QR codes
3
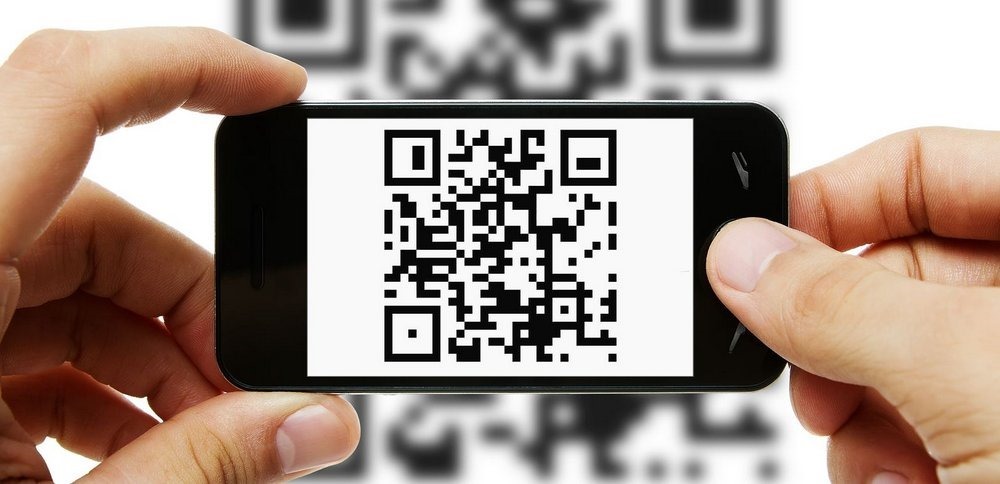
QR code should work with any mobile camera phone that has a QR reader, which is freely available online for most devices.
Why is it significant?
4
The idea of linking spaces to information is not new, but QR codes combine simple creation with easy access to QR code readers.
What are the downsides?
5
Not everyone like QR codes. Taken as a whole, it is impractical to expect students to be able to capture coursework information from QR codes without some support.
2
QR codes are popular in Japan, where they are used for commercial tracking, logistics, inventory con-trol, and advertising.
1
QR codes are two-dimensional bar codes that can contain any alphanumeric text and often feature URLs that direct users to sites where they can learn about an object or place.

What are the implications for
teaching and learning?
7
In this way, the codes support experien-tial learning, bringing scholarship out of the classroom and into physical experience. QR codes help students engaged in study abroad can use the codes to read websites in their native languages.

Where is it going?
6
Commercial packaging will display codes with detailed nutritional information or links to web-sites where users can play the latest product-associated gameor register for updates or coupons.
QR codes might lead students to open forums where they could join in com-munity discussions about what they’ve heard or seen.