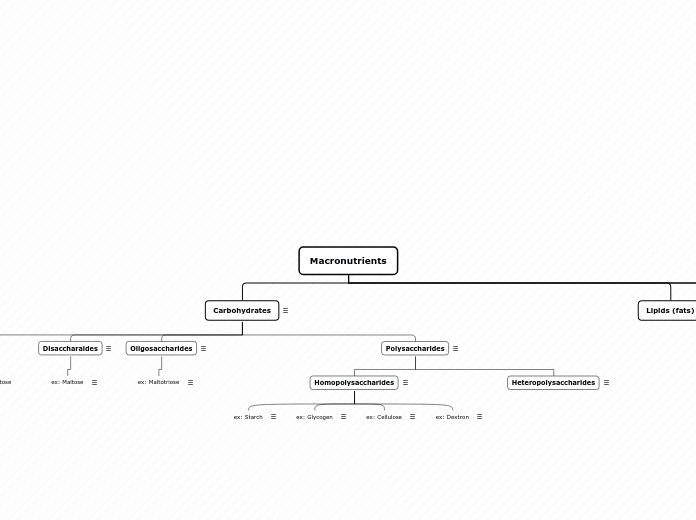
Macronutrients
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
ex: Glucose
ex: Fructose
ex: Galactose
Disaccharaides
ex: Maltose
Oligosaccharides
ex: Maltotriose
Polysaccharides
Homopolysaccharides
ex: Starch
ex: Glycogen
ex: Cellulose
ex: Dextron
Heteropolysaccharides