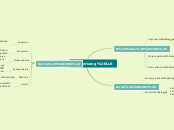
Categorising LLS
O'Malley (1985)
Cognitive Strategies
Limited to certain learning task consisting more direct manipulation of learning material itself
Repetition, resourcing, translation, grouping, note taking, deduction, recombination, imagery, auditory representation, keyword, contextualization, elaboration, transfer, inferencing
Metacognitive Strategies
Strategies which require planning for learning, thinking about learning process, monitoring of ones production comprehension and evaluating learning after an activity is completed
Socioeffective Strategies
Cooperation and questions for clarification
Rubin (1987)
Communication Strategies
Less directly related to language learning since their focus is on the process of participating in a conversation and getting meaning across or clarifying what the speaker intended.
Social Strategies
Activities that expose learners to practise their knowledge
Contribute indirectly towards learning
Oxford (1990)
Cognitive
Making associations between new and already known information
Mnemonic
Making associations between new and already known information through use of formula, phrase, verse
Metacognitive
Controlling own cognition through the co-ordination of the planning, organisation and evaluation of the learning process
Compensatory
Using context to make up for missing information in reading and writing
Affective
on of emotions, motivation and attitude towards learning
Social
The interaction with other learners to improve language learning and cultural understanding