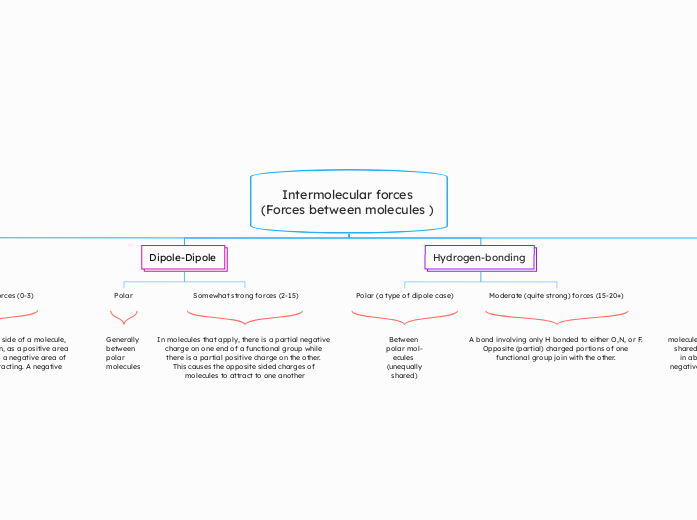
Intermolecular forces
(Forces between molecules )
Dispersion
Non-polar
weak/temporary forces (0-3)
Dipole-Dipole
Polar
Somewhat strong forces (2-15)
Hydrogen-bonding
Polar (a type of dipole case)
Moderate (quite strong) forces (15-20+)
Ionic-dipole
Polar
Moderate (quite strong) forces (10-20+)
If an electron is found on one side of a molecule, there's a momentary attraction, as a positive area of one molecule is exposed to a negative area of one molecules, therefore attracting. A negative
A bond involving only H bonded to either O,N, or F. Opposite (partial) charged portions of one functional group join with the other.
The opposite charges of molecules
attract to each other
molecules that have unequally
shared electrons resulting
in absolute positive or
negative charged functional
groups
Generally
between
polar
molecules
Between
polar mol-
ecules
(unequally
shared)
Occurs
between
non-polar
molecules
In molecules that apply, there is a partial negative charge on one end of a functional group while there is a partial positive charge on the other.
This causes the opposite sided charges of molecules to attract to one another