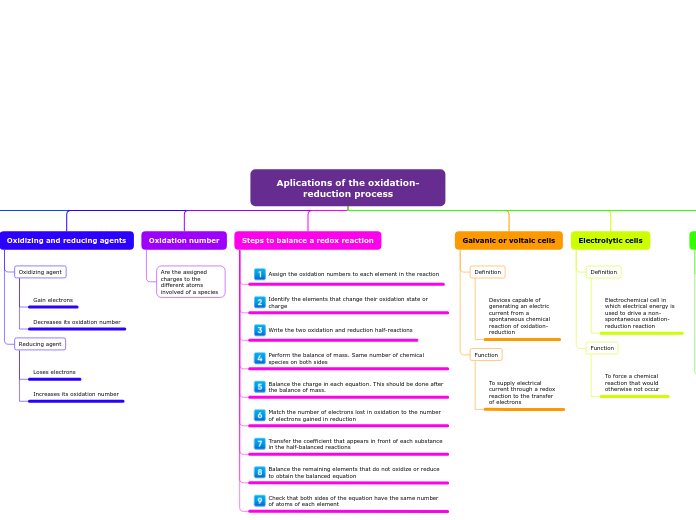
Aplications of the oxidation-reduction process
Oxidation and reduction concepts
Whenever one species is reduced, there is another that is oxidized
Oxidation: loss of electrons
Reduction: electron gain
Oxidizing and reducing agents
Oxidizing agent
Gain electrons
Decreases its oxidation number
Reducing agent
Loses electrons
Increases its oxidation number
Oxidation number
Are the assigned charges to the different atoms involved of a species
Steps to balance a redox reaction
Assign the oxidation numbers to each element in the reaction
Identify the elements that change their oxidation state or charge
Write the two oxidation and reduction half-reactions
Perform the balance of mass. Same number of chemical species on both sides
Balance the charge in each equation. This should be done after the balance of mass.
Match the number of electrons lost in oxidation to the number of electrons gained in reduction
Transfer the coefficient that appears in front of each substance in the half-balanced reactions
Balance the remaining elements that do not oxidize or reduce to obtain the balanced equation
Check that both sides of the equation have the same number of atoms of each element
Galvanic or voltaic cells
Definition
Devices capable of generating an electric current from a spontaneous chemical reaction of oxidation-reduction
Function
To supply electrical current through a redox reaction to the transfer of electrons
Electrolytic cells
Definition
Electrochemical cell in which electrical energy is used to drive a non-spontaneous oxidation-reduction reaction
Function
To force a chemical reaction that would otherwise not occur
Applications of electrochemical reactions
Nature
Nerve impulses generated neurons
Electric eels
Corrosion in metals
Industry
Electric batteries: They are the industrialized and commercial formats of galvanic cells. (car batteries are the traditional battery model)
Mettalic coatings, electroplating: applying a thin layer of metal on an electronic current conducting surface
Molten NaCl electrolysis: method widely used in industry to obtain sodium and chlorine in its elemental state