, Fourth Edition
Copyright© 2000 by Houghton Mifflin Company.
Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
opinion
( P ) opinion: log in for this definition of opinion and
other entries in
Merriam-Webster Dictionary of Law, available only to Dictionary.com
Premium members.
Source: Merriam-Webster Dictionary of Law,© 1996 Merriam-
Webster, Inc.
opinion
( P ) opinion: log in for this definition of opinion and
other entries in
Merriam-Webster Medical Dictionary, available only to
Dictionary.com Premium members.
Source: Merriam-Webster Medical Dictionary,© 2002 Merriam-
Webster, Inc.
opinion
\O*pin"ion\, n. [F., from L. opinio. See Opine.] 1. That which
is
opined; a notion or conviction founded on probable evidence; belief
stronger than impression, less strong than positive knowledge;
settled judgment in regard to any point of knowledge or action.
Opinion is when the assent of the understanding is so far gained
by
evidence of probability, that it rather inclines to one persussion than
to another, yet not without a mixture of incertainty or doubting. --Sir
M. Hale.
I can not put off my opinion so easily. --Shak.
2. The judgment or sentiment which the mind forms of persons or
things; estimation.
I have bought golden opinions from all sorts of people. --Shak.
Friendship . . . gives a man a peculiar right and claim to the
good
opinion of his friend. --South.
However, I have no opinion of those things. --Bacon.
3. Favorable estimation; hence, consideration; reputation; fame;
public sentiment or esteem. [Obs.]
Thou hast redeemed thy lost opinion. --Shak.
This gained Agricola much opinion, who . . . had made such early
progress into laborious . . . enterprises. --Milton.
4. Obstinacy in holding to one's belief or impression; opiniativeness;
conceitedness. [Obs.] --Shak.
5. (Law.) The formal decision, or expression of views, of a judge,
an
umpire, a counselor, or other party officially called upon to consider
and decide upon a matter or point submitted.
To be of opinion, to think; to judge.
To hold opinion with, to agree with. [Obs.] --Shak.
Syn: Sentiment; notion; persuasion; idea; view; estimation. See
Sentiment.
Source: Webster's Revised Unabridged Dictionary,© 1996, 1998
MICRA, Inc.
opinion
\O*pin"ion\, v. t. To opine. [Obs.]
Source: Webster's Revised Unabridged Dictionary,© 1996, 1998
MICRA, Inc.
opinion
n 1: a personal belief that is not founded on proof or certainty;
"my
opinion differs from yours"; "what are your thoughts on Haiti?" [syn:
sentiment, persuasion, view, thought] 2: a belief or sentiment shared
by most people; the voice of the people; "he asked for a poll of public
opinion" [syn: public opinion, popular opinion, vox populi] 3: a
message expressing a belief about something; "his opinions
appeared frequently on the editorial page" [syn: view] 4: the legal
document stating the reasons for a judicial decision; "opinions are
usually written by a single judge" [syn: judgment, judgement] 5: the
reason for a court's judgment (as opposed to the decision itself) [syn:
ruling]
Estimation
Intention
Synonyms:intention, intent, purpose, goal,
end, aim, object, objective
IntentionIt is my intention to take a vacation next month.IntentThe executor complied with the testator's intent.PurposeGoalThe college's goal was to raise
ten million
dollars for a new library.EndThe candidate wanted to win
and pursued
every means to achieve that end.AimThe
aim of most students is to graduate.objectThe
object of chess
is to capture your opponent's king.ObjectiveThe
report outlines the committee's objectives.These nouns refer to what one plans to do or achieve.simply signifies a course
of action that one
proposes to follow:more strongly
implies
deliberateness:strengthens
the idea of
resolution or determination:“His purpose was to discover how long these guests intended to stay”
(Joseph
Conrad).may suggest an idealistic or long-term purpose:suggests a long-range goal:stresses the direction one's efforts take in pursuit
of an end:Anis an end that one tries to carry out:often implies that the end or goal can be reached:
Aim
Goal
Result
Intelligence
- The capacity to acquire
and apply knowledge.
- The faculty of thought
and reason.
- Superior powers of mind.
See Synonyms at.mind
- Secret information,
especially about an actual or potential enemy.
- An agency, staff, or
office employed in gathering such information.
- Espionage agents, organizations,
and activities considered as a group:“Intelligence is nothing if not an
institutionalized black market in perishable commodities” (John le Carré).
An intelligent,
incorporeal being, especially an angel. Information; news. See Synonyms at.news
In*tel"li*gence\,
n. [F. intelligence, L. intelligentia, intellegentia. See.] 1. The act or state
of knowing;
the exercise of the understanding.2. The capacity to know or understand; readiness of comprehension; the intellect, as a gift or an endowment.And dimmed with darkness their intelligence. --Spenser.3. Information communicated; news; notice; advice.Intelligence is given where you are hid. --Shak.4. Acquaintance; intercourse; familiarity. [Obs.]He lived rather in a fair intelligence than any friendship with the favorites. --Clarendon.5. Knowledge imparted or acquired, whether by study, research, or experience; general information.I write as he that none intelligence Of meters hath, ne flowers of sentence. --Court of Love.6. An intelligent being or spirit; -- generally applied to pure spirits; as, a created intelligence.
--Milton.The great Intelligences fair That range above our mortal state, In circle round the blessed gate, Received
and
gave him welcome there. --Tennyson.
, an office where information may be obtained, particularly
respecting servants to be hired.Syn: Understanding; intellect; instruction; advice; notice; notification; news; information; report.
IntelligentIntelligence office
Intimacy
Information
News
Facts
Capacity
Potential
Maximum
Capability
Ability
Knowledge
n : the psychological
result of perception and learning and reasoning [syn:]cognition
Meaning
Interpretation
Agreement
Comprehension
Experience
Familiarity
Cognition
Learning
Recall
rea·son(rn.Pronunciation
Key
The basis or motive for an action, decision, or conviction. See Usage Note at.
See Usage Note at.becausewhy
A declaration made to explain or justify action, decision, or conviction:inquired about her reason for leaving.
An underlying fact or cause that provides logical sense for a premise or occurrence:There is reason to believe that the accused did not commit this crime.
The capacity for logical, rational, and analytic thought; intelligence.
Good judgment; sound sense.
A normal mental state; sanity:He has lost his reason.
Logic.A premise, usually the minor premise, of an argument.
To use the faculty of reason; think logically.
To talk or argue logically and persuasively.
Obsolete.To engage in conversation or discussion.
To determine or conclude by logical thinking:reasoned out a solution to the problem.
To persuade or dissuade (someone) with reasons.
Because of.in reasonWith good sense or justification; reasonably.within reasonWithin the bounds of good sense or practicality.with reasonWith good cause; justifiably.[Middle English, from Old Frenchraison, from Latinrati, fromratus, past participle
ofr,. Seeto consider, thinkar-in Indo-European
Roots.]rea·ern.Synonyms:reason, intuition, understanding, judgment
ReasonIntuitionI trust my intuitions when it comes to
assessing someone's character.UnderstandingJudgmentThese nouns
refer to the intellectual faculty by which humans seek or attain knowledge or truth.is the power to think rationally and logically and to draw inferences:“Mere reason is insufficient to convince us of its [the Christian religion's]
veracity” (David Hume).is perception or
comprehension, as of truths or facts, without the use of the rational process:is the faculty by which one understands, often together with the resulting
comprehension:“The greatest dangers to liberty lurk in insidious encroachment by men of zeal, well-meaning but without understanding” (Louis D. Brandeis).is the ability to assess situations or circumstances and draw sound conclusions:“At twenty years of age, the will reigns; at thirty, the wit; and at forty, the judgment” (Benjamin Franklin). See also synonyms atSee also synonyms atSee
also synonyms atcausemindthink
v.v.intr.rea·soned,rea·son·ing,rea·sons
v.tr.Idioms:by reason of
Source:The American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth EditionCopyright© 2000 by Houghton Mifflin Company.Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
reserved.
Source:Merriam-Webster Dictionary of Law,© 1996
Merriam-Webster, Inc.Source:Webster's Revised Unabridged Dictionary,© 1996, 1998
MICRA, Inc.Source:Webster's Revised Unabridged Dictionary,© 1996, 1998
MICRA, Inc.Source:Webster's Revised Unabridged Dictionary,© 1996, 1998
MICRA, Inc.
[]Download or Buy
Nowreason
( P ):
log in for this definition ofand other entries
in, available only
toreasonMerriam-Webster Dictionary of Lawmembers.reasonDictionary.com
Premium
reason
\Rea"son\, n. [OE. resoun, F.
raison, fr. L. ratio (akin to Goth. rapj? number, account, garapjan
to count, G. rede speech, reden to speak), fr. reri, ratus, to
reckon, believe, think. Cf.,,,.]
1. A thought or a consideration offered in support of a
determination or an opinion; a just ground for a conclusion
or an action; that which is offered or accepted as an
explanation; the efficient cause of an occurrence or a
phenomenon; a motive for an action or a determination; proof,
more or less decisive, for an opinion or a conclusion;
principle; efficient cause; final cause; ground of
argument.I'll give him reasons for it. --Shak.The reason of the motion of the balance in a wheel watch is by the motion of the next wheel. --Sir M. Hale.This reason did the ancient fathers render, why the church was called ``catholic.'' --Bp. Pearson.Virtue and vice are not arbitrary things; but there is a natural
and eternal reason for that goodness and virtue, and against vice and wickedness. --Tillotson.2. The faculty of capacity of the human mind by which it is
distinguished from the intelligence of the inferior animals; the higher as distinguished from the lower cognitive faculties, sense, imagination, and memory, and in contrast to the feelings and desires. Reason comprises conception, judgment, reasoning, and the
intuitional faculty. Specifically, it is the intuitional faculty, or the faculty of first truths, as distinguished from the understanding, which is called the discursive or ratiocinative faculty.We have no other faculties of perceiving or knowing anything divine or human, but by our five senses and our reason. --P. Browne.In common and popular discourse, reason denotes that power by which we distinguish truth from falsehood, and right from wrong, and by which we are enabled to combine means for the attainment of particular ends. --Stewart.Reason is used sometimes to express the whole of those powers which elevate man above the brutes, and constitute his rational nature, more especially, perhaps, his intellectual powers; sometimes to express the power of deduction or argumentation. -- Stewart.By the pure reason I mean the power by which we become possessed of
principles. --Coleridge.The sense perceives; the understanding, in its own peculiar operation, conceives; the reason, or rationalized understanding,
comprehends. --Coleridge.
ArraignRateRatioRation
reason
\Rea"son\, v. t. [imp.&p.
p.; p.
pr.&vb. n..]
[Cf. F. raisonner. See,
n.] 1. To exercise the rational faculty; to deduce inferences
from premises; to perform the process of deduction or of
induction; to ratiocinate; to reach conclusions by a
systematic comparison of facts.2. Hence: To carry on a process of deduction or of induction, in
order to convince or to confute; to formulate and set forth
propositions and the inferences from them; to argue.Stand still, that I may reason with you, before the Lord, of all
the righteous acts of the Lord. --1 Sam. xii. 7.3. To converse; to compare opinions. --Shak.
ReasonedReasoningReason
reason
\Rea"son\, v. t. 1. To arrange
and present the reasons for or against; to examine or discuss by arguments; to debate or discuss; as, I reasoned the matter with my friend.When they are clearly discovered, well digested, and well reasoned
in every part, there is beauty in such a theory. --T. Burnet.2. To support with reasons, as a request. [R.] --Shak.3. To persuade by reasoning or argument; as, to reason one into a belief; to reason one out of his plan.Men that will not be reasoned into their senses.
--L'Estrange.4. To overcome or conquer by adducing reasons; -- with down; as, to reason down a passion.5. To find by logical process; to explain or justify by reason or argument; -- usually with out; as, to reason out the causes of the librations of the moon.
reason
n 1: a rational motive for a belief or action; "the reason that war was declared"; "the grounds for their declaration"
[syn:] 2: an explanation of the cause of some phenomenon; "the reason a steady state was never reached was that the back pressure built up too slowly" 3: the capacity for rational thought or inference or discrimination; "we are told that man is endowed with reason and capable of distinguishing good from evil"
[syn:,] 4: the state of having good sense and sound judgment; "his rationality may have been impaired"; "he had to rely less on reason than on rousing their emotions"
[syn:,] 5: a justification for something existing or happening; "he had no cause to complain"; "they had good reason to rejoice"
[syn:,] 6: a fact that logically justifies some premise or conclusion; "there is reason to believe he is lying" v 1: decide by reasoning; draw or come to a conclusion; "We reasoned that it was cheaper to rent than to buy a house"
[syn:,] 2: present reasons and arguments
[syn:] 3: think logically ground understanding intellectrationality reasonableness cause grounds reason outconcludeargue
Explain
Clarify
Interpret
Debate
Argue
Consider
Deduction
Synthesis
Implication
Logic
Relationships
Principles
Inference
Decision
Determination
Conclusion
Judgement
Motivation
Purpose
Need
Incentive
Feelings
The sensation involving
perception by touch.
A sensation experienced through
touch.
A physical sensation:a
feeling of warmth.
An affective state of consciousness, such as that resulting from emotions, sentiments, or desires:experienced a feeling of excitement.
An awareness or impression:He had the feeling that he was being followed.
An emotional state or disposition; an emotion:expressed deep feeling.
A tender emotion; a fondness.
Capacity to experience the higher emotions; sensitivity; sensibility:a man of feeling.
feelingsSusceptibility to emotional response; sensibilities:The child's feelings are easily hurt.
Opinion based more on emotion than on reason; sentiment.
A general impression conveyed by a person, place, or thing:The stuffy air gave one the feeling of being in a tomb.
Appreciative regard or understanding:a feeling for propriety.
Intuitive awareness or aptitude; a feel:has a feeling for language.
Having the ability to react or feel emotionally; sentient; sensitive.
Easily moved emotionally; sympathetic:a feeling heart.
Expressive of sensibility or emotion:a feeling glance.
feel·lyadv.
adj.Synonyms:feeling,
emotion, passion, sentiment
feelingemotionfeelingEmotionPassionSentimentWe
expressed our sentiments about the government's policies.These nouns refer to complex and usually strong subjective human response. Althoughandare sometimes interchangeable,is the more general and neutral:“Poetry is the spontaneous overflow of powerful feelings: it takes its origin from emotion recollected in tranquillity” (William Wordsworth).often implies the presence of excitement or agitation:“Poetry is not a turning loose of emotion, but an escape from emotion” (T.S. Eliot).is intense, compelling emotion:“They seemed like ungoverned children inflamed with the fiercest passions o men” (Francis Parkman).often applies to a thought or opinion arising from or influenced by emotion:The word can also refer to delicate, sensitive, or higher or more refined feelings:“The mystic reverence, the religious allegiance, which are essential to a true monarchy, are imaginative sentiments that no legislature can manufacture in any people”(Walter Bagehot). See also synonyms atopinion
Emotion
Energize
Provocation
Joy
Agitation
Foment
Disturb
Passion
Lust
Craving
Abandon
Wildness
Enthusiasm
Excitement
Sentiment
Nostalgia
Romance
Fascination
Love
Sensitivity
Suspicion
Doubt
Instinct
Inborn
Innate
Aptitude
Talent
Unconscious
Involuntary
Thought
think(th(thôt)v.v.tr.thought,think·ing,thinks
Pronunciation
Key
Requiring much thought to create or assimilate:a think book.
To have or formulate in the mind.
To reason about or reflect on; ponder:Think how complex language is. Think the matter through.
To decide by reasoning, reflection, or pondering:thinking what to do.
To judge or regard; look upon:I think it only fair.
To believe; suppose:always thought he was right.
To expect; hope:They thought she'd arrive early.
To intend:They thought they'd take their time.
To call to mind; remember:I can't think what her name was.
To visualize; imagine:Think what a scene it will be at the reunion.
To devise or evolve; invent:thought up a plan to get rich quick.
To bring into a given condition by mental preoccupation:He thought himself into a panic over the impending examination.
To concentrate one's thoughts on:“Think languor” (Diana Vreeland).
To exercise the power of reason, as by conceiving ideas, drawing inferences, and using judgment.
To weigh or consider an idea:They are thinking about moving.
To bring a thought to mind by imagination or invention:No one before had thought of bifocal glasses.
To recall a thought or an image to mind:She thought of her childhood when she saw the movie.
To believe; suppose:He thinks of himself as a wit. It's later than you think.
To have care or consideration:Think first of the ones you love.
To dispose the mind in a given way:Do you think so?
v.intr.adj.Informaln.
Reason
Consideration
Examination
Search
Test
Question
Reflection
Contemplation
Meditation
Imagination
Creation
Production
Initiation
Fantasy
Daydream
Delusion
Illusion
Deception
Vision
Mysticism
Non-Rational
Faith
Foresight
Precognition
Design
Draw
Represent
Depict
Innovate
Introduce
Form
Compose
Essence
Shape
Outline
Summary
Method
Technique
Order
System
Plan
Strategy
Conception
Attention
Concentration of the mental powers upon an object; a close or careful observing or listening. The ability or power to concentrate mentally. Observant consideration; notice:Consideration or courtesy:Acts of courtesy, consideration, or gallantry, especially by a suitor. A military posture, with the body erect, eyes to the front, arms at the sides, and heels together.Your suggestion has come to our attention.attention to others' feelings.attentions
Impression
Idea
Opinion
Feeling
Belief
Trust
Influence
Direction
Effect
Power
Care
Interest
Attraction
Curiosity
Concern
Anxiety
Sympathy
Observation
Measurement
view
Concentration
Distinguish
Focus
Emphasis
Clarity
Perception
Sensation
Awareness
Consciousness
Alertness
Stimulation
Arousal
Recognition
Recollection
Identification
Acceptance
Insight
Understanding
Intuition