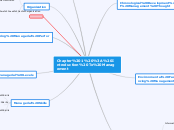
Chapter 1 : Introduction To Management
Chronological Development Of Management Thought
Classical Approach
Scientific,,Administrative & Bureaucratic Management are combine for focusing on the individual worker's productivity, functions of management & overall organizational system.
Behavioural Approach
The development of thought adapted the classical perspective of management.
Quantitative Perspective
Characterized by its use of mathematics,statistics and other quantitative technique for management decision making and problem solving.
System Approach
An approach to problem solving that attacks complex system by breaking them down into their constituent elements.
Contingency Approach
A view that proposes that there is no one best approach to management for all situation.
Environmental Factors Influencing Management Thought
Economic Influences
Social Influences
Political Influences
Technological Influences
Global Influences
Managerial Roles
Informational Roles
Monitor
Disseminator
Spokesperson
Decisional Roles
Entrepreniur
Disturbance Handler
Resource Allocator
Negotiator
Interpersonal Roles
Figurehead
Leader
Liaison
Managerial Skills
Technical Skills
Ability to use the procedures, techniques, & knowledge of an specialized field.
Human Skills
Ability to work effectively with other people.
Conceptual Skills
Ability to coordinate & integrate the organization's interests & activities.
Definition Of Management
The process of planning,controlling,leading & organizing that encompasses human,material,financial & information to achieve goals.
Organization
Manager- An organizational member who is responsible for planning,organizing,leading & controlling the activities of organization so that its goal are achieve.
Why do we need an organization
Accomplish objective
Preserve knowladge
Serve society
Provide cereers
Measuring Managerial Performance
Effeciency
Ability to get things done correctly and doing things right
Effectiveness
Ability to choose appropriate objectives & doing the right things.
Managerial Levels
Top Manager
Establish objectives, policy & Strategy, make long term decisions. E.g.: CEO,President
Middle Manager
Interpret top management directives into operating plans, make implementation decision. E.g.: Marketing Manager, H.R. Manager
first Line Manager
Direct & support work on non-managerial personnel, make short term operating decision. E.g.: Clerk