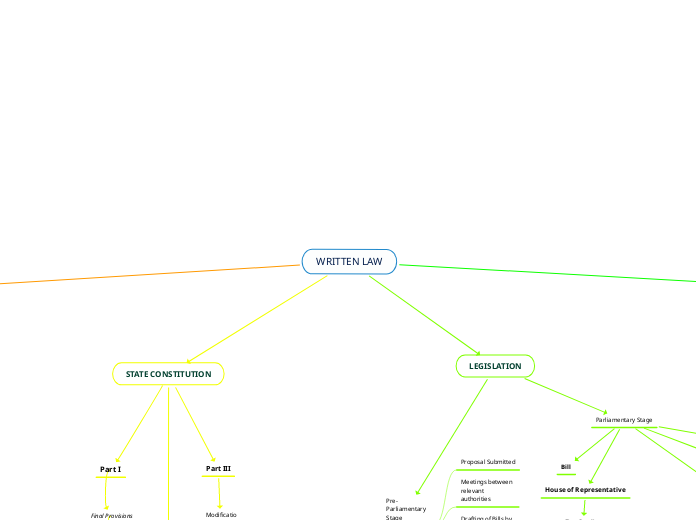
WRITTEN LAW
SUBSIDIARY LEGISLATION
Legislative control
Laying Procedures
Affirmative resolution laying procedure
Negative Resolution
Simple Laying
Consultation
Judicial Control
Examples of cases
Ghazali v. Public Prosecutor (1964) MLJ 156
Low Leng Huat v PP (1917) FMSLR 12
McEldowney v Forde [1971] AC 632
LEGISLATION
Parliamentary Stage
Publication
Royal Assent
Senate
House of Representative
First Reading
Second Reading
Committee Stage
Third Reading
Bill
Pre-Parliamentary Stage
Cabinet Approval
Drafting of Bills by Attorney General Chambers
Meetings between relevant authorities
Proposal Submitted
STATE CONSTITUTION
Part III
Modification of Parts I and II in relation to Malacca and Penang
Part I
Final Provisions
Impartial Treatment of State Employees
Amendments of the Constitution
Provisions in respect of Yang Di-Pertua Negeri in relation to the States of Malacca, Penang, Sabah and Sarawak
Part II
Temporary Provisions Alternative to Provisions in Part I
FEDERAL CONSTITUTION
Malaysia as a Federation
Malaysia as a Constitution Monarchy
Malaysia as a Parliamentary Democracy
Islam & Freedom of Religion
Fundamental Liberties
Supremacy of the Constitution
Amendment to Constitution
Method of Amendment
Rule of Law
Doctrine of Separation of Powers