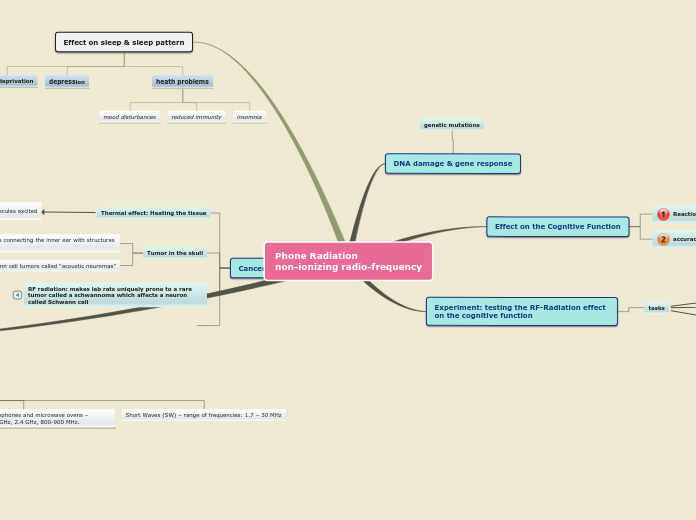
Phone Radiation
non-ionizing radio-frequency
DNA damage & gene response
genetic mutations
Effect on the Cognitive Function
Reaction times
accuracy of the response
Experiment: testing the RF-Radiation effect on the cognitive function
tasks
spatial compatibility
verbal item recognition
spatial item recognition
Effect on sleep & sleep pattern
sleep deprivation
depression
heath problems
mood disturbances
reduced immunity
insomnia
Cancer
Thermal effect: Heating the tissue
Through gettin its molecules excited
Tumor in the skull
affects the nerve cells connecting the inner ear with structures inside the brain
benign Schwann cell tumors called "acoustic neuromas"
RF radiation: makes lab rats uniquely prone to a rare tumor called a schwannoma which affects a neuron called Schwann cell
Types of Radiation
Long Waves (LW): frequencies lower than 300 kHz
Very High Frequency (VHF) for radio broadcasting - range: 30-88 MHz
WiFi and Bluetooth data communication– frequency ranges: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and others.
Cellular communication networks, analog and digital mobile phones, and marine and aerospace radar.
Wireless household telephones and microwave ovens – frequency ranges: 5.8 GHz, 2.4 GHz, 800-900 MHz.
Short Waves (SW) – range of frequencies: 1.7 – 30 MHz