von Rider Keopuhiwa Vor 3 Jahren
386
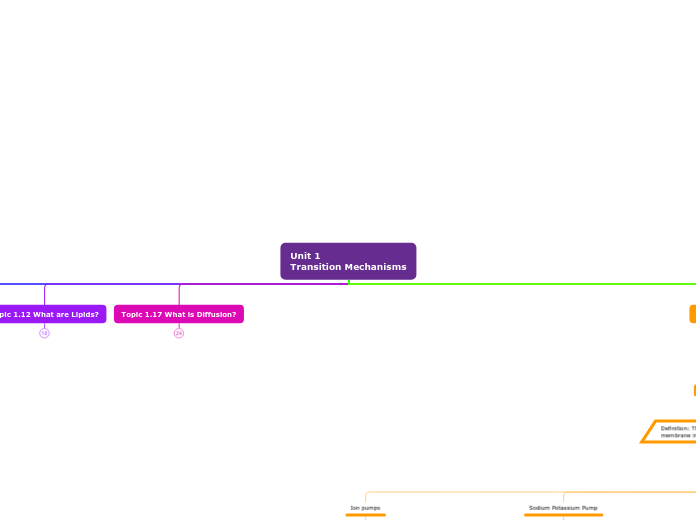
Mind Map Assignment
von Rider Keopuhiwa Vor 3 Jahren
386

Mehr dazu
Definition: The movement of ions or molecules across the cell membrane into a region of higher concentration.
Five Types
Bulk Transport
The movement of large amounts of molecules across a membrane.
Cotransport
Coupling of the down hill diffusion of one substance to the uphill.
Proton Pumps
Pathway for acid and secretion in gastric parietal cells
Sodium Potassium Pump
Moves sodium and potassium ions aganst large concentration gradients
Ion pumps
Channels that use the ATP hydrolysis energy to transfer ions from one side of a membrane to the other aganist their electrochemical gradient.
Understanding the veariebles that influence deffusion.
Mass of solute
Temperature of environment
Solvent density
Distance traveled
Passive Transport
Molecules move through cell membrane with no energy, and goes with concentration gradient
Active Transport
Energy-requiring processthat move matireals across cell membrane against a concentration gradient (Ion pumps, Co-transport proteins)
Facilitated Diffusion
utilizes three different forms of channel proteins that facilitate movement of ions large solute molecules and water
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a cell permeable membrane. (Water movement with conccntration with gradient)
Aquaporin
Only allows water to pass through
Non-Spacific
allows many different ions to pass through
Spacific
only allows a specific ion to pass through
Simple Diffusion
Kinetic energy is what drives simple diffusion, small non polar molecules may pass through the cell membrane through simple diffusion with enough kinetic energy.
1. the fats such as saturated and unsaturated are used for storing energy, Phospholipids makes up the membrane and the steroids is the communication.
Unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds inside their fatty acid chains and stays liquid at a room temperature making them not so packed closely together
two types of unsaturated fats include cyst and trans fat. Cyst fats link and can easily break away from each other while trans fat tend to build up on each other and can cause heart attacks due to the build up
Saturated fats are a type of fatty acid chain that have single bonds. They stay solid at room temperature which makes them more closely packed together
These are some three dimensional shapes that Carbon can make, and these bio-molecules are all formed by Covalent bonds. (CH20 is the generic formula for carbs and liquids)
1. the waters role as a solvent helps cells transport 2. Cohesive is when water molecules stick with each other, while adhesive is when water molecules stick to other substances, like in the example of Xylem. 3. universal solvent, high heat compacity ( maintains constant temperature ) , a polar covalent molecule that is both adhesive and cohesive and forms a lattice
Subtopic
Cohesive: Water molecules stick to each other.
Ion: a charged atom or particle
Surface Tension: property allowing liquid to resist external force
Lattice: A pattern created by molecules in a crystal