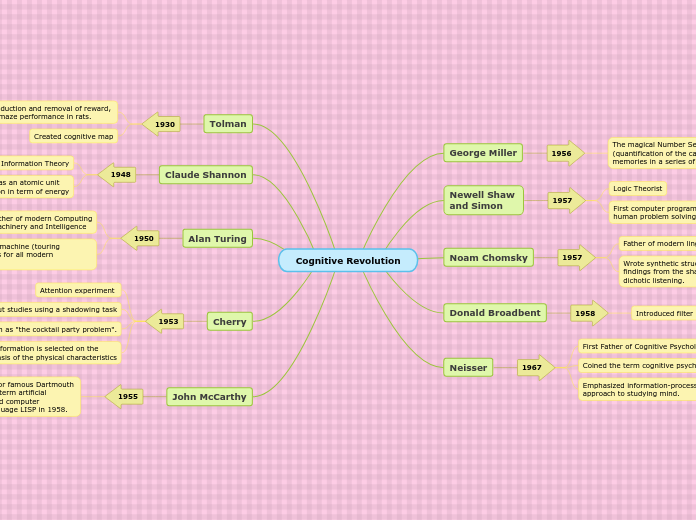
Cognitive Revolution
George Miller
1956
The magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two
(quantification of the capacity of our working
memories in a series of behavioral tests.
Newell Shaw
and Simon
1957
Logic Theorist
First computer program stimulating
human problem solving.
Noam Chomsky
1957
Father of modern linguistics theory
Wrote synthetic structures based on
findings from the shadowing and
dichotic listening.
Donald Broadbent
1958
Introduced filter model of Attention.
Neisser
1967
First Father of Cognitive Psychology Book
Coined the term cognitive psychology
Emphasized information-processing
approach to studying mind.
Tolman
1930
Introduction and removal of reward,
and maze performance in rats.
Created cognitive map
Claude Shannon
1948
Created Information Theory
Binary digit as an atomic unit
of information in term of energy
Alan Turing
1950
Father of modern Computing
machinery and Intelligence
Specified a Theoretical machine (touring machine) which is basis for all modern computing.
Cherry
1953
Attention experiment
Carried out studies using a shadowing task
Also known as "the cocktail party problem".
Information is selected on the
basis of the physical characteristics
John McCarthy
1955
In a proposal written for famous Dartmouth
conference coined the term artificial
intelligence and created computer
programming (AI) language LISP in 1958.