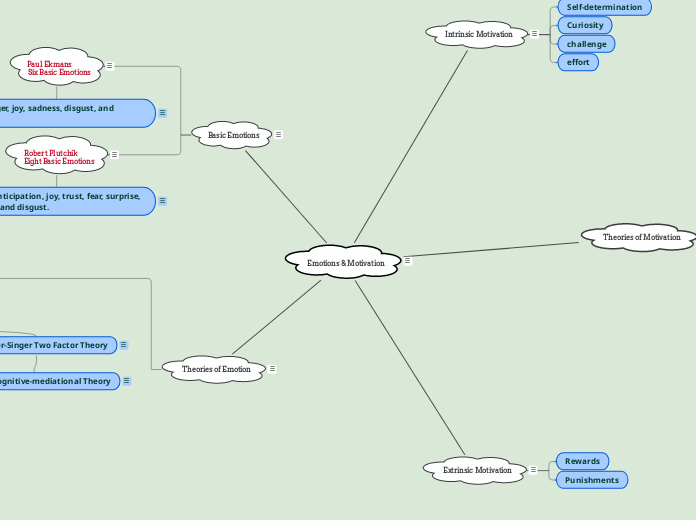
Emotions & Motivation
Intrinsic Motivation
Self-determination
Curiosity
challenge
effort
Evolutionary
Behaviourist
Cognitive
Humanistic
Add text
Evolutionary Understanding
of Motivation
Drive
Drive Theory
Homeostasis
Conflict
Three Types
of Conflict
Approach- approach
Avoidance- Avoidance
Approach-avoidance
Need
Extrinsic Motivation
Rewards
Punishments
Basic Emotions
Paul Ekmans
Six Basic Emotions
fear, anger, joy, sadness, disgust, and surprise
Robert Plutchik
Eight Basic Emotions
anger, anticipation, joy, trust, fear, surprise, sadness and disgust.
Theories of Emotion
James -Lange Theory
Cannon-Bard Theory
Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
Self Awareness
Self Regulation
Empathy
Skilled Relationship
Schachter-Singer Two Factor Theory
Lazarus' Cognitive-mediational Theory