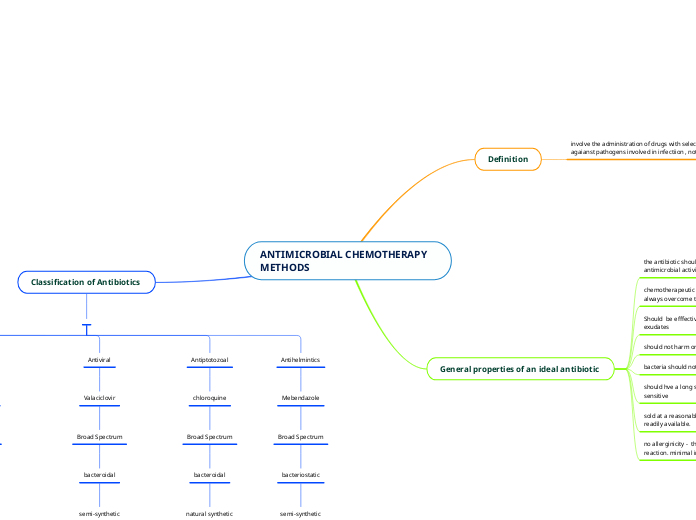
ANTIMICROBIAL CHEMOTHERAPY METHODS
Definition
involve the administration of drugs with selective toxicity agaianst pathogens involved in infectiion , not host cells .
General properties of an ideal antibiotic
the antibiotic should exhibit selective and effective antimicrobial activity
chemotherapeutic index-the efficacy of the molecule should always overcome the toxic reactions or adverse reactions
Should be efffective in the presences of body fluids and exudates
should not harm or eliminate normal flora
bacteria should not develop resistance to the drug
should hve a long shelf life- shoulf not be light,temperature sensitive
sold at a reasonable cost -it should be cost effective and readily available.
no allerginicity - the molecule should not cause an alllergic reaction. minimal irritation.
Classification of Antibiotics
Antibacterial
Penicillin
Narrow Spectrum
bacteriostatic
Semi-synthetic
Inhibit cell wall synthesis
Antifungal
Amphotericin B
Broad Spectrum
bacteriostatic
Natural synthetic
Increase permability in the cell wall
Antiviral
Valaciclovir
Broad Spectrum
bacteroidal
semi-synthetic
Inhibit (disrupt) the DNA from replicating
Antiptotozoal
chloroquine
Broad Spectrum
bacteroidal
natural synthetic
Inhibits protein synthesis
Antihelmintics
Mebendazole
Broad Spectrum
bacteriostatic
semi-synthetic
inhibits tublin polymeriztion