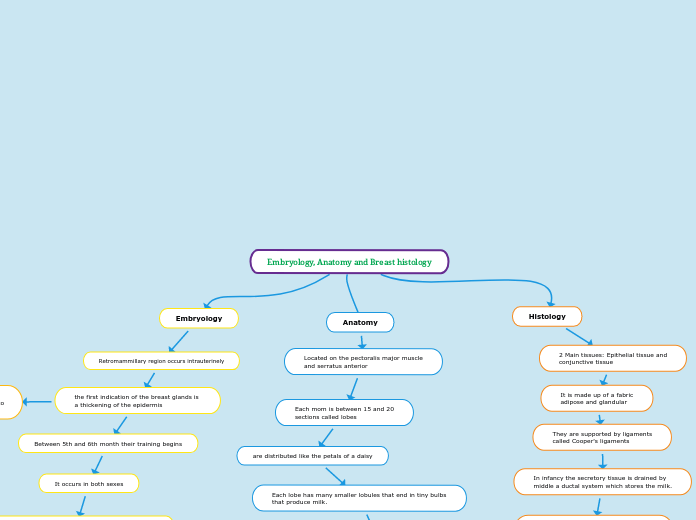
Embryology, Anatomy and Breast histology
Anatomy
Located on the pectoralis major muscle
and serratus anterior
Each mom is between 15 and 20
sections called lobes
are distributed like the petals of a daisy
Each lobe has many smaller lobules that end in tiny bulbs that produce milk.
The lobes, lobules and bulbs
are joined by fine ducts
called pipelines.
These ducts lead to the nipple
Located in the center of a
dark area of skin
called areola.
Fat fills in the gaps
between the lobes and the ducts.
Each breast also contains vessels
blood vessels and vessels that carry lymph
lymphatic vessels
lead to organs
small denominated
lymph nodes
they are clusters that meet
in many other parts of the body.
Embryology
Retromammillary region occurs intrauterinely
the first indication of the breast glands is
a thickening of the epidermis
Between 5th and 6th month their training begins
It occurs in both sexes
It goes from the axillary region to the inguinal region.
It is called the mammary ridge.
Form 8 aligned mammary foci
sequentially, called milk line
The 4th focus will be the adult breast
as it evolves the rest of the foci will atrophy
Towards the end of intrauterine life, the shoots
epithelial cells canalize and form milk ducts
the mammary line at seven
weeks of gestation extend to
both sides of the body
Histology
2 Main tissues: Epithelial tissue and
conjunctive tissue
It is made up of a fabric
adipose and glandular
They are supported by ligaments
called Cooper's ligaments
In infancy the secretory tissue is drained by
middle a ductal system which stores the milk.
The lobes end through a tubular system
in the galactophore ducts that discharge
at the level of the nipple.
epithelial tissue lines
the inside of the ducts
galactophores