eMarketing
THINK
WHAT IS MARKETING?
The creation and satisfaction of demand for your product or service.
WHAT IS DIGITAL MARKETING?
Drives the creation of demand using the power of the Internet, and satisfies this demand in new and innovative ways.
It's so important to make a marketing strategy
UNDERSTANDING MARKETING STRATEGY
Business strategy asks the questions:
• ‘What is the business challenge we are facing that prevents us from making more revenue?’
• ‘What business objective should we strive for in order to increase the money in the bank?’
The brand is the vessel of value in this equation.
• How aware are people of the brand?
• Does it hold positive associations and perceived value?
• How loyal are people to the brand?
When you have the answer to this question, you can formulate a MARKETING STRATEGY
3. MARKETING STRATEGY
Strategy must understand what are the factors that affect the business?
THE ENVIRONMENT
Consider influences (PESTLE):
• Political
• Economic
• Social,
• Technological
• Legal
• Environmental
THE BUSINESS
A crucial consideration is the brand itself.
• What does it stand for?
• What does it mean?
• What associations, ideas, emotions and benefits do people associate with it?
• What makes it unique?

THE COSTUMERS
Try not to make assumptions about why people like and transact with your brand
You may find their values and motives of what particular benefit or feature your business provides to your customers to capitalise on your MARKETING CONTENT.
THE COMPETITORS
It’s important to know
• Who else is marketing to your potential customers
• What they offer
• How you can challenge or learn from them.
• Who are capturing your customers’ attention
2.DIGITAL MARKETING STRATEGY
Should be:
• Constantly iterating and evolving.
• Flexible and dynamic
Allows greater opportunities for interaction and consumer engagement creating interactive experiences for consumers.
CRAFTING A DIGITAL MARKETING STRATEGY
A strategy needs to cover the questions of:
• Who are you?
• What are you offering?
• To whom, why and how you are doing.
Should be aware of:
1. Context:
• PESTLE factors
• Customers, needs and desires
• Competitors
• What/ why/ how makes your brand useful and valuable
2.Value exchange:
What extras, beyond the basic product or service, do you offer to customers?
3.Objectives
There are four key aspects to consider:
> Objectives (SMART)
• Specific
• Measurable
• Attainable – based on available resources.
• Realistic
• Time-bound – must be linked to a specific timeframe.
> Tactics
Tactics are the specific tools you will use to meet your objectives
> Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Data that you will look at to determine if your tactics are performing well and meeting your objectives.
> Targets
The specific values that are set for your KPIs to reach within specific time period.
4. Tactics and evaluation:
Many digital tools and tactics are available once you have defined your digital marketing objectives.
• SEO
• Search advertising
• Online advertising
• Affiliate marketing
• Video marketing
• Social media
• Email marketing
5. Ongoing optimisation:
Digital marketing strategy should be iterative, innovative and open to evolution.
4.CONTENT MARKETING STRATEGY
The Content Marketing Institute offers the following definition:
Content marketing is a marketing technique of creating and distributing relevant and
valuable content to attract, acquire, and engage a clearly defined and understood
target audience – with the objective of driving profitable customer action (Content
Marketing Institute, 2013).

Content components
• Substance: Who are you trying to reach, and why?
• Structure: Where is your content? How is it organised? How do people
find your content?
People components
• Workflow: How does your content happen?
• Governance: Politics, guidelines and standards (Halvorson, 2010).
Strategic building blocks
Translating your brand essence
• The brand essence is a sentence which sums up the unique attributes of a brand and the basis for its emotional connection with customers.
• Can be a useful guide for ensuring that the content you créate
Market research and consumer personas
The content marketing lies in:
• The brand personality and the consumer motivation for paying any attention
• The persona assists you in segmenting and understanding your target market
Creating content pillars
These are areas of focus that support the creation of content that match to a consumer’s interest according to the brand essence
Matching content formats to objectives
The role of the content marketer is to select the right medium based on overall objectives, production capabilities, and the needs of the audience. Consider the illustration below.
It is necessary to plan the contents according to objectives.

Subtema
Content audit
The content audit involves a review of all existing content provided by the brand to see if it matches the needs of the brand's content
CONTENT CREATION
Brand as publisher
It is necessary to consider content creation in terms of delivery and engagement
CONTENT MODELS
Stock and flow
Stock content refers to bigger contents that require more investment and will be interesting in six months as well as today.
Destination and distributed thinking
Rather than focusing on driving readers to your website, consider to create content that engages with your target audience
Content channel distribution
Algorithmic curation
Each algorithm will use a number of factors to determine what is actually relevant and interesting to the person doing a search, or looking at their news feed.
TOOLS OF THE TRADE
Brand style guides
This document guides anyone creating content for a brand at anytime.
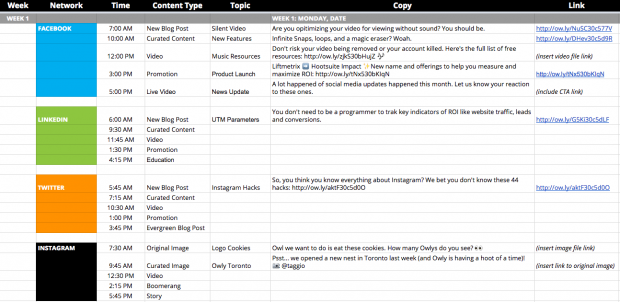
Content calendars
Content calendars assist the content marketer in planning the content they will be sharing, across which platforms, and when.
Subtema
Workflow map
• Who has final sign off?
• Is it a duplicate of existing content?
• Where else can it be used?
Persona map
Assists content creators in focusing on those for whom they are creating content, and what the motivations of consumers would be.
THE BUILDINGS BLOCKS OF MARKETING STRATEGY - will help you structure a marketing strategy.
Porter’s Five Forces analysis
Is a business tool that helps determine the competitive intensity and attractiveness of a market.

THE FOUR P'S How your brand is positioned in the mind of your consumer will ultimately determine your success.
1. Products (and services)
Products and services are what a company sells
2. Price
• VALUE
• Customers feel they are getting something more than just the product.
Value is a combination of:
• Service
• Perceived benefits
• Price
3. Placement (or distribution)
• Product distribution and markets no longer have to be dictated by location.
4. Promotion
Interacting with customers helps build relationships, and the web makes this sort of communication easy.
5. A new P: People
This element speaks to examining the human element that the digitally connected world permits:
• Personalisation
• Peer-to-peer sharing
• Communities
• Consumer- centric organisations
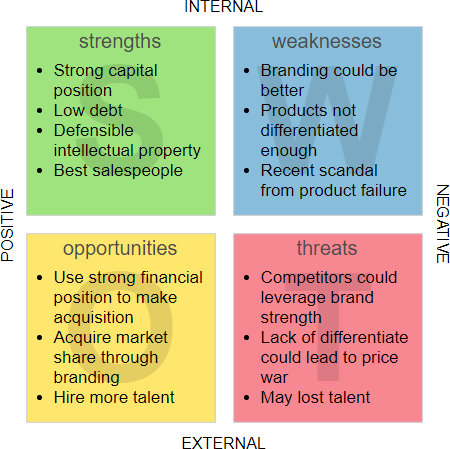
SWOT analysis
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is an ideal way to understand your business and your market.
MARKETING RESEARCH
How can you keep your brand current and ensure you are meeting your customers’ needs?
ONLINE MARKET RESEARCH
It’s the process of learning about your audience by engaging and observing them online.
• Info about consumers:
• Understand the changes in your industry and business
• Discover new market trends
• Find new potential sales avenues, customers, products
• Find and engage new audiences
KEY CONCEPTS IN MARKET RESEARCH
Research methodology
Research should involve certain steps:
1. Establish the goals of the project
2. Determine your sample
3. Choose a data collection method
4. Collect data
5. Analyse the results
6. Formulate conclusions and actionable insights
Primary and secondary research
Primary research is conducted when new data is gathered for a particular product or hypothesis
Secondary research uses existing, published data as a source of information.
The Internet is an ideal starting point for conducting secondary research based on published data and findings.
Quantitative and qualitative data
Differences between quantitative and quialitative research:
Quantitative
Data gathered Numbers, statistics, objective data
Question answered - What?
Group size - Large
Data sources - Surveys, web analytics data
Purpose - Tests known issues or hypotheses.
Advantages Statistically reliable results to determine if one option is better than the alternatives
Challenges - Issues can be measured only if they are known before to starting.
Sample size must be sufficient for predicting the population
Qualitative
Data gathered - Opinions, feelings, motivations, subjective data.
Question answered - why?
Group size – Small
Data sources – Focus group, social media
Purpose – Put data in context
Advantages - understand perspectives
Challenges - Shouldn’t be used to evaluate pre-existing ideas.
SAMPLING
Sample size should be representative of the population you are targeting as a whole.
Needs to be sufficient to make statistically observations about the population.
ONLINE RESEARCH METHODOLOGIES
SURVEYS
TYPES OF SURVEYS QUESTIONS
1. Open-ended
Allow respondents to answer in their own words. (qualitative data)
2. Closed
These questions give respondents specific responses from which to choose. (quantitative data)
3. Ranked or ordinal
Respondents are given a numeric scale to indicate order (quantitatuve data)
4. Matrix and rating
These types of questions can be used to quantify qualitative data. Respondents are asked to rank behaviour or attitude
ONLINE FOCUS GROUP
Ideal for engaging consumers and collecting qualitative data
ONLINE MONITORING
OTHER AVENUES FOR ONLINE RESEARCH
• Observation/Online ethnography
• Personal interviews
• Online research communities
• Listening labs
• Conversion optimisation - covers tools for running tests, such as A/B split testing and multivariate testing.
CREATE
5
UX design
experience physical, sensorial, emotional, mental
six cualities for good UX
usefulness
findability
accessibility
mobile UX
limitations of mobile
slow hardware
slow connection speeds
difficult inputs
small screens
mobile users
locally focused
search dominant
time conscious
goal orientated
mobile devices
five categories of mobiles
feature phones
basic phones
Smartphones
tablets
others (ebook reader, netbook, game consoler, etc)
universal mobile UX principles
mobile websites
native and web applications
responsive websites
principles
encourage exploration
simplify
reduce loading time
give feedback
communicate consistently
predict what's your user wants
tools of the trade
(UX range from rudimentary pen a paper
to highly sophisticated web applications)
-Balsamic
-axure
-gilfly
-Morae
durability
usability
navigation menus at the top or left of the web page
links that are blue and underline
the logo in the top left hand corner, (the user can be back of the home page)
search boxes place at the top of the page
credibility
how it look?
numbers and addresses
no errors
informative and personal about us
genuine testimonials
logos of associations and awards
step by step
conduct research and discovery
content strategy
what the site should achieve, wants and need
create the site's basic structure
information architecture
hierarchical structure
where i am?
how did i get there?
where can i go next?
how do i get home?
sitemap
defiding homepage, main navigation, arraiging your pages
and add extra pages below this
create content
keypoints
structure:
highlighting key phrases and words, bulleteds lists, paragraphs, descriptive and distinct headings
layout
wireframes: the header, the central content area, the sidebar, the footer
the most important consideration for any page is
the content what be incluided
hieranchy:
pyramid style
relevance:
must be relevant for the user
Subtema
define the visual design
colour:
be aware of legibility and accessibility concerns
imagery:
need to do a lot of testing
conduct testing
giving one or more users access to a
prototype and observing how they behave
when useing it
create a test:
how mucho time and money do i have for this test?
what facilities are available?
how many participants do i want to test?
at what satge is the project?
usert-testing methodologies
hallway testing: quick/informal test
observation and user labs
split testing
eye tracking
surveys
find subjects
-what kind of person i choose?
test
analyse
report
implement
start again
don't do
never resize windows or launch
don't use entry or splash pages
never build a site entirely in flash
don't distract users
benefits
excellent way to differentiate yourself in the market
competitive advantage
you give them will become loyal clients
simplicity
lots of empty space
fewer options
plain language
sticking to conventions
extra elements
calls to action
clickyability
accuracy
positioning
forms
step and sections
search
relevance
validation
assistance
6
web design
creating all the visuals aspects of the interface
is what the user sees and interacts with
navigation
layout
headers
footers
credibility
fonts
kind of your message should be easy to learn and search
arial
georgia
trebuchet
comic sans
impacto
verdana
courier new
times new roman
visual identity
"how do users know it´s us?"
logo
menu
button style
collectin and collating desing assets
brand guidelines or style guide
logo and others keybrand elements
image libraries
font folders
brand colours
any existing creative assets
website copy
any additional assets
the fold: imaginary line at the bottom
rfo the monitor
consistently: perceive it as one message on multiple
touchpoint
white space: allows the eye to travel ease
between of the information
colour theory
psychological effect in the people
can be used to inform and stell the user´s experience
colours also hold different meanings and
associations for people
red is used for warnings, error messages and problems
green is used for successful actions, next steps and correct submissions
blue is best used for hyperlinks
contrast is very important when displaying
text online
web development
process of taking finished web designs and transforming
them into fully functioning
should your website be static or should it have a content managgement sistem (CMS)?
which server-side language should be used?
whoch front-end should be used'
static website
is one that does not change often
should new content is requiered, a web developer would need
to add them
three kind of CMS:
bespoke
off the shelf
open source
example:
WordPress
Joomla
Drupal
meta and little tag customisation
URLs
customisable navigation
The CMS needs to have good suport
Robots.txt magnament
server-side/front-end language:
cost
features
scalabity
browser and OS support
open-source or propietary software
Examples:
HTML5
CSS
JavaScript
Flash
mobile development
whichi mobile experienche should you create?
mobile websites make it possible for users to access information about your brand on the move
a native mobile app is software designed to help users
perform particular task.
responsive website:
is a besite that changes its layout depending on the device
it is displayed on (adapts to the smaller/bigger screen size)
Subtema
designing a mobile style
responsive style
-flexible grid
-media queries
-flexible images
step-bystep
bulgind a website
step 1: planning and research
step 2: choosing a domain name
step 3: UX an content strategy
step 4: engine visibility
*search engine optimisation
step 5: design
step 6: development
step 7: test and lauching
7
writing for digital
who is my audience?
what actions do i want them to take?
what information do they need in orden to feel confident taking action?
person:
male, female, mixture
old
other demographics and psychographics
types of web copy:
-clear and concise
-easy to read
-well writen
-well structured
short copy
especially true of banner and search
calls to action
titles and subject lines
they are important enough to be discussed as stand-alone
short copy
they tell a reader whether or not they should read further
examples:
guide to online copywriting
the steps to online copywriting that sells
search adverbs:
heading: max 25 characters
two lines off advert copy: max 35 characters
whichi can be displayed on one line: max 35 characters
URL: max 35 characters
social copy
aallows brands to have conversations with their customers
research is vital
remember that it´s a conversation
write shareable content
avoid overly promotional content
have a solid communication protocol
long copy
it also covers longers pieces of content
news releasese
artices for online syndication
emails
blog posts
advertorials
website
HTML for formating
hyperText Markup Language
tags tell browsers how to present content
HTML tags are writteng in brakets ><
SEO copywriting
optimisin for human and machine users
key prhases
-page title
-page URL
-meta description
-meta keywords
-heading and sub-heading
-on page copy
-links to your optimised page
-images
does your copy convey a creative idea?
does the layout of your copy make it easier to read?
is you meaning celar and direct?
language:
active voice
neologism and buzzwords
features and benefits
logic
ENGAGE
8
Customer RElationship Management
Can help turn a prospect into a customer
customer focused approach to business
Enables businesses to inform business strategies Drive business processes, support brand development and maximise ROI
trouhg innovarions in digital technologies iroduction of mass personalisation
Fostering long term meaninful relationships
Gain customer loyality
CONSUMER TOUCHPOINTS
Can be brand or customer initiated
Deliver a rewarding experience.
Phases
PRE-PURCHASE
gain customers,heighten brand awareness , highlight the benefits,how the brand provides value and fulfils the needs and wants,educate consumers about products and services
PURCHASE
instil confidence,deliver value,reinforce the purchase decision,heighten brand perceptions
POST-PURCHASE
develop a relationship,maximise customer experience,deliver on the brand promise,increase brand loyalty,remain top of mind,invite repeat purchases
DATA
Drive consumer loyalty across all possible touchpoints.
Data on its own is meaningless if it is not analysed and acted upon.
Through analysis, data can be turned into insights
It can enable a company to create real value for the custome
Database, conducting surveys, focus groups or dipstick telephonic research can help you
information commercially relevant,
capture additional contact details,
consider anything that adds value to the relationship,
user’s privacy must always be taken into account.
CRM data capture and analysis.
Traditional CRM system data
Capture data for sales support and marketing purposes
demographic details
transactional data
psychographic data
service and support records
customer reviews
web registration data
shipping and fulfilment dates.
Data mining
Analysing data to discover unknown patterns or connections.
Conducted on large datasets and looks for patterns that are not obvious.
To better understand customers and their behaviour.
To make more informed business decisions.
Analytics data
Generally captured through specialised analytics software packages.
Can be used to measure most digital marketing campaigns.
Social media monitoring data
Can cover everything from quantitative data about number of fans and interactions
Qualitative data about the sentiment towards your brand in the social space.
For generic data...
You must continuously monitor trends and note what causes changes over time.
Useful identifying gaps in data when a business evolves.
Analysing data for marketing
The customer acquisition source can be recorded and analysed against sales data.
This leads to a very accurate ROI calculation.
ROI
Stands for return on investment
It’s key to understanding whether marketing efforts have been successful.
Subtema
campaign analysis,
personalisation,
event monitoring,
predictive modelling,
improved customer, segmentation.
Effective CRM
increased revenue and profitability,
improved customer satisfaction and loyalty,
improved service delivery and operational efficiencies,
decreased acquisition costs
The different ways CRM is implemented.
Marketing
conduct personalised targeting and profiling,
place the right mix of a company’s products and services,
understand what customers do and want.
Sales
ensure the customer receives the correct product,
ensure correct sales-related processes are carried out within the organisation,
include systems that put sales reps directly in touch with customers at the point of sale.
Service and service fulfilment
Services invoked by the customer
• Create and manage systems or capabilities that can be directly invoked by the customer:
Places the customer’s needs first in all dealings with the brand.
CRM social
Social media can also be used to drive CRM.
Social media platforms allow customers to easily share their brand experience
Communication multi-directional (brand to consumer, consumer to brand, consumer to consumer).
9
Search Engine Optimisation
Involves optimising websites to achieve high rankings on search engines for certain selected key phrases.
An extremely effective way of generating new business to a site.
Main strategies
On-page optimisation.
Making changes to the HTML code, content and structure of a website
More accessible for search engines
Off-page optimisation
Building links to the website, and covers activities like social media and digital PR.
Main areas
Search engine friendly website structure
Technical challenge
To ensure that search engines can access your content, you must remove technical barriers.
Make sure that there are direct HTML links
Flash
Avoid building sites or delivering key content in Flash.
Key phrases
Understanding search psychology.
There are four things to consider when choosing a keyword
• Search Volume
• Competition
• Propensity to convert
• Value per lead
Create relevant, targeted content aimed at your selected key phrases.
Where use the key phrase...
1. Title tag
2. H1 header tag
3. Body content
4. Bold
5. URL
6. Meta description
7. Link anchor text
8. Domain name
Optimising media
Images, video and other digital assets should also be optimised with the relevant keywords.
Proper optimisation can give a brand more ownership of the SERP real estate
Be used effectively to target competitive terms.
Link popularity
The purpose of a link is to allow a user to go from one web page to another.
Links help send signals of trust.
Trusted sites can transfer trust to unknown sites via links.
Links help to validate relevance.
The text that makes up the link can help validate relevance.
How does a website get more links?
Some ways to go about increasing links to their websites.
Create excellent, valuable content that others want to read
Make sure that valuable content is themed around your key phrases.
Infographics can encourage lots of traffic and inbound links.
Create tools and documents that others want to use
Create useful PDF guides for your industry that people can download from your site.
Create games
The theme of the game is based on the key phrases for your website
Capitalise on software and widgets
Create a widget
That the link is included, and let people spread these around the web for you.
User insights
User data is the most effective way of judging the true relevance and value of a website.
How do search engines access this data?
Use cookies to maintain a history of a user’s search activity.
Social information is playing an ever-increasing role in search.
Can appear in the SERPs
Factors to consider
1. Use social media properties to dominate brand SERPs.
2. Social links are used as signals of relevance.
3. Personalised results are influenced by your online social network.
4. Optimise for social search engines.
Mobile searches tend to be different from desktop searches.
Mobile users can search by voice, or by using images or scanning barcodes.
1. A usable, crawlable site is very important.
2. Content is important, and should be formatted for mobile usage.
3. Links are important.
4. Submit a mobile XML sitemap.
5. Use the word ‘mobile’ on the mobile website, or use mobile top-level domains.
Design websites for users first and foremost
Don’t try to trick the search engines.
10
Search Advertising
There are some small differences from platform to platform in terms of editorial policy.
Each system has a different user interface.
Google AdWords
Considered the industry standard
It allows users to transact in the currency of their choice
Is tied to a comprehensive analytics tool, and offers training programmes and certifications.
The best contextual and geographical targeting worldwide
Should be structured to reflect your business and marketing strategy.
Organise your search adverts in groupings
According to your strategy and the ads you are running.
Help you to easily oversee your advertising spend
Offers seven text Ad Extensions
1. Location Extensions
2. Call Extensions
3. Social Extensions
4. Seller Ratings
5. Sitelinks
6. Offer Extensions
7. Image Extensions
Keyword match types
• Broad match
Your advert will appear for the keywords you have entered
• Broad match modifier
An additional targeting option that gives you tighter control than broad match
• Phrase match
Your advert will appear only for search terms that have your keywords in them, in the same order.
• Exact match
The advert will appear for search terms only exactly the same as the keywords selected.
• Negative match
Your advert will not appear in searches using that word
Quality Score
Determined by
• The relevance of the keyword to the search term.
• The relevance of the advert copy to the search term.
• The relevance of the landing page to the search term.
• The historic CTR of that advert.
Elements
Heading Two lines of advert copy.Sometimes shown on one line.www.DisplayURL.comAd extensionAd extension
The three main components are:
• Keyword-optimised ad text
• The link to your owned property
• Ad extensions
Text
The advert copy is the only tool available to attract attention, convey a message and entice action.
Use compelling and well-crafted Calls to Action
‘try now’, ‘sign up now’, ‘buy now’.
Display URL
Deep-linking.
Send users to a web page that is as specific to their search, and the PPC advert, as possible.
Landing pages
Can increase the Quality Score of the advert, and lower the CPC of the keyword.
CPC
Is determined by a variety of factors, and is based on a bidding system.
Ad Extensions
Ways to add value or information to search adverts.
Offer a way to get additional information into a search advert
Creates the copy for an advertisement.
Determines the landing page for the advert.
Selects the keywords.
Chooses the maximum amount
Conversion
The advertiser can track how many of the users that clickthrough to the website
With a goal set up
Goals can be:
• Buying a product
• Filling in a form or quote
• Downloading a white paper
• Sending an enquiry
• Booking a flight
11
ONLINE ADVERTISING
OBJECTIVES
BUILDING BRAND AWARENESS
Making people aware of a brand or product using an online advertising promoting brand and making people familiar with its colours, logo and overall feel.
CREATING DEMAND
It’s a three-step process:
• Inform
• Persuade
• Remind.
SATISFYING DEMAND
Let know the customer how their brand or product will best meet that need
FLOATING ADVERTS
GETTING YOUR ADDS ONLINE
PREMIUM BOOKED MEDIA
The advertiser contacts the premium media provider and discusses options for placing an advert.
ADVERTISING NETWORDS
Is a group of websites on which adverts can be purchased through a single sales entity
ADVERTISING EXCHANGES
Where unsold advertising space is placed by publishers for bidding.
SOCIAL MEDIA ADVERTISING PLACEMENTS
• Facebook ads
• Facebook engagement ads
• Sponsored stories
• Promoted posts
• Promoted tweets
• Promoted accounts
• Promoted trends
YOUTUBE
LINKDN
MOBILE ADVERTISING
BLIND NETWORKS
These networks target a large number of independent mobile publishers, and
generally allow you to target by country or type of content, but not by specific
websites
PREMIUM BLIND NETWORKS
Allow the advertiser to target better-known brands and high-traffic sites
PREMIUM NETWORKS
Often offer sales as a direct extension of the big brands that they offer.
AD SERVERS
Servers that store advertisements and serve them to web pages.
12
AFFILIATE MARKETING
ACTION AND REWARD
• Cost per Action (CPA) – a fixed commission for a particular action.
• Cost per Lead (CPL) – a fixed commission for a lead (that is, a potential sale).
• Revenue share (also CPS or Cost per Sale) – an agreed-on percentage of the
purchase amount.
• Cost per Click (CPC) – a fixed amount for each clickthrough to the website
(although this forms a very small part of the affiliate marketing mix
TRACKING
Tracking software is used to track affiliate campaigns, and this is usually supplied and supported by an affiliate network
Affiliate tracking software collects information
• Impressions
• Clicks
• Conversions
How do affiliates promote merchants?
•Personal websites
•Content and niche sites
•Email lists
•Loyalty sites
•Cupon and promoting sites
•Search advertising
TOOLS OF THE TRADE
Any retailer should have a product feed, in either XML or CSV.
A product feed will
probably contain the following information for each product:
• Product name
• Product URL
• Picture
• Price
• Description
• Shipping price
• Stock status: in stock / out of stock
13
Video Marketing
Video Content Strategy
Going Viral
Address a currently trending topic
Find something that people are already excited about or interested in
Make it enticing
Craft the videos description, title and thumbnail so that they draw attention
Make it remarkable
Funny, astonishing, sacry, shocking or informational.
Make it unique
Be truly creative and inventive
Make it shareable
Include the tools and incentives to make your video easy to share.
Camera, Software, microphone
Video Content
Entertain, inform, share updates or otherwise enlighten or delight the viewer
Video ADS
TV commercials that are shared online, or custom ads made specifically for the web.
Video production step by step
Identifying your audience, Planning and concept, Producing the video, Choosing and uploading to platform, Optimising, Promoting, Engaging the community, Reporting
Optimising
1.- Video title is very important. 2.- Use informative, long descriptions. 3.- Use the tags to input several keywords. 4.- Encourage comments, subscriptions, ratings, embedding and sharing. 5.- Optimise the thumbnail. 6.- Use annotations 7.- Upload videos regularly
Video Promotion
Search SEO • Users follows recommendations for others • Knows exactly what they are looking for and navigates to the appropriate URL directly. • The user finds the video through paid advertisements and promotions.
YouTube
Titles • Descriptions • Tags • Playlist additions • Inbound links
TrueView
YouTube offers a wide variety of video ad types
TrueView In-Search TrueView In-Display TrueView In-Stream
• Video views • Channel views • Ratings • Comments • Shares • Embeds • Subscribers • Age of video
Social Sharing
ask your viewers to post your video on social networks, aggregators, social bookmarking sites and other channels
Tools of the trade
AdWords for Video
Allows you to link your existing Google paid advertising account to your YouTube channel
Feed
Allow you to upload the video once, and then automatically upload that video to all of your chosen profiles and platforms
TubeMogul
Lets you buy paid video placements across the web
Brightcove
Gives you everything you need to deliver professional quality video to audiences on every screen
14
Social Media Channel
Social Media Channels
Social media is all about the ways in which we create, connect and share content online
social network
Social media is all about the ways in which we create, connect and share content online
content creation
Using social channels to create and share content.
bookmaking and agregating
Social curation and sharing content.
Location
A subset of social networks that are based on location
Social Networking
Forming and maintaining online social networks for communities
Pages
• A cover image (the large banner at the top)
• A profile image that represents the brand
• Some ‘About’ information that can include links and more detailed
information
• The ‘Wall’, where the brand’s posts and interactions are displayed in a
chronological timeline
Applications
Applications are a way for organisations to create branded experiences for their Facebook fans.
Promotions and competitions
Brands can run promotions and competitions through their Facebook Pages
Fb Connect
Allows users to log into services external to Facebook using
their Facebook login details.
News Fedd
The news feed is the stream of content that users see when they log in to Facebook.
Like Button
Allows users to indicate that they like or recommend content, images, media or websites
Content Creation
Image Sharing
Images tend to attract higher engagement than text-only posts
Video Sharing
Online video consumption continues to grow year on year as bandwidth gets faster and cheaper.
YouTube and marketing
Blogging
Author, Title, Tag, Comment, TrackBack.
Writing Post, Replying comments, building relashionships.
RSS feed, Categories, Blogroll, Archive
Microblogging
Allows a user to publish short text updates
Tweet, Hashtag, Trending, Retweet
Podcasting
digital radio
Targetable, Controllable, responsive, Bandary free, Measurable, Relatively inexpensive.
Location and social media
Allow users to "check in" at locations they visit with equipment such as mobile phones and tablets
Tracking social media campaigns
FB Insights
Demographic, Information about the people connecting with your content.
YT Analytics
Showing video views and popularity broken up by geographical territorial.
Twitter Analytics
Include how many people interact with your content by clicking through on links.
15
Social Media Strategy
Using social media to solve business challenges
Communication and outreach
Social media offers brands an effective two-way communication and real-time broadcast channel.
Community management
Is a role that has risen to prominence as more organisations start using social media,
Support and customer service
the businesses with which they transact will also respond to customer queries in the social space,
Reputation management
Social media are in one of the spaces where a brand or individual can easily respond to mentions, create a stir, or find ways to further their own agenda.
Advertising and awareness
The more time people spend in social media, the more brands want to advertise there
Sales and lead generation
Can be based overtly on social connections, or on inferred connections based on behaviour.
Search engine optimisation (SEO)
It provides additional assets that can be optimised so that a brand ‘owns’ the results page for searches for their brand.
Insight and research
Social media can provide a rich source of data, both demographic and preference based.
Creating a Social Media Strategy
Here is one method to approaching social media strategically.
Get buy in
A number of stakeholders will need to be aware of your social media plans
Listen and understand the landscape
Social media is more than the social spaces you may interact with in your personal capacity
Analyse
Think critically about social media and your brand, as well as your brand’s broader marketing, communication and business challenges
Set objectives
•Specific: Details exactly what needs to be done
•Meadurable: Archievement or progress can be measurable
•Achievable: Objective is accepted by those responsable for achieving it
•Realistic: Objective is posible to attain (important for motivational effect)
•Timed: Time period for achievement is clearly stated
Create an action plan
you need to make sure that you have created the necessary documents and processes that form the foundation of your plan.
Implement
Set up your platforms according to the guidelines they specify. Alert stakeholders that you are starting your engagement plans, and make sure you have tracking in place
Track, analyse, optimise
Platform insights, web analytics, URL shorteners, Online monitoring software, Social Media dashboards.
Documents and processes
• Community guidelines • Content plan • Communication and escalation protocol
Dealing with opportunities and threats
When to talk (and when not to)
1. When everything being said is nice 2. When everything being said is neutral 3. When negative things are being said
Responding
Responding involves recognising that consumers hold the upper hand in the relationship
Guide for recovering from an online brand attack
1. Be prepared 2. Act immediately! 3. If the attack on your brand is factually incorrect, send the person evidence that they are wrong 4. If the mention is negative but true, send your side of the story and try as hard as you can to take the conversation offline 5. Keep the negative pages out of the search engines
Social media risks and challenges
No one cares.
Make sure you are interacting in the spaces where your customers are, and where they are happy to hear from you.
The social media space is used by unhappy customers
Even if the only feedback you are getting is negative, this is
good feedback! Now you have an opportunity to do something about it.
It requires ongoing attention and monitoring.
Understand what your objectives are for using social media, and budget the time required to meet those.
It can be difficult to measure the impact of the campaign.
Start with measuring things that can be measured easily, and watch for case studies in this space that will help you to turn your social media investment into revenue for your organisation.
16
Email Marketing
Email strategy and planning
Email marketing can be used as a tool to help you achieve your business and website goals.
Promotional emails
Users make a purchase • Users download some content • Users request further information
Email service providers, Email for mobile phones, Rules and regulations.
Newsletters
Useful KPIs include:
• Open rate
• Clickthrough rate
• Number of emails forwarded
• ROI
• Number of social shares
• Database growth
• Conversion rate (activity on your site generated by the email)
• Delivery or bounce rate
Process
Growing a database
Name, surname and title • Date permission granted • Source of permission • Gender • Country • Telephone number, preferably mobile • Date of birth • Frequency (how often they’d like to hear from you)
Put the sign-up form where it can be seen – above the fold and on every page. • State your anti-spam stance explicitly, and be clear that you value subscribers’ privacy. • Clearly state what the subscriber’s information will be used for. • Use a clear Call to Action. • Tell subscribers what they will get, and how often they will get it. Include a benefit statement. • Ensure the email address is correct by checking the syntax. • Test to see what works best!
Designing an email
Parts of an email
Sender information, Subject line, Preheader, Header, Personalised greeting, body, footer, Unsubscribe link
1.Working with templates 2. Design considerations 3. General design guidelines 4. Designing for the preview pane 5. Email and images 6. The Call to Action 7. Testing
Creating content
Humour • Research • Information • Promotions • Exclusive content
improve the service you give to current customers,
include the development of problem resolution systems, workflow automation and field service dispatch systems.
Segmenting your database
Segmenting a database can allow for customisation across demographics or purchase history.
Deploying
Email reputation is a score given to you depending on how well your emails are regarded by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and your subscribers.
Measuring
Number of emails delivered. • Number of bounces • Number of unique emails opened • Unsubscribes • Pass-on rate • Clickthrough rates and conversion
Testing
• Subject lines • Send times • Best day to send • Layout • Text vs. button links • Database segmentation • Call to Action Testing and monitoring your
17
Market mobile
Communicate and engage with their audience in an interactive and relevant manner through any mobile device or network
The role of mobile in personal communicationL
Six unique features of mobile
1-Are personal 2-Are always carried 3-Are always on 4-Have a built-in payment system. 5-Are available at the point of creative inspiration. 6-Allow accurate audience measurement.
Mobile devices: An overview
People make the final purchasing decision at a desktop computer
Mobile messaging channels
-SMS
-MMS
-Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
-USSD
-Instant messaging
-QR codes
-Automated voicemail messages
-Voice technologies
Location and mobile
If services and useful information can be shared based on a user’s location, the possibilities for conversion naturally increase.
Geo-location
Mobile social networks
Considerations for location-based mobile marketingprovide
method for people to unsubscribe
Mobile commerce
Mobile shopping
nine mobile principles that define a user’s mobile shopping experience
Location
Goal orientation
Attentiveness
Killing time
Taking my time
Urgency
Routine
Passion
Trust and security
Near-Field Communication and mobile wallets
Mobile ticketing and coupons
Mobile currency
Carrier-based payments
Mobile banking
Augmented reality
Mobile analytics
desafíos para el análisis móvil:
-Not all mobile browsers are compatible. -Detecting the capacity of the handset can be a challenge for some packages, and is not offered as a standard
Advantages and challenges
the mobile phone is so personal, permission and privacy need to be at the core of any mobile campaign
they present innumerable screen sizes
OPTIMICE
18
Conversion Optimisation
What can you test?
The short answer
Email marketing
Display and search advertising
Social media
Landing pages
eCommerce
Designing tests
Types of tests
A/B tests
Length of tests and sample size
Number of participants, Change in conversion rate, Number of variations
Step-by-step guide to conversion optimisation
1. Gather data
2. Analyse data
3. Fix anything that’s broken
4. Design tests
5. Run tests
6. Report and repeat
Tools of the trade
19
Data Analytics
Working with data
In the digital age, information is absolutely everywhere
Performance monitoring and trends
Big data massive data sets
require specialised software and massive computers to process
Measure trends, not absolute figures.
Focus on patterns
Investigate anomalies
Data mining
Target
personal, psychographic and demographic data of the clients
• Age • Marital status • If the client has children and how many • Estimated salary • Location • If they moved recently • What credit cards they use • What websites they visit
A world of data
Online data, Databases, Software data, App store data, Offline data
Setting objectives, goals and KPIs
The objective
of a website or online campaign is aligned with the strategic outcomes of the business
“What do we want to achieve with this marketing campaign?”
The goal
of a website or campaign in web analytics refers to an action that a user takes on a website or a type of user behaviour
-“What do we need users to do in order to achieve our objective?”
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
are metrics that are used to indicate whether objectives are being met
“What data do we need to look at to see if goals are being completed?”-
Tracking and collecting data
How information is captured
Cookie-based tracking
Server-based tracking
Comparing the options
Universal analytics
The type of information captured
Building-block terms
Visit characteristics
Content characteristics
Conversion metrics
Mobile metrics
Analysing data
Key elements to analyse
behaviour
Click density análisis, Segmentation, Behaviour and content metrics
outcomes
Analysing goals and KPIs indicates where there is room for improvement
user experience
Segmentation
Referral source
Landing pages
Connection speed, operating system, browser
Subtema
Subtema
