Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
The Process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration are essential in sustainable ecosystems
chemical energy
During the process of cellular respiration, biotic species convert food energy into chemical energy, which is used to. fuel life processes.
food energy
solar energy
When plants are performing photosynthesis, they transform solar energy into food energy.
Trophic Levels
Indicates the feeding level of an organism. Stems from the Greek word "troph," which means feeder.
heterotroph
Heterotroph = other-feeder or consumer. These organisms cannot create their own food and rely on eating other organisms to get energy.
fourth trophic level
Organisms feed on secondary consumers. They are called tertiary consumers.
tertiary consumer
Examples:
third trophic level
Organisms feed on the primary consumers. They are called secondary consumers.
secondary consumer
Examples:
second trophic level
Organisms are the first to feed on another organism. They are called primary consumers.
primary consumer
Examples:
autotroph
Autotroph = self-feeder or producer. These organizations can create their own food energy.
first trophic level
Organisms use photosynthesis to create their own food. They are called producers.
producers
Examples:
Earths Four Spheres
biosphere
The regions of Earth where living things exist.
atmosphere
The layer of air above the Earth's surface.
hydrosphere
All the water found on Earth, including lakes, oceans and groundwater.
lithosphere
The solid, outer part of the Earth.
Nutrient Cycling
Carbon gets recycled using photosynthesis, and the carbon moves from the atmosphere and into living things; when this organic matter respires or decomposes, carbon is sent back into the atmosphere.
Energy Transfer
Energy flows in a one-way path; organisms that need photosynthesis use energy from the sun to create food energy in the form of glucose; in cellular respiration, this glucose is turned into ATP, which is a molecule with a lot of chemical energy in its bonds.
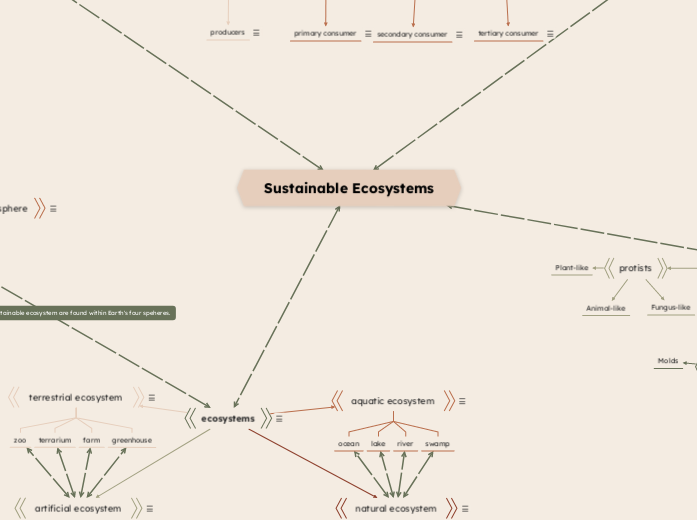
ecosystems
Communities in a particular area interacting with their abiotic environment.
artificial ecosystem
Man-made structures that are not sustainable and can stop functioning without human help.
natural ecosystem
A natural ecosystem is one that is found naturally in nature, they are self-sustaining and do not need human help to thrive.
aquatic ecosystem
Ecosystems found in water.
swamp
river
lake
ocean
terrestrial ecosystem
Ecosystems found on land.
greenhouse
farm
terrarium
zoo
communities
Biotic populations living and interacting in a particular area.
fungus
Yeast
Mushrooms
Molds
protists
Fungus-like
Animal-like
Plant-like
bacteria
Spirochetes
Bacteria with a corkscrew shape.
Vibrios
Bacteria with a curved-rod-like shape.
Spirilla
Bacteria that have a curved shape.
Bacilli
Bacteria with a rod-like shape.
Cocci
Bacteria with a round shape.
plants
Creepers
Plants that creep along the ground and have very fragile, long, thin stems that can't stand tall or support all their weight
Examples
- Pumpkins
- Watermelons
- Strawberries
Climbers
Climbers have very thin, long, and weak stems that can't stand upright, but rather use external support to grow vertically and carry their weight.
Examples
- Ivy
- Grapevine
- Morning Glory
Trees
They have very thick, woody, and hard stems called the trunk. This single main stem or trunk gives rise to many branches that bear leaves, flowers, and fruits.
Examples
Herbs
Short-sized plants with soft, green, delicate stems without woody tissues.
Examples
Shrub
Medium-sized, woody plants that are taller than herbs and shorter than a tree.
Examples:
animals
Insects
Amphibians
Reptiles
Birds
Mamals
biotic
commensalism
Commensalism is an interaction between two species in which only one benefits.
Cactus and Cactus Wren
Frogs and Plants
Remoras and Sharks
mutualism
Mutualism is an interaction between two species in which they both benefit.
Oxpeckers and Rhinos
Bees and Flowers
Coral and Fish
competition
Competition is a species rivalry for resources such as food, mates, or land.
Humans
Plants
Fighting for sunlight, space, water, and pollinators.
Lion prides
parasitism
Parasitism is where a parasite lives with/on/in a host, harming the host species.
Ticks and Dogs
Tapeworms and Cows
Lice and Humans
predation
Predation is where one species hunts and kills another.
Sharks and Seals
Lions and Gazelles
Owls and Mice
abiotic characteristics
Soil
Nutrients
Light
Oxygen
Water
Sustainable Ecosystems