Lung Cancer
What is it?
Cancer that begins in the lungs
Leading cause of death in US
Small Cell Lung Cancer
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
Men
Women
Causes?
Tobacco (Smoking)
Second hand smoking
Smoker's vicinity is affected
Radon Exposure
Colorless and Odorless gas
Air Pollution
Number of pollutants that can affect air quality
Vehicle Exhaust
Carcinogens
Coal-Fired Power Plants
Chemicals/Substances
Asbestos
Radiations
Environmental
Medical
Tests
Genetics
how cells function, grow and divide
Symptoms?
Small Cell (SCLC)
Weight Loss
Shortness Of Breath
Chest Pain
Coughing
Blood and Mucus
Facial or Neck Swelling
Non Small Cell (NSCLC)
Systems Impacted
Respiratory System
Respiratory System
Levels of oxygen in the blood become low
overload of toxins clogging up the cells
damage of respiration enzymes
Organs Impacted
Lungs
Airways
Bronchi
Alveoli
Chest Wall
Tissues Impacted
Pleura
Smooth Muscle
Ciliated Epithelium
Specialized Cells Impacted
Goblet Cells
Lung alveolar epithelium
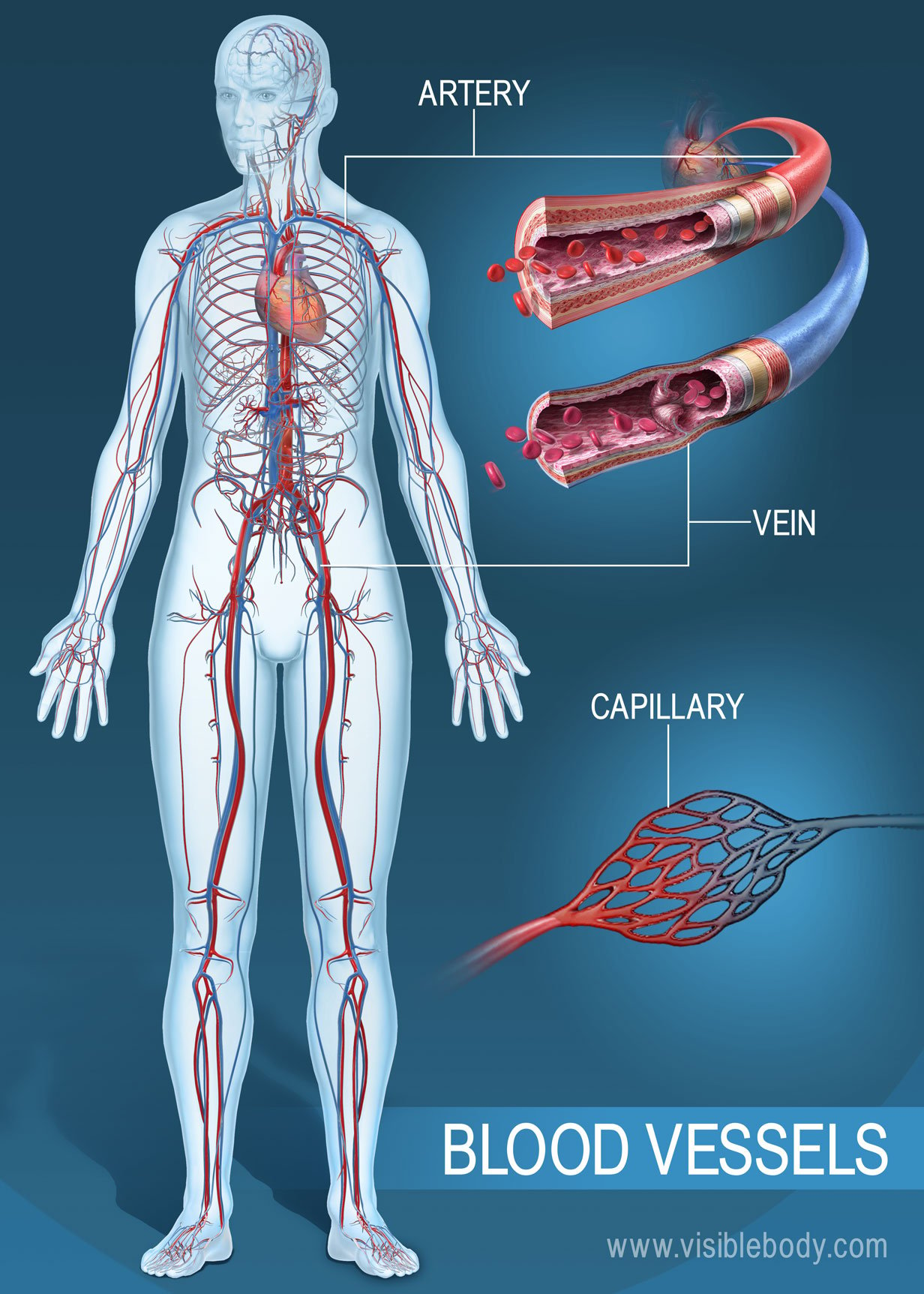
Circulatory System
Cancerous cells can spread
from lungs
Bloodstream
other organs
Systems Impacted
Circulatory System
Shortness Of Breath
Heart failure & Blood Clots
Liver / Kidney/Lymph Glands
Metastasizing
Term for when cancerous cells
are carried to other organs
Organs Impacted
Heart
Interstitium
Tissues Impacted
Pericardial sac
Specialized Cells Impacted
Red Blood Cells
White Blood Cells
Epithelial tissue
Connective Tissue
Blood Vessels
Diagnosis
Various tests and procedures
Endobronchial
ultrasound (EBUS)
CT Scans
X Rays
Biopsy
Malignant
Benign
Cells and Tissues
Treatment
Surgery
Tumor cells
Early-stage cancer treatment
Radiotherapy
Destroys rapidly dividing cancer cells
X Rays
Nausea/ Vomiting/ Fatigue/ Loss of appetite
←
Avoiding recurrence
Reliving Pain
Controlling Symptoms
Avoiding brain metastases
Chemotherapy
Kills cancer cells
Drugs
Systemic Therapy