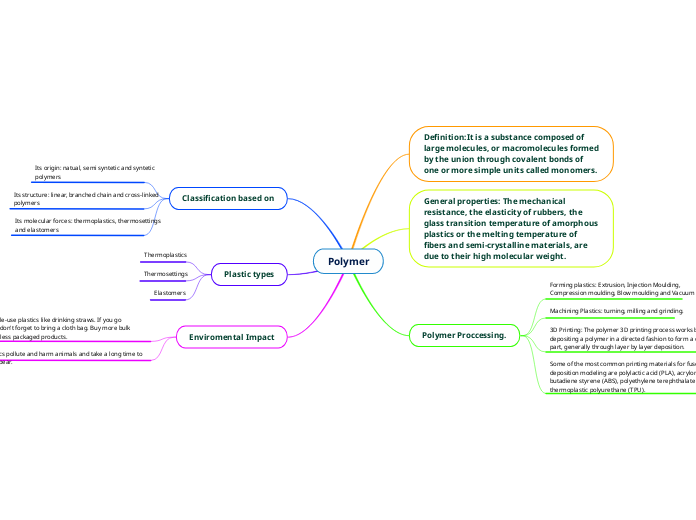
Polymer
Definition:It is a substance composed of large molecules, or macromolecules formed by the union through covalent bonds of one or more simple units called monomers.
General properties: The mechanical resistance, the elasticity of rubbers, the glass transition temperature of amorphous plastics or the melting temperature of fibers and semi-crystalline materials, are due to their high molecular weight.
Polymer Proccessing.
Forming plastics: Extrusion, Injection Moulding,
Compression moulding, Blow moulding and Vacuum
Machining Plastics: turning, milling and grinding.
3D Printing: The polymer 3D printing process works by depositing a polymer in a directed fashion to form a completed part, generally through layer by layer deposition.
Some of the most common printing materials for fused deposition modeling are polylactic acid (PLA), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU).
Classification based on
Its origin: natual, semi syntetic and syntetic
polymers
Its structure: linear, branched chain and cross-linked
polymers
Its molecular forces: thermoplastics, thermosettings
and elastomers
Plastic types
Thermoplastics
Thermosettings
Elastomers
Enviromental Impact
Avoid single-use plastics like drinking straws. If you go shopping, don't forget to bring a cloth bag. Buy more bulk foods and less packaged products.
Plastics pollute and harm animals and take a long time to disappear.