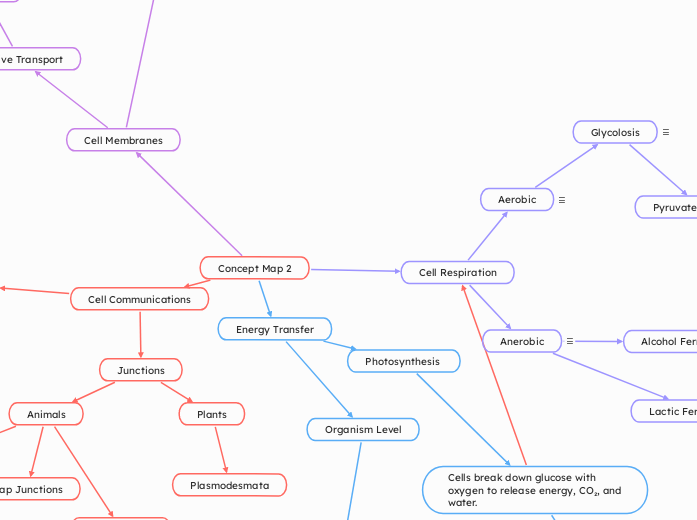
Concept Map 2
Cell Communications
Junctions
Animals
Desmosomes
Gap Junctions
Tight Junctions
Plants
Plasmodesmata
Signalling
Long Distance
Hormal Signalling
Local
Paracrine signalling
Synaptic Signalling
Cell Membranes
Passive Transport
Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Osmosis
Subtopic
Active Transport
Proton Pump
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Ion Channels
Electrogenic Pumps
Contransport
Subtopic
Cell Respiration
Anerobic
Lactic Fermentation
Alcohol Fermentation
Aerobic
Glycolosis
Pyruvate Oxidation
Citric Acid Cycle
Oxidative Phospohlation
Electron Transport Chain
Chemiosmosis
Energy Transfer
Photosynthesis
Cells break down glucose with oxygen to release energy, CO₂, and water.
ATP Production: Energy from respiration is stored in ATP molecules for cellular functions
Energy Loss as Heat: Not all energy is stored; some is lost as heat during metabolic processes.
Organism Level
Metabolic rate how much energy an organism uses, affecting energy needs.
Energy Flow in Populations: Individual energy needs impact group energy consumption.
Energy Loss Between Levels (Community): Only about 10% of energy is passed up each trophic level; the rest is lost as heat.