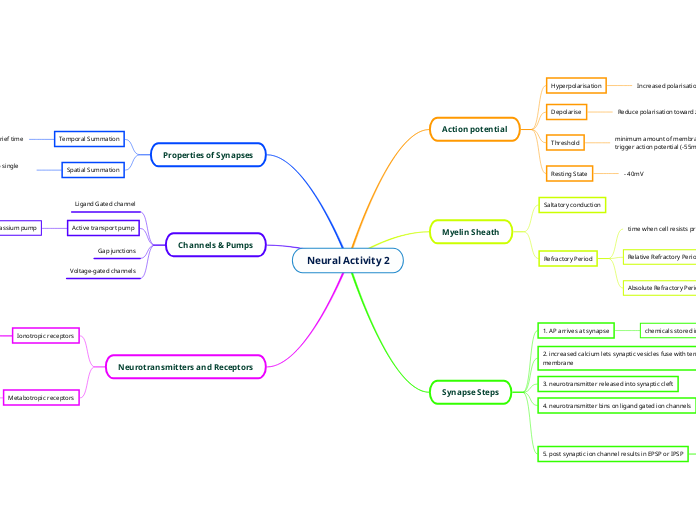
Neural Activity 2
Action potential
Hyperpolarisation
Increased polarisation across membrane
Depolarise
Reduce polarisation toward zero across membrane (+40mV)
Threshold
minimum amount of membrane depolarisation necessary to trigger action potential (-55mV)
Resting State
- 40mV
Myelin Sheath
Saltatory conduction
Refractory Period
time when cell resists production of further action potential
Relative Refractory Period
Time after absolute refractory period that requires stronger stimulus to initiate action potential
Absolute Refractory Period
Unable to produce action potential
Synapse Steps
1. AP arrives at synapse
chemicals stored in vesicles of pre-synaptic terminal
Opens calcium ions
Calcium evokes release of neurotransmitter into cleft
2. increased calcium lets synaptic vesicles fuse with terminal membrane
3. neurotransmitter released into synaptic cleft
4. neurotransmitter bins on ligand gated ion channels
5. post synaptic ion channel results in EPSP or IPSP
Excitatory post synaptic potential
Depolarisation
Inhibitory post synaptic potential
Hyperpolarisation
Properties of Synapses
Temporal Summation
Cumulative effect of repeated stimuli within brief time
Spatial Summation
Combination of effects of two or more synapses into single neuron
Channels & Pumps
Ligand Gated channel
Active transport pump
sodium-potassium pump
Transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell.
Gap junctions
Voltage-gated channels
Neurotransmitters and Receptors
Ionotropic receptors
Receptor binding immediately opens ion channels
Glutamate receptor (NMDA & AMPA)
ESPS
Depolarises neuron from influx of positive ions causing action potential
GABA receptor
ISPS
Hyperpolarisation of neuron from influx chloride
Metabotropic receptors
Activation of second messanger without opening channel
Activation of G-protein.