IMAGE EDITION
TYPES

BIT MAP IMAGES
They are images made up of Pixels (each pixel is a small square that stores information about color, brightness, contrast, etc.)
FILE FORMATS
BMP: (Bit Mapped Picture) Bitmap. Format used by Windows (it is the format of the Paint program).

GIF FORMAT
GIF: (Graphics Interchange format). It is the most used on the Web. It has a Depth of 8 bits, works with 256 Colors and allows animations.

BEFUNKY

VECTOR IMAGES
Vector Images: They are digital images formed by independent geometric objects (segments, polygons, arcs, etc.), each of them defined by mathematical calculations. The advantages of this type of images are the possibility of enlarging their size without losing quality and the ease of indentifying and modifying each of the parts.

JPG OR JPEG
JPG or JPGE: (Jaint Photographic Experts Groups). Widely used for digital imaging, it supports 16 million Colors in a small space due to its high Comprehension.
PROPERTIES OF THE BITMAPS

BMP (Bit Mapped Picture)
BMP: (Bit Mapped Picture) Bitmap. Format used by Windows (it is the format of the Paint program)
Format PNG
PNG: ( Portable Network Graphics). It was created to replace the GIF and is similar to this one, although it has better quality and takes up less space.

PNG
PNG: (Portable Network Graphics). It was created to replace the GIF and is similar to it, although it has better quality and takes up less space
CHARACTERISTICS
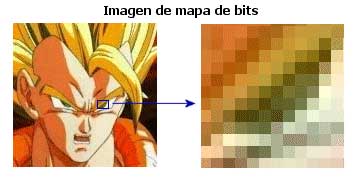
DIMENSIONS OR SIZE
Dimensions or Size: The Size of a bit Map Image is defined by the product of two integers corresponding to the numberof pixels in the width and height of the image. For example: 1600*1200 (Width*Height).

RESOLUTION
Resolution: It is the parameter that tells us with how much detail an image can be observed. We can define it as the number of pixels per inch (1 inch = 2,54 cm), that is, it expresses the pixel density of the image. Logically, the more pixels there are in an inch, the better the image will look an the more it can be enlarged without losing quality. The resolution is expressed in pixels per inch (dpi) we can say that the Resolution.
GRAPHICS EDITING PROGRAMES AND VIEWERS

GIMP
Gimp: Digital Image Editing, in continuos Development.

PHIXR
PHOTOSCAPE

PHOTOSHOP
Photoshop: Digital Image Editing, (very powerful, the most used).
XNVIEW
XnView: Viewing Images, (Also used as a Photo Organizer).

ONLINE GRAPHIC EDITING PROGRAMS
Online Graphic Editing Programs: In addition to the Graphic Editing Programs, there are websites that allow us to Edit Images Online with very similar functions. Furthermore, we can find more and more Websites with a Large Number of Advanced Options.
PAINT SHOP PRO
Paint Shop Pro: Digital Image Editing, (From the Corel Family).
PICASA
Picasa: Image viewer and editor (Allows you to store and share on the Web).
PIXLR
PIxlr: Very complete. It has three Variants. Editor, very complete and Professional, with a large number of options; Express, more basic and for quick touch-ups; and O-Matic, which applies touch-ups, frames, filters and effects to the entire image automatically. No registration required.

PICMAGICK

PINKMONKEY

PHOTOSHOP EXPRESS EDITOR

FOTOR
PHO.TO
CONCEP MAP

TIF OR TIFF
TIF or TIFF: Provides high quality images ( which implies a large size of the Files and is very widespread.

XCF
XCF: (Experimental Computing Facility). Used in GIMP, it allows you to save layers, channels, transparencies, etc, to later edit them.

PSD
PSD: (Photoshop Document). Used in Photoshop it has the same characteristics as XCF.

